An Inverse Relationship Between Ceramide Synthesis and Clinical Severity in Patients with Psoriasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. nikim@khmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Medical Nutrition, Graduate School of East-West Medical Science, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1778569
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.6.859
Abstract
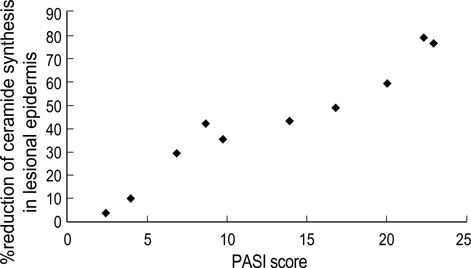
- Ceramides play major roles in maintaining the epidermal barrier. It has been sus-pected that the depletion of ceramides, associated with disrupted barrier function in the epidermis, leads to the clinical manifestation of dryness and inflammation seen in patients with psoriasis. The aim of the present study was to determine the relation-ship between the level of ceramide synthesis in the epidermis and the clinical severity in patients with psoriasis. Samples from lesional and unlesional epidermis obtained from psoriasis patients were incubated with [14C]serine, an initiator of ceramide syn-thesis. otal ceramide was fractionated using high performance thin layer chromato-graphy, and the radioactivity was measured. The clinical severity of psoriasis was graded according to the psoriasis area and severity index scoring system. The level of ceramide synthesis in the lesional epidermis of patients was significantly lower than that in the unlesional epidermis and bore a negative correlation with the clinical severity of psoriasis. The present results suggest that the decreased level of ceramide synthesis in the epidermis contributes to the clinical severity of psoriasis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Ceramides and Cell Signaling Molecules in Psoriatic Epidermis: Reduced Levels of Ceramides, PKC-α, and JNK
Bark-Lynn Lew, Yunhi Cho, Jungmin Kim, Woo-Young Sim, Nack-In Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2006;21(1):95-99. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.1.95.A Study on Altered Expression of Serine Palmitoyltransferase and Ceramidase in Psoriatic Skin Lesion
Kyung-Kook Hong, Hee-Ryung Cho, Won-Chul Ju, Yunhi Cho, Nack-In Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2007;22(5):862-867. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.5.862.The Effect of Gromwell (Lithospermum erythrorhizon) Extract on the Stratum Corneum Hydration and Ceramides Content in Atopic Dermatitis Patients
Hee Ryung Cho, Yunhi Cho, Juyoung Kim, Dae Bang Seo, Sung Han Kim, Sang Jun Lee, Nack In Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2008;20(2):56-66. doi: 10.5021/ad.2008.20.2.56.Altered Levels of Sphingosine and Sphinganine in Psoriatic Epidermis
Sung-Hyuk Moon, Ju-Young Kim, Eun-Hwa Song, Min-Kyung Shin, Yun-Hi Cho, Nack-In Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2013;25(3):321-326. doi: 10.5021/ad.2013.25.3.321.
Reference
-
1. Elias PM, Menon GK. Structural and lipid biochemical correlates of the epidermal permeability barrier. Adv Lipid Res. 1991. 24:1–26.
Article2. Rogers J, Harding C, Mayo A, Banks J, Rawlings A. Stratum corneum lipids; the effect of ageing and the seasons. Arch Dermatol Res. 1996. 288:765–770.
Article3. Gray GM, White RJ, Williams RH, Yardley HJ. Lipid composition of the superficial stratum corneum cells of pig epidermis. Br J Dermatol. 1982. 106:59–63.
Article4. Hedberg CL, Wetz PW, Downing DT. The time course of lipid biosynthesis in pig epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1988. 91:169–174.
Article5. Grubauer G, Feingold KR, Harris RM, Elias PM. Lipid content and lipid type as determinants of the epidermal permeability barrier. J Lipid Res. 1989. 30:89–96.
Article6. Wertz PW, Cho ES, Downing DT. Effect of essential fatty acid deficiency on the epidermal sphingolipids of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983. 753:350–355.
Article7. Imokawa G, Abe A, Jin K, Higaki Y, Kawashima M, Hidano A. Decreased level of ceramides in stratum corneum of atopic dermatitis: an etiologic factor in atopic dry skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991. 96:523–526.
Article8. Matsumoto M, Umemoto N, Sugiura H, Uehara M. Difference in ceramide composition between "dry" and normal skin in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh). 1999. 79:246–247.9. Burr GO, Burr MM. Nutrition classics from J Biol Chem 82: 345-67, 1929. A new deficiency disease produced by the rigid exclusion of fat from the diet. Nutr Rev. 1973. 31:248–249.10. Chung S, Kong S, Seong K, Cho Y. γ-Linolenic acid in borage oil reverses epidermal hyperproliferation in guinea pigs. J Nutr. 2002. 132:3090–3097.
Article11. Motta S, Monti M, Sesana S, Mellesi L, Ghidoni R, Caputo R. Abnormality of water barrier function in psoriasis. Role of ceramide functions. Arch Dermatol. 1994. 130:452–456.12. Williams ML. Lipids in normal and pathological desquamation. Adv Lipid Res. 1991. 24:211–262.
Article13. Serup J, Blichmann C. Epidermal hydration of psoriasis plaques and the relation to scaling. Measurement of electrical conductance and transepidermal water loss. Acta Derm Venereol. 1987. 67:357–359.14. Macheleidt O, Kaiser HW, Sandhoff K. Deficiency of epidermal protein-bound ω-hydroxyceramides in atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2002. 119:166–173.
Article15. Tohyama J, Oya Y, Ezoe T, Vanier MT, Nakayasu H, Fujita N, Suzuki K. Ceramide accumulation is associated with increased apoptotic cell death in cultured fibroblasts of sphingolipid activator protein-deficient mouse but not in fibroblasts of patients with Farber disease. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1999. 22:649–662.
Article16. Uchida Y, Hara M, Nishio H, Sidransky E, Inoue S, Otsuka F, Suzuki A, Elias PM, Holleran WM, Hamanaka S. Epidermal sphingomyelins are precursors for selected stratum corneum ceramides. J Lipid Res. 2000. 41:2071–2082.
Article17. Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951. 193:265–275.
Article18. Tang W, Ziboh VA. Reversal of epidermal hyperproliferation in essential fatty acid deficient guinea pigs is accompanied by rapid generation of inositol triphosphate. Arch Dermatol Res. 1988. 280:286–292.
Article19. Wertz PW, Swartzendruber DC, Abraham W, Madison KC, Downing DT. Essential fatty acids and epidermal integrity. Arch Dermatol. 1987. 123:1381–1384.
Article20. Elias PM, Brown BE. The mammalian cutaneous permeability barrier: defective barrier function in essential fatty acid deficiency correlates with abnormal intercellular lipid deposition. Lab Invest. 1978. 39:574–583.21. Akimoto K, Yoshikawa N, Higaki Y, Kawashima M, Imokawa G. Quantitative analysis of stratum corneum lipids in xerosis and asteatotic eczema. J Dermatol. 1993. 20:1–6.
Article22. Bouwstra JA, Gooris GS, Dubbelaar FE, Weerheim AM, Ijzerman AP, Ponec M. Role of ceramide 1 in the molecular organization of the stratum corneum lipids. J Lipid Res. 1998. 39:186–196.
Article23. Imokawa G. Lipid abnormalities in atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001. 45:S29–S32.
Article24. Jin K, Higaki Y, Takagi Y, Higuchi K, Yada Y, Kawashima M, Imokawa G. Analysis of beta-glucocerebrosidase and ceramidase activities in atopic and aged dry skin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1994. 74:337–340.25. Aioi A, Tonogaito H, Suto H, Hamada K, Ra C, Ogawa H, Maibach H, Matsudas H. Impairment of skin barrier function in NC/Nga Tnd mice as a possible model for atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2001. 144:12–18.
Article26. Hara J, Hoguchi K, Okamoto R, Kawashima M, Imokawa G. High expression of sphingomyelin deacylase is an important determinant of ceramide deficiency leading to barrier disruption in atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2000. 115:406–413.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Altered Levels of Sphingosine and Sphinganine in Psoriatic Epidermis
- Relation between the Peripherofacial Psoriasis and Scalp Psoriasis
- Inverse Psoriasis Developed in a Patient with Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma
- A Study on Altered Expression of Serine Palmitoyltransferase and Ceramidase in Psoriatic Skin Lesion
- Clinical Analysis of Nail Involvement in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis