J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Feb;21(1):95-99. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.1.95.
Ceramides and Cell Signaling Molecules in Psoriatic Epidermis: Reduced Levels of Ceramides, PKC-alpha, and JNK
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. nikim@khmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Medical Nutrition, Graduate School of East-West Medical Science, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2157790
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.1.95
Abstract
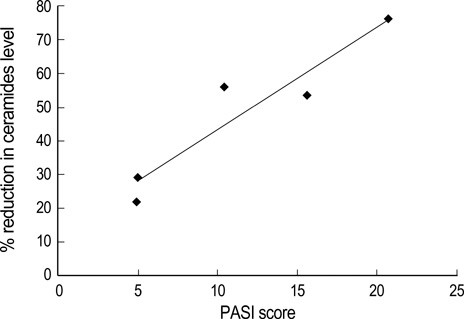
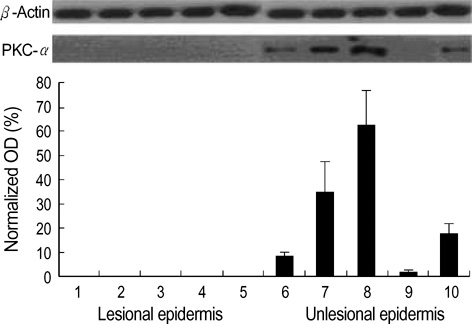
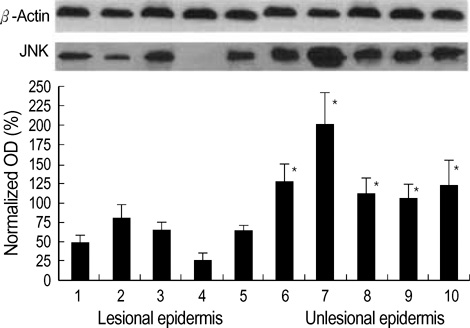
- Ceramides are the main lipids in the stratum corneum and are generated during cellular stress and apoptosis by de novo synthesis or by the action of sphingomyelinase. In addition, they are lipid second messengers produced by sphingolipid metabolism and trigger important cell responses, including protein kinase C-alpha (PKC-alpha) activation and the stimulation of signal transduction pathways with apoptosis and stress-activated protein kinases (SAPK), such as c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Thus, ceramides have anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects. This study measured the changes in the levels of epidermal ceramides and ceramide-related apoptotic signaling molecules in psoriasis patients. Samples from lesional and non-lesional epidermis were obtained from psoriasis patients. Total ceramides were fractionated using thin-layer chromatography, and the levels of PKC-alpha and JNK expression were measured using Western blot analysis with specific antibodies. The ceramide level was reduced significantly, and this was associated with the downregulation of apoptotic signaling molecules, such as PKC-alpha and JNK, in the lesional epidermis of psoriasis patients. These results suggest that the decreased level of ceramides downregulates the apoptotic pathway, leading to epidermal proliferation in psoriasis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Apoptosis/physiology
Blotting, Western
Ceramides/*metabolism
Chromatography, Thin Layer
Epidermis/metabolism/pathology/physiopathology
Female
Humans
JNK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases/metabolism
Male
Protein Kinase C-alpha/metabolism
Psoriasis/metabolism/*pathology/physiopathology
Severity of Illness Index
Signal Transduction/*physiology
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Altered Levels of Sphingosine and Sphinganine in Psoriatic Epidermis
Sung-Hyuk Moon, Ju-Young Kim, Eun-Hwa Song, Min-Kyung Shin, Yun-Hi Cho, Nack-In Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2013;25(3):321-326. doi: 10.5021/ad.2013.25.3.321.
Reference
-
1. Elias PM, Menon G. Elias PM, editor. Structural and lipid biochemical correlates of the epidermal permeability barrier. Adv Lipid Research. 1991. 24:1–26.
Article2. Imokawa G, Abe A, Jin K, Higaki Y, Kawashima M, Hidano A. Decreased level of ceramides in stratum corneum of atopic dermatitis: an etiologic factor in atopic dry skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991. 96:523–526.
Article3. Matsumoto M, Umemoto N, Sugiura H, Uehara M. Difference in ceramide composition between "dry" and normal skin in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh). 1999. 79:246–247.4. Chung S, Kong S, Seong K, Cho Y. γ-Linolenic acid in borage oil reverses epidermal hyperproliferation in guinea pigs. J Nutr. 2002. 132:3090–3097.
Article5. Aschrafi A, Franzen R, Shabahang S, Fabbro D, Pfeilschifter J, Huwiler A. Ceramide induces translocation of protein kinase C-alpha to the Golgi compartment of human embryonic kidney cells by interacting with the C2 domain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003. 1634:30–39.6. Huwiler A, Fabbro D, Pfeilschifter J. Selective ceramide binding to protein kinase C-alpha and -delta isoenzymes in renal mesangial cells. Biochemistry. 1998. 37:14556–14562.7. Ruvolo PP. Ceramide regulates cellular homeostasis via diverse stress signaling pathways. Leukemia. 2001. 15:1153–1160.
Article8. Macheleidt O, Kaiser HW, Sandhoff K. Deficiency of epidermal protein-bound ω-hydroxyceramides in atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2002. 119:166–173.
Article9. Tohyama J, Oya Y, Ezoe T, Vanier MT, Nakayasu H, Fujita N, Suzuki K. Ceramide accumulation is associated with increased apoptotic cell death in cultured fibroblasts of sphingolipid activator protein-deficient mouse but not in fibroblasts of patients with Farber disease. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1999. 22:649–662.
Article10. Uchida Y, Hara M, Nishio H, Sidransky E, Inoue S, Otsuka F, Suzuki A, Elias PM, Holleran WM, Hamanaka S. Epidermal sphingomyelins are precursors for selected stratum corneum ceramides. J Lipid Res. 2000. 41:2071–2082.
Article11. Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951. 193:265–275.
Article12. Motta S, Monti M, Sesana S, Mellesi L, Ghidoni R, Caputo R. Abnormality of water barrier function in psoriasis. Role of ceramide functions. Arch Dermatol. 1994. 130:452–456.13. Cho Y, Lew BL, Seong K, Kim NI. An inverse relationship between ceramide synthesis and clinical severity in patients with psoriasis. J Korean Med Sci. 2004. 19:859–863.
Article14. Imokawa G. Lipid abnormalities in atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001. 45:S29–S32.
Article15. Jin K, Higaki Y, Takagi Y, Higuchi k, Yada Y, Kawashima M, Imokawa G. Analysis of beta-glucocerebrosidase and ceramidase activity in atopic and aged dry skin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1994. 74:337–340.16. Aioi A, Tonogaito H, Suto H, Hamada K, Ra CR, Ogawa H, Maibach H, Matsuda H. Impairment of skin barrier function in NC/Nga Tnd mice as a possible model for atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2001. 144:12–18.
Article17. Hara J, Hoguchi K, Okamoto R, Kawashima M, Imokawa G. High expression of sphingomyelin deacylase is an important determinant of ceramide deficiency leading to barrier disruption in atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2000. 115:406–413.18. Spiegel S, Foster D, Kolesnick R. Signal transduction through lipid second messengers. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996. 8:159–167.
Article19. Fisher GJ, Tavakkol A, Leach K, Burns D, Basta P, Loomis C, Griffiths CE, Cooper KD, Reynolds NJ, Elder JT. Differential expression of protein kinase C isoenzymes in normal and psoriatic adult human skin: reduced expression of protein kinase C-beta II in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 1993. 101:553–559.20. Visnjic D, Batinic D, Banfic H. Different roles of protein kinase C alpha and delta isoforms in the regulation of neutral sphingomyelinase activity in HL-60 cells. Biochem J. 1999. 344:921–928.21. Verheij M, Bose R, Lin XH, Yao B, Jarvis WD, Grant S, Birrer MJ, Szabo E, Zon LI, Kyriakis JM, Haimovitz-Friedman A, Fuks Z, Kolesnick RN. Requirement for ceramide-initiated SAPK/JNK signalling in stress-induced apoptosis. Nature. 1996. 380:75–79.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on Altered Expression of Serine Palmitoyltransferase and Ceramidase in Psoriatic Skin Lesion
- Altered Levels of Sphingosine and Sphinganine in Psoriatic Epidermis
- Synthesized Ceramide Induces Growth of Dermal Papilla Cells with Potential Contribution to Hair Growth
- An Inverse Relationship Between Ceramide Synthesis and Clinical Severity in Patients with Psoriasis
- Ceramides: Nutrient Signals that Drive Hepatosteatosis