Korean J Hematol.
2012 Sep;47(3):178-185. 10.5045/kjh.2012.47.3.178.
Aurora A kinase expression is increased in leukemia stem cells, and a selective Aurora A kinase inhibitor enhances Ara-C-induced apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia stem cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. minbrmmnd@yuhs.ac
- 2Medical Research Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2251951
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2012.47.3.178
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
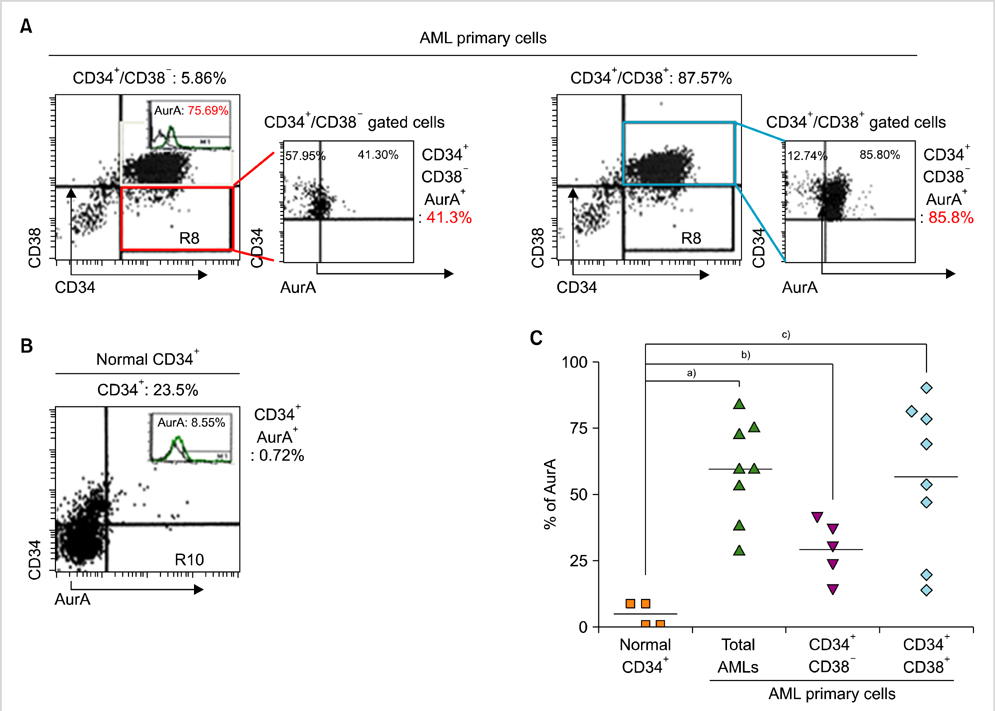
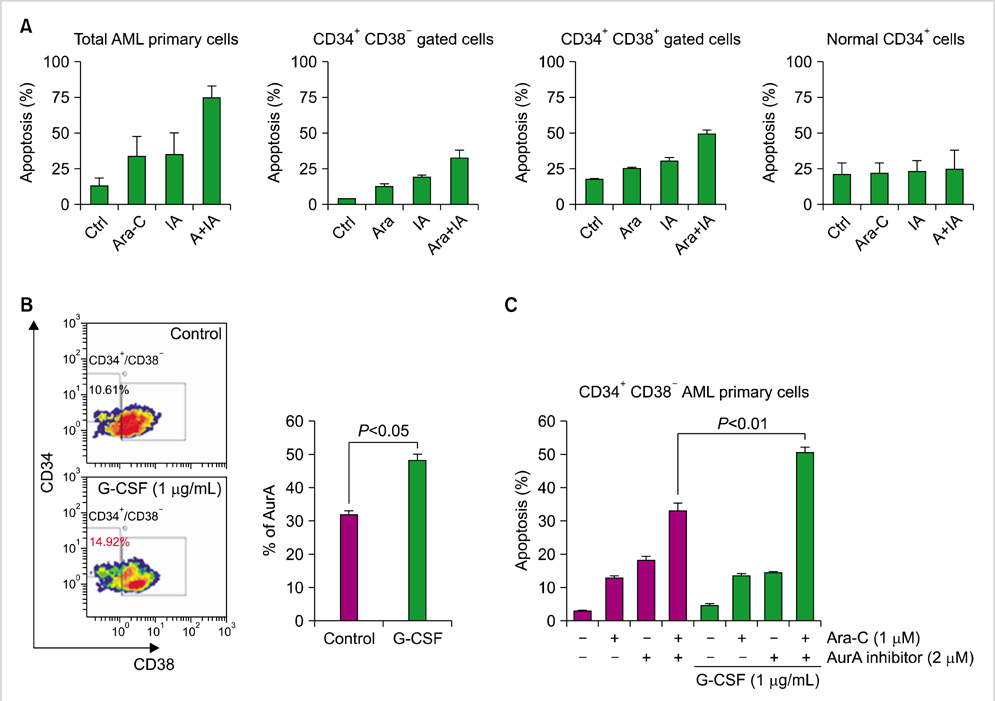
The overexpression of Aurora A kinase (AurA) has been reported in various malignancies, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML). However, the expression of AurA and the effects of AurA inhibition in cancer stem cells are not yet fully understood. We investigated the expression and inhibition of AurA in AML stem cells (CD34+/CD38-).
METHODS
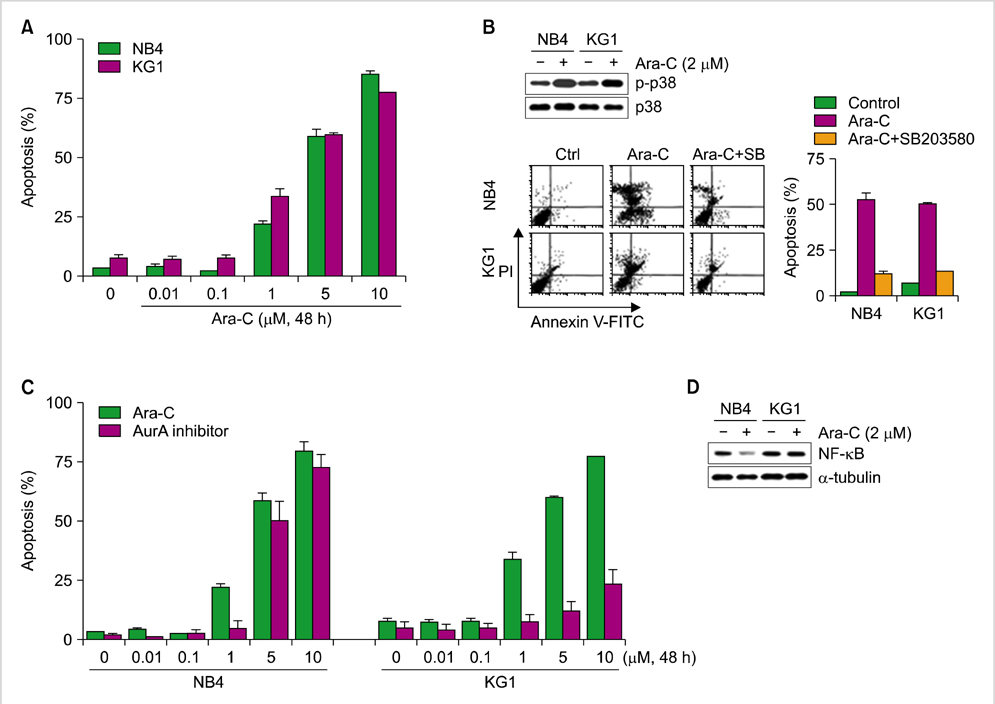
Expression of AurA was investigated in cell lines (NB4 and KG1) that express high levels of CD34 and low levels of CD38. Primary AML cells were harvested from 8 patients. The expression of AurA and cell death induced by inhibition of AurA were analyzed in CD34+/CD38- cells.
RESULTS
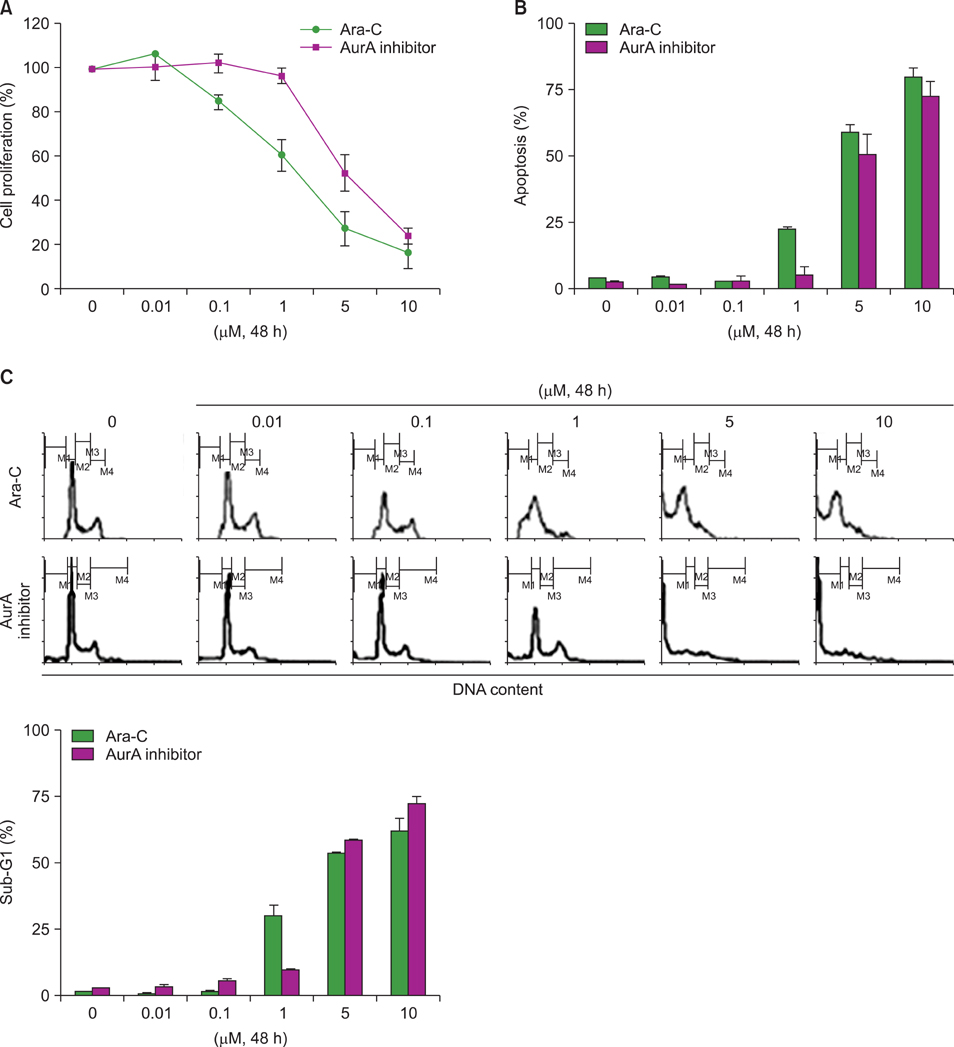
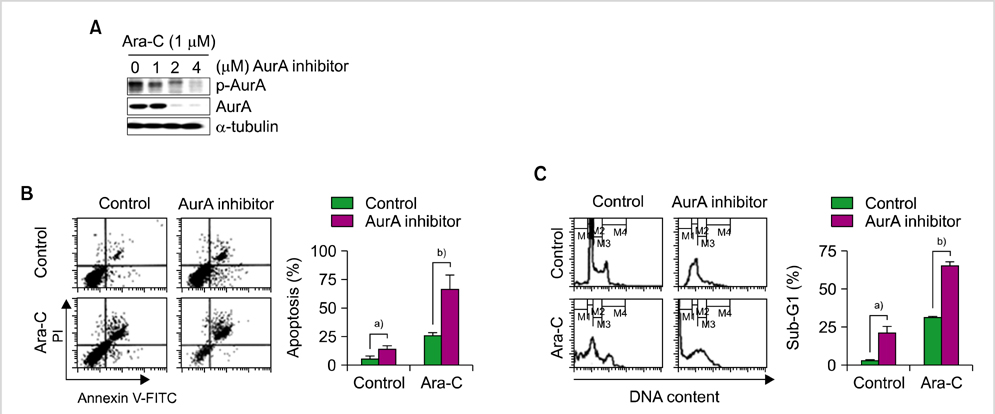
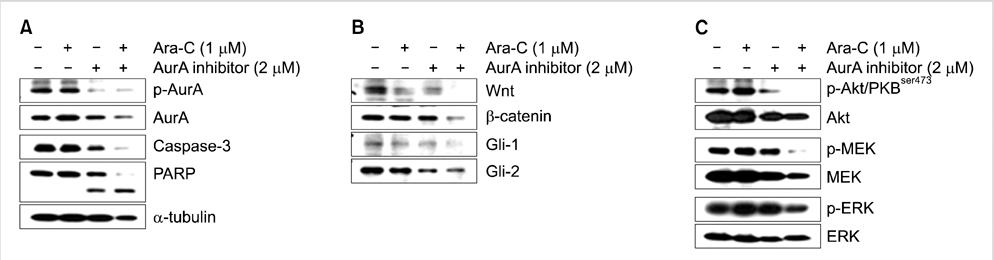
AurA was shown to be overexpressed in both primary AML cells and leukemia stem cells (LSCs) compared to normal hematopoietic stem cells. Inhibition of AurA plus cytarabine treatment in LSCs resulted in increased cytotoxicity compared to cytarabine treatment alone. Additional stimulation with granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) increased the cell death caused by AurA inhibition plus cytarabine treatment.
CONCLUSION
To our knowledge, this is the first report describing increased expression of AurA in LSCs. Our results suggest that selective AurA inhibition may be used to reduce LSCs, and this reduction may be enhanced by stimulation with G-CSF. Further exploration of relationship between nuclear factor kappa-B and AurA inhibition and the potential of AurA inhibition for use in leukemia treatment is needed.
MeSH Terms
-
Apoptosis
Cell Death
Cell Line
Cytarabine
Epilepsy
Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Humans
Leukemia
Leukemia, Myeloid, Acute
Neoplastic Stem Cells
Phosphotransferases
Protein-Serine-Threonine Kinases
Stem Cells
Cytarabine
Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor
Phosphotransferases
Protein-Serine-Threonine Kinases
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Targeting the protein kinases for anti-cancer therapy
Soo-Mee Bang
Korean J Hematol. 2012;47(3):157-158. doi: 10.5045/kjh.2012.47.3.157.
Reference
-
1. Andrews PD, Knatko E, Moore WJ, Swedlow JR. Mitotic mechanics: the auroras come into view. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003. 15:672–683.
Article2. Carmena M, Earnshaw WC. The cellular geography of aurora kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003. 4:842–854.
Article3. Gritsko TM, Coppola D, Paciga JE, et al. Activation and overexpression of centrosome kinase BTAK/Aurora-A in human ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. 9:1420–1426.4. Jeng YM, Peng SY, Lin CY, Hsu HC. Overexpression and amplification of Aurora-A in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. 10:2065–2071.
Article5. Kurai M, Shiozawa T, Shih HC, et al. Expression of Aurora kinases A and B in normal, hyperplastic, and malignant human endometrium: Aurora B as a predictor for poor prognosis in endometrial carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2005. 36:1281–1288.
Article6. Reiter R, Gais P, Jütting U, et al. Aurora kinase A messenger RNA overexpression is correlated with tumor progression and shortened survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. 12:5136–5141.
Article7. Lassus H, Staff S, Leminen A, Isola J, Butzow R. Aurora-A overexpression and aneuploidy predict poor outcome in serous ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 2011. 120:11–17.
Article8. Vader G, Lens SM. The Aurora kinase family in cell division and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. 1786:60–72.
Article9. Farag SS. The potential role of Aurora kinase inhibitors in haematological malignancies. Br J Haematol. 2011. 155:561–579.
Article10. Cammareri P, Scopelliti A, Todaro M, et al. Aurora-a is essential for the tumorigenic capacity and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2010. 70:4655–4665.
Article11. Chefetz I, Holmberg JC, Alvero AB, Visintin I, Mor G. Inhibition of Aurora-A kinase induces cell cycle arrest in epithelial ovarian cancer stem cells by affecting NFκB pathway. Cell Cycle. 2011. 10:2206–2214.
Article12. Saito Y, Uchida N, Tanaka S, et al. Induction of cell cycle entry eliminates human leukemia stem cells in a mouse model of AML. Nat Biotechnol. 2010. 28:275–280.
Article13. Testa U. Leukemia stem cells. Ann Hematol. 2011. 90:245–271.
Article14. Cheong JW, Jung HI, Eom JI, Kim SJ, Jeung HK, Min YH. Aurora-A kinase inhibition enhances the cytosine arabinoside-induced cell death in leukemia cells through apoptosis and mitotic catastrophe. Cancer Lett. 2010. 297:171–181.
Article15. Wang J, Yang S, Zhang H, et al. Aurora-A as an independent molecular prognostic marker in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 2011. 26:23–32.
Article16. Fajtova M, Babusikova O. Immunophenotype characterization of hematopoietic stem cells, progenitor cells restricted to myeloid lineage and their leukemia counterparts. Neoplasma. 2010. 57:392–400.
Article17. Ye D, Garcia-Manero G, Kantarjian HM, et al. Analysis of Aurora kinase A expression in CD34(+) blast cells isolated from patients with myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematop. 2009. 2:2–8.
Article18. Guzman ML, Neering SJ, Upchurch D, et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB is constitutively activated in primitive human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood. 2001. 98:2301–2307.
Article19. Colado E, Alvarez-Fernández S, Maiso P, et al. The effect of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib on acute myeloid leukemia cells and drug resistance associated with the CD34+ immature phenotype. Haematologica. 2008. 93:57–66.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Pharmacological Inhibition of ERK5 Enhances Apoptosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells
- Characterization of the Indirubin Derivative LDD970 as a Small Molecule Aurora Kinase A Inhibitor in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells
- The Bromodomain Inhibitor JQ1 Enhances the Responses to All-trans Retinoic Acid in HL-60 and MV4-11 Leukemia Cells
- Elevated Aurora Kinase A Protein Expression in Diabetic Skin Tissue
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF AURORA-2 KINASE IN THE ORAL SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA