Cancer Res Treat.
2014 Jul;46(3):297-306.
Interleukin-17 Indirectly Promotes M2 Macrophage Differentiation through Stimulation of COX-2/PGE2 Pathway in the Cancer Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Structural and Cellular Biology and Orthopaedic Surgery, Tulane Cancer Center and Louisiana Cancer Research Consortium, Tulane Center for Stem Cell Research and Regenerative Medicine, and Tulane Center for Aging, Tulane University Health Sc
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China.
- 3Department of Thoracic Surgery, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China. lunxu_liu@aliyun.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) is a proinflammatory cytokine that plays important roles in inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. The purpose of this study was to determine if IL-17 indirectly regulates macrophage differentiation through up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in the cancer cell lines.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Human cervical cancer HeLa, human lung cancer A549, and mouse prostate cancer Myc-CaP/CR cell lines were treated with recombinant IL-17; Western blot analysis, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis were utilized to examine the cellular responses.
RESULTS
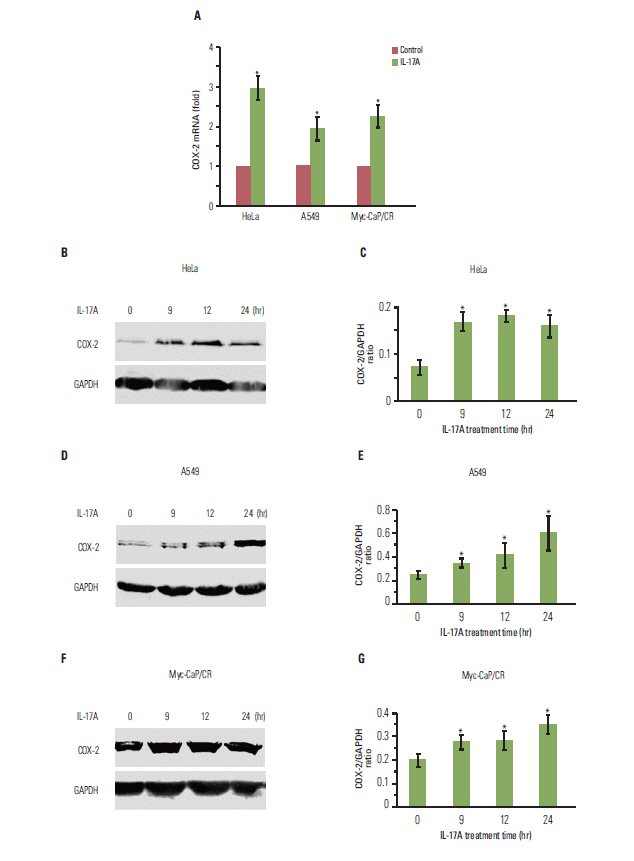
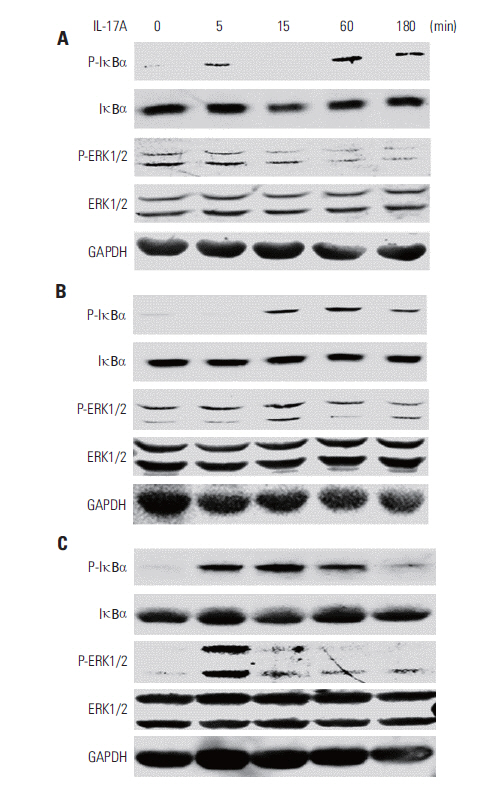
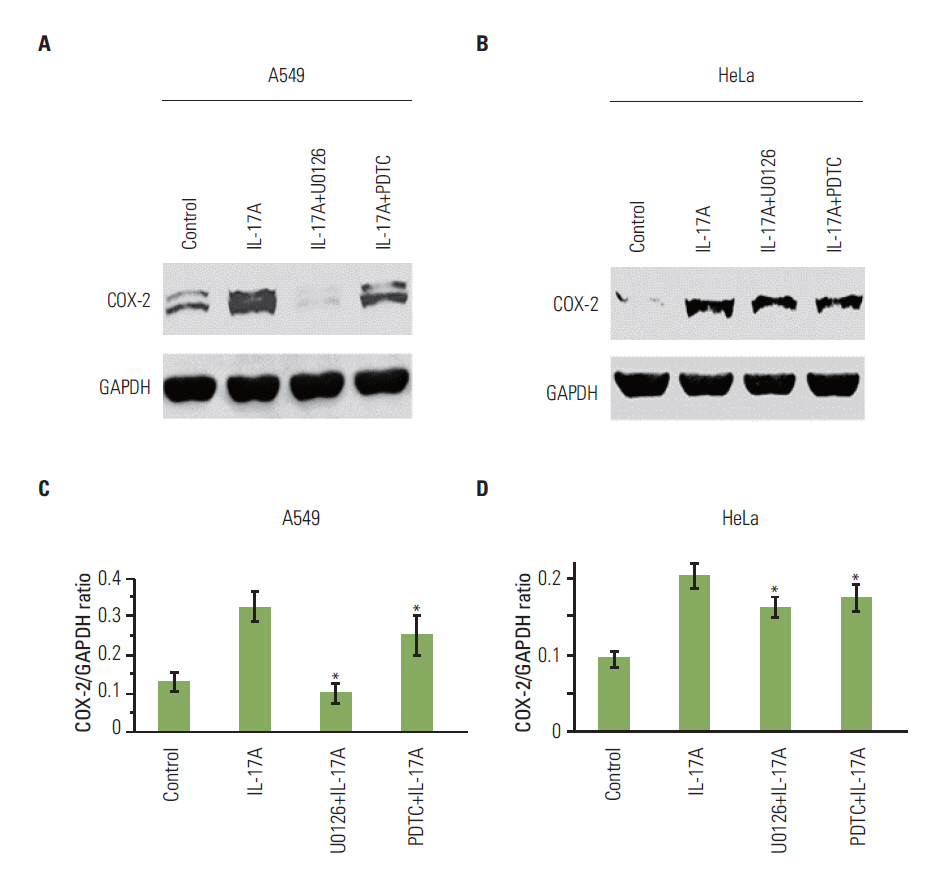
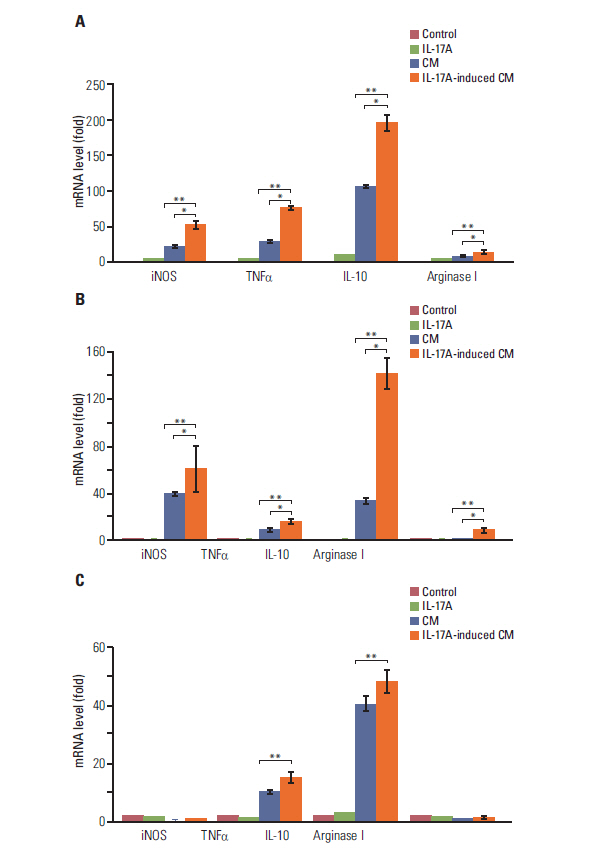
IL-17 up-regulated expression of COX-2 mRNA and protein in HeLa, A549, and Myc-CaP/CR cell lines. IL-17's effects were mediated through nuclear factor-kappaB and ERK1/2 signaling pathways as the inhibitors of these pathways could inhibit IL-17-induced COX-2 expression. The conditional medium obtained from the cancer cells contained prostaglandin E2, the levels of which were increased by IL-17 treatment. When treated with the conditional medium, particularly with the IL-17-induced conditional medium, mouse RAW264.7 macrophages and human THP-1 monocytes expressed higher levels of IL-10 (a marker of M2 macrophages) than inducible nitric oxide synthase or tumor necrosis factor alpha (markers of M1 macrophages). In contrast, when RAW264.7 and THP-1 cells were treated directly with IL-17, expression of these marker genes was not markedly changed.
CONCLUSION
The results of this study suggest that IL-17 indirectly promotes M2 macrophage differentiation through stimulation of the COX-2/PGE2 pathway in the cancer cells, thus IL-17 plays an indirect role in regulating the tumor immune microenvironment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Autoimmunity
Blotting, Western
Cell Line
Cyclooxygenase 2
Dinoprostone
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Humans
Inflammation
Interleukin-10
Interleukin-17*
Lung Neoplasms
Macrophages*
Mice
Monocytes
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type II
Prostatic Neoplasms
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA, Messenger
Tumor Microenvironment
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Up-Regulation
Uterine Cervical Neoplasms
Cyclooxygenase 2
Dinoprostone
Interleukin-10
Interleukin-17
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type II
RNA, Messenger
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Mantovani A, Sica A, Locati M. New vistas on macrophage differentiation and activation. Eur J Immunol. 2007; 37:14–6.
Article2. Gordon S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003; 3:23–35.
Article3. Mantovani A, Sica A, Locati M. Macrophage polarization comes of age. Immunity. 2005; 23:344–6.
Article4. Mantovani A, Bottazzi B, Colotta F, Sozzani S, Ruco L. The origin and function of tumor-associated macrophages. Immunol Today. 1992; 13:265–70.
Article5. Ma J, Liu L, Che G, Yu N, Dai F, You Z. The M1 form of tumorassociated macrophages in non-small cell lung cancer is positively associated with survival time. BMC Cancer. 2010; 10:112.
Article6. Liu L, Ge D, Ma L, Mei J, Liu S, Zhang Q, et al. Interleukin-17 and prostaglandin E2 are involved in formation of an M2 macrophage-dominant microenvironment in lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2012; 7:1091–100.
Article7. Onishi RM, Gaffen SL. Interleukin-17 and its target genes: mechanisms of interleukin-17 function in disease. Immunology. 2010; 129:311–21.
Article8. Liu C, Qian W, Qian Y, Giltiay NV, Lu Y, Swaidani S, et al. Act1, a U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase for IL-17 signaling. Sci Signal. 2009; 2:ra63.
Article9. Hata K, Andoh A, Shimada M, Fujino S, Bamba S, Araki Y, et al. IL-17 stimulates inflammatory responses via NF-kappaB and MAP kinase pathways in human colonic myofibroblasts. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002; 282:G1035–44.10. Ellis L, Lehet K, Ramakrishnan S, Adelaiye R, Pili R. Development of a castrate resistant transplant tumor model of prostate cancer. Prostate. 2012; 72:587–91.
Article11. Lai T, Wang K, Hou Q, Zhang J, Yuan J, Yuan L, et al. Interleukin 17 induces up-regulation of chemokine and cytokine expression via activation of the nuclear factor kappaB and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathways in gynecologic cancer cell lines. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011; 21:1533–9.12. Greenhough A, Smartt HJ, Moore AE, Roberts HR, Williams AC, Paraskeva C, et al. The COX-2/PGE2 pathway: key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and adaptation to the tumour microenvironment. Carcinogenesis. 2009; 30:377–86.
Article13. Steiner GE, Newman ME, Paikl D, Stix U, Memaran-Dagda N, Lee C, et al. Expression and function of pro-inflammatory interleukin IL-17 and IL-17 receptor in normal, benign hyperplastic, and malignant prostate. Prostate. 2003; 56:171–82.
Article14. Chen Z, Ding J, Pang N, Du R, Meng W, Zhu Y, et al. The Th17/Treg balance and the expression of related cytokines in Uygur cervical cancer patients. Diagn Pathol. 2013; 8:61.
Article15. Tartour E, Fossiez F, Joyeux I, Galinha A, Gey A, Claret E, et al. Interleukin 17, a T-cell-derived cytokine, promotes tumorigenicity of human cervical tumors in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1999; 59:3698–704.16. He D, Li H, Yusuf N, Elmets CA, Li J, Mountz JD, et al. IL-17 promotes tumor development through the induction of tumor promoting microenvironments at tumor sites and myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Immunol. 2010; 184:2281–8.
Article17. Chung AS, Wu X, Zhuang G, Ngu H, Kasman I, Zhang J, et al. An interleukin-17-mediated paracrine network promotes tumor resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Med. 2013; 19:1114–23.
Article18. Hayata K, Iwahashi M, Ojima T, Katsuda M, Iida T, Nakamori M, et al. Inhibition of IL-17A in tumor microenvironment augments cytotoxicity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in tumorbearing mice. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e53131.
Article19. Olsson Akefeldt S, Maisse C, Belot A, Mazzorana M, Salvatore G, Bissay N, et al. Chemoresistance of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells is regulated by IL-17A. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e56865.
Article20. Liao R, Sun J, Wu H, Yi Y, Wang JX, He HW, et al. High expression of IL-17 and IL-17RE associate with poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2013; 32:3.
Article21. Yamada Y, Saito H, Ikeguchi M. Prevalence and clinical relevance of Th17 cells in patients with gastric cancer. J Surg Res. 2012; 178:685–91.
Article22. Chen WC, Lai YH, Chen HY, Guo HR, Su IJ, Chen HH. Interleukin-17-producing cell infiltration in the breast cancer tumour microenvironment is a poor prognostic factor. Histopathology. 2013; 63:225–33.
Article23. Zhang GQ, Han F, Fang XZ, Ma XM. CD4+, IL17 and Foxp3 expression in different pTNM stages of operable non-small cell lung cancer and effects on disease prognosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012; 13:3955–60.
Article24. Liu J, Duan Y, Cheng X, Chen X, Xie W, Long H, et al. IL-17 is associated with poor prognosis and promotes angiogenesis via stimulating VEGF production of cancer cells in colorectal carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011; 407:348–54.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Regulation of Osteoclast Differentiation by Cytokine Networks
- Viperin Deficiency Promotes Polarization of Macrophages and Secretion of M1 and M2 Cytokines
- Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Houttuynia Cordata Thunb in Activated Raw 264.7 Cells Activated with Lipopolysaccharide and Interferon Gamma
- Interleukin-1beta-Mediated MUC5AC Gene Expression and Mucin Secretion via PKC-ERK/p38-COX-2-PGE2 in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- IL-1beta Mediated COX-2 Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells