J Rheum Dis.
2012 Aug;19(4):196-205. 10.4078/jrd.2012.19.4.196.
DICAM Inhibits Activation of Macrophage by Lipopolysaccharide
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratory for Arthritis and Bone Biology, Fatima Research Institute, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea. kiefe73@gmail.com
- 2Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2223071
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.4.196
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
DICAM, a dual Ig domain containing adhesion molecule, is involved in cell-cell adhesion through direct interaction with alphavbeta3 integrin. In our previous study showing the inhibitory role of DICAM in osteoclast differentiation, we found that DICAM also has a suppressive role in macrophage, the precursor cell of osteoclast. The role of DICAM in macrophage activation at the inflammatory milieu, however, remains obscure.
METHODS
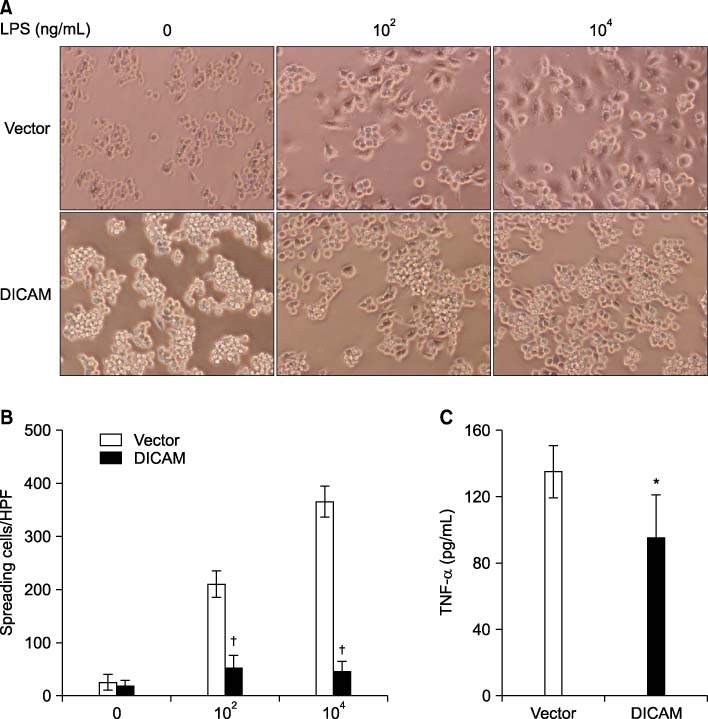
Expression pattern of DICAM by inflammatory cytokines and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was studied with RAW264.7, a murine macrophage cell line. To study the role of DICAM on macrophage activation, we stably transduced DICAM, or empty vector, into RAW264.7, and then compared the LPS-mediated activation such as spreading and TNF-alpha production.
RESULTS
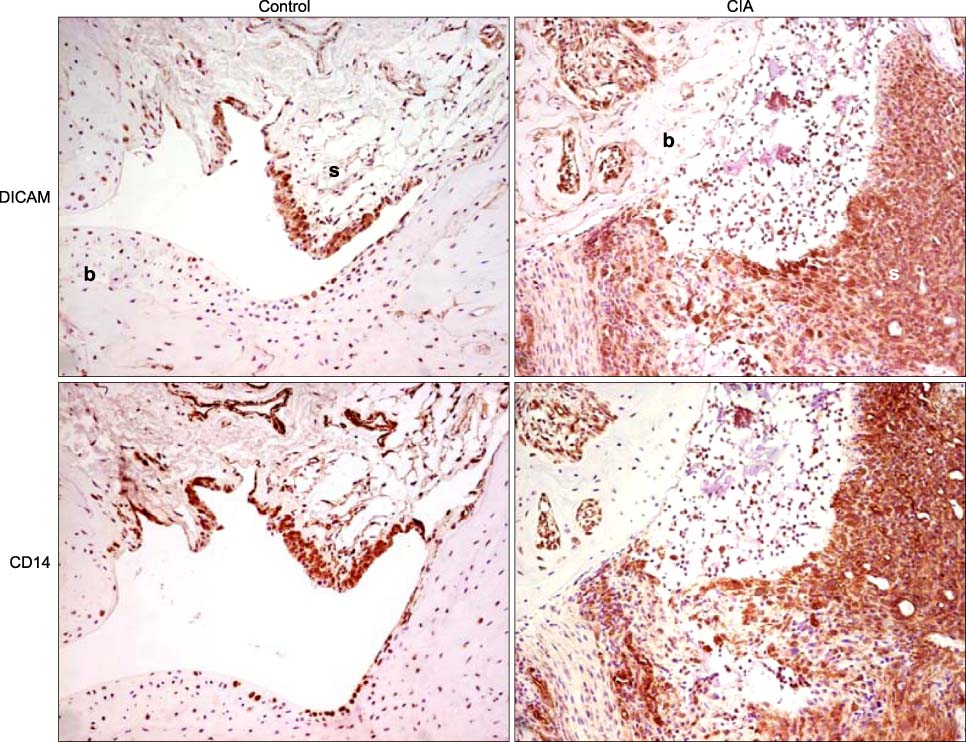
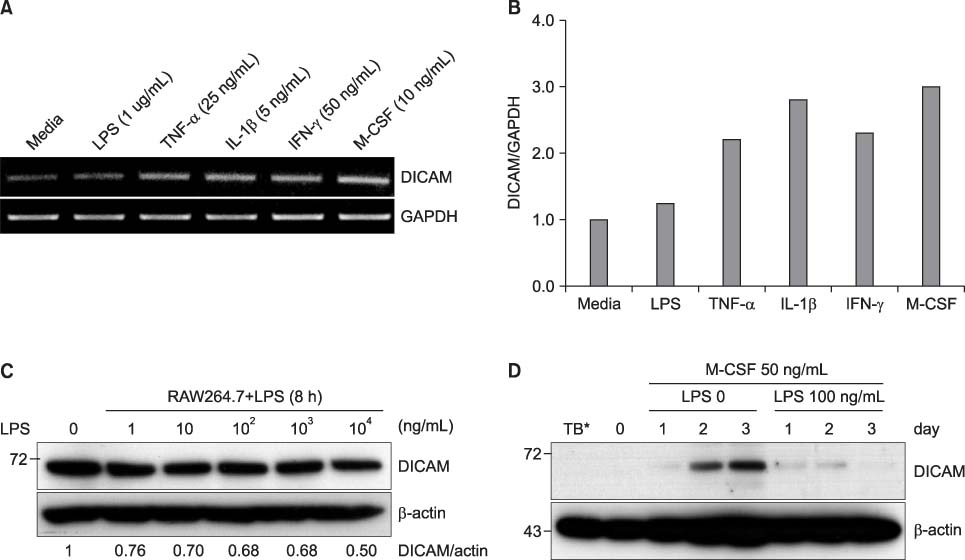
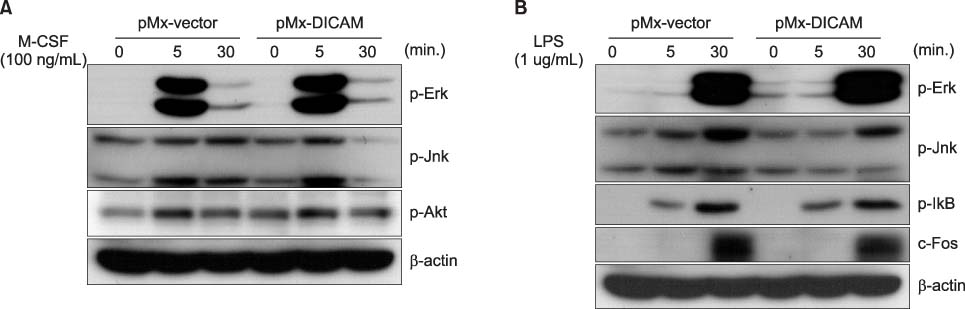
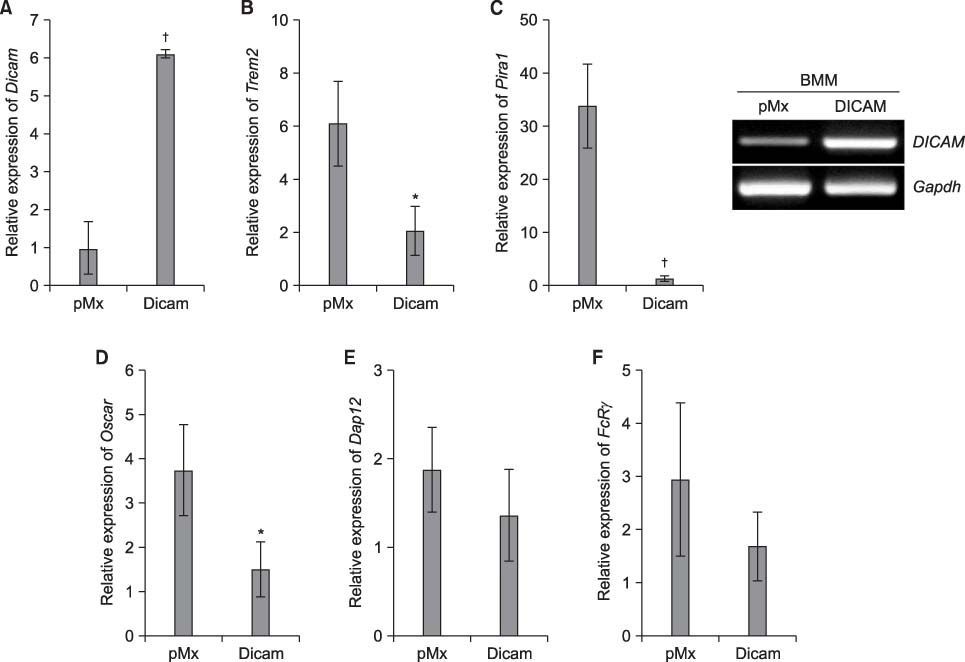
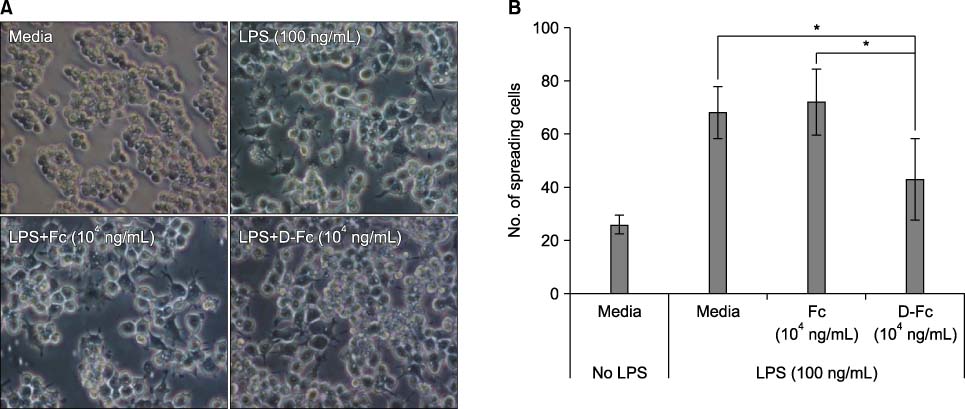
DICAM was abundantly expressed in the synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis. When we assessed the expression of DICAM in RAW264.7 cells by mediators of inflammation, inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and IFN-gamma, and M-CSF increased the expression of DICAM; however, LPS decreased. Functionally, DICAM that stably transduced-RAW264.7 cells showed attenuation of LPS-mediated macrophage activation including spreading and TNF-alpha production. DICAM decreased the phosphorylation of JNK MAP kinase by M-CSF and LPS stimulation, which was corroborated by a decrease in the expression of ITAM-associated receptors including Trem2, Pira1, and Oscar. Finally, a recombinant ectodomain of DICAM suppressed LPS-induced activation of RAW264.7 cells.
CONCLUSION
These results indicate that DICAM acts as a negative regulator of LPS-mediated macrophage activation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Arthritis, Experimental
Cell Line
Cytokines
Inflammation Mediators
Macrophage Activation
Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
Macrophages
Monocytes
Osteoclasts
Phosphorylation
Phosphotransferases
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Cytokines
Inflammation Mediators
Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
Phosphotransferases
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
DICAM-mediated Inhibition of Type 1 Interferon System during Macrophage Differentiation of THP-1 Cells
Bo Yeon Kim, In Park, Youn Kwan Jung, Min Su Han, Gun Woo Kim, Seung Woo Han
J Rheum Dis. 2014;21(3):122-131. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2014.21.3.122.
Reference
-
1. Mosser DM, Edwards JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008. 8:958–969.2. McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007. 7:429–442.3. Choi Y, Arron JR, Townsend MJ. Promising bone-related therapeutic targets for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009. 5:543–548.4. Konisti S, Kiriakidis S, Paleolog EM. Hypoxia--a key regulator of angiogenesis and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012. 8:153–162.5. Taylor PC, Feldmann M. Anti-TNF biologic agents: still the therapy of choice for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009. 5:578–582.6. Murray PJ, Wynn TA. Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011. 11:723–737.7. Gordon S, Taylor PR. Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005. 5:953–964.8. Lawrence T, Natoli G. Transcriptional regulation of macrophage polarization: enabling diversity with identity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011. 11:750–761.9. Fang H, Pengal RA, Cao X, Ganesan LP, Wewers MD, Marsh CB, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophage inflammatory response is regulated by SHIP. J Immunol. 2004. 173:360–366.10. Jang SI, Kim BH, Lee WY, An SJ, Choi HG, Jeon BH, et al. Stylopine from Chelidonium majus inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory mediators in RAW 264.7 cells. Arch Pharm Res. 2004. 27:923–929.11. Kim JB, Han AR, Park EY, Kim JY, Cho W, Lee J, et al. Inhibition of LPS-induced iNOS, COX-2 and cytokines expression by poncirin through the NF-kappaB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007. 30:2345–2351.12. Mukaida N, Ishikawa Y, Ikeda N, Fujioka N, Watanabe S, Kuno K, et al. Novel insight into molecular mechanism of endotoxin shock: biochemical analysis of LPS receptor signaling in a cell-free system targeting NF-kappaB and regulation of cytokine production/action through beta2 integrin in vivo. J Leukoc Biol. 1996. 59:145–151.13. Rovina P, Jaritz M, Bornancin F. Transcriptional repression of ceramide kinase in LPS-challenged macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. 401:164–167.14. Aesif SW, Anathy V, Kuipers I, Guala AS, Reiss JN, Ho YS, et al. Ablation of glutaredoxin-1 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung inflammation and alveolar macrophage activation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011. 44:491–499.15. Gu H, Cui M, Bai Y, Chen F, Ma K, Zhou C, et al. Angiopoietin-1/Tie2 signaling pathway inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. 392:178–182.16. Suzuki M, Tachibana I, Takeda Y, He P, Minami S, Iwasaki T, et al. Tetraspanin CD9 negatively regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophage activation and lung inflammation. J Immunol. 2009. 182:6485–6493.17. Wang SY, Tai GX, Zhang PY, Mu DP, Zhang XJ, Liu ZH. Inhibitory effect of activin A on activation of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells. Cytokine. 2008. 42:85–91.18. Jung YK, Jeong JH, Ryoo HM, Kim HN, Kim YJ, Park EK, et al. Gene expression profile of human chondrocyte HCS-2/8 cell line by EST sequencing analysis. Gene. 2004. 330:85–92.19. Jung YK, Jin JS, Jeong JH, Kim HN, Park NR, Choi JY. DICAM, a novel dual immunoglobulin domain containing cell adhesion molecule interacts with alphavbeta3 integrin. J Cell Physiol. 2008. 216:603–614.20. Jung YK, Han SW, Kim GW, Jeong JH, Kim HJ, Choi JY. DICAM inhibits osteoclast differentiation through attenuation of the integrin αVβ3 pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 2012. (In press).21. Trinchieri G, Sher A. Cooperation of Toll-like receptor signals in innate immune defence. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007. 7:179–190.22. Monaco C, Terrando N, Midwood KS. Toll-like receptor signaling: common pathways that drive cardiovascular disease and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011. 63:500–511.23. Ospelt C, Brentano F, Rengel Y, Stanczyk J, Kolling C, Tak PP, et al. Overexpression of toll-like receptors 3 and 4 in synovial tissue from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: toll-like receptor expression in early and longstanding arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. 58:3684–3692.24. Pierer M, Wagner U, Rossol M, Ibrahim S. Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in inflammatory and joint destructive pathways in collagen-induced arthritis in DBA1J mice. PLoS One. 2011. 6:e23539.25. Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Joosten LA, Roelofs MF, Radstake TR, Matera G, Popa C, et al. Inhibition of Toll-like receptor 4 breaks the inflammatory loop in autoimmune destructive arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. 56:2957–2967.26. Bulut Y, Shimada K, Wong MH, Chen S, Gray P, Alsabeh R, et al. Chlamydial heat shock protein 60 induces acute pulmonary inflammation in mice via the Toll-like receptor 4- and MyD88-dependent pathway. Infect Immun. 2009. 77:2683–2690.27. Triantafilou M, Triantafilou K. Heat-shock protein 70 and heat-shock protein 90 associate with Toll-like receptor 4 in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. 32:636–639.28. Vabulas RM, Braedel S, Hilf N, Singh-Jasuja H, Herter S, Ahmad-Nejad P, et al. The endoplasmic reticulum-resident heat shock protein Gp96 activates dendritic cells via the Toll-like receptor 2/4 pathway. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:20847–20853.29. Okamura Y, Watari M, Jerud ES, Young DW, Ishizaka ST, Rose J, et al. The extra domain A of fibronectin activates Toll-like receptor 4. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:10229–10233.30. Termeer C, Benedix F, Sleeman J, Fieber C, Voith U, Ahrens T, et al. Oligosaccharides of Hyaluronan activate dendritic cells via toll-like receptor 4. J Exp Med. 2002. 195:99–111.31. Campo GM, Avenoso A, D'Ascola A, Prestipino V, Scuruchi M, Nastasi G, et al. Inhibition of hyaluronan synthesis reduced inflammatory response in mouse synovial fibroblasts subjected to collagen-induced arthritis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012. 518:42–52.32. Sofat N, Robertson SD, Wait R. Fibronectin III 13-14 domains induce joint damage via Toll-like receptor 4 activation and synergize with interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor. J Innate Immun. 2012. 4:69–79.33. Campo GM, Avenoso A, D'Ascola A, Scuruchi M, Prestipino V, Nastasi G, et al. The inhibition of hyaluronan degradation reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines in mouse synovial fibroblasts subjected to collagen-induced arthritis. J Cell Biochem. 2012. 113:1852–1867.34. Heinzelmann M, Polk HC Jr, Miller FN. Modulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced monocyte activation by heparin-binding protein and fucoidan. Infect Immun. 1998. 66:5842–5847.35. Billiet L, Furman C, Larigauderie G, Copin C, Brand K, Fruchart JC, et al. Extracellular human thioredoxin-1 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-1beta expression in human monocyte-derived macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2005. 280:40310–40318.36. Janciauskiene S, Larsson S, Larsson P, Virtala R, Jansson L, Stevens T. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-mediated human monocyte activation, in vitro, by alpha1-antitrypsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. 321:592–600.37. Shi C, Simon DI. Integrin signals, transcription factors, and monocyte differentiation. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2006. 16:146–152.38. Faccio R, Takeshita S, Zallone A, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL. c-Fms and the alphavbeta3 integrin collaborate during osteoclast differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2003. 111:749–758.39. Huynh L, Wang L, Shi C, Park-Min KH, Ivashkiv LB. ITAM-coupled receptors inhibit IFNAR signaling and alter macrophage responses to TLR4 and Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 2012. 188:3447–3457.40. Zeisel MB, Druet VA, Sibilia J, Klein JP, Quesniaux V, Wachsmann D. Cross talk between MyD88 and focal adhesion kinase pathways. J Immunol. 2005. 174:7393–7397.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- DICAM-mediated Inhibition of Type 1 Interferon System during Macrophage Differentiation of THP-1 Cells
- Mouse Dual Ig Domain Containing Cell Adhesion Molecule Protein Expression and Purification Using the Baculovirus Expression Vector System
- Regulation of Macrophage Activation and Differentiation in Atherosclerosis
- Paclitaxel inhibits the hyper-activation of spleen cells by lipopolysaccharide and induces cell death
- Silymarin Inhibits Morphological Changes in LPS-Stimulated Macrophages by Blocking NF-kappaB Pathway