Ann Dermatol.
2013 Aug;25(3):321-326. 10.5021/ad.2013.25.3.321.
Altered Levels of Sphingosine and Sphinganine in Psoriatic Epidermis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. nikim@khmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Medical Nutrition, Graduate School of East-West Medical Science, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2265872
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2013.25.3.321
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Ceramides are the main lipid component of the stratum corneum and are a structurally heterogeneous and complex group of sphingolipids of which sphingoid bases are the basic structural constituents. Altered levels of sphingoid bases have been reported in skin conditions that involve dryness and barrier disruption, including atopic dermatitis.
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study was to investigate the altered levels of sphingoid bases in psoriatic epidermis and their relationship with the clinical severity of the psoriasis.
METHODS
Samples from the lesional and non-lesional epidermis were obtained from eight psoriasis patients. Levels of sphingosine and sphinganine were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography. The expression of ceramide synthase and ceramidase proteins, which are related to sphingosine and sphinganine metabolism, were measured using Western blot analysis.
RESULTS
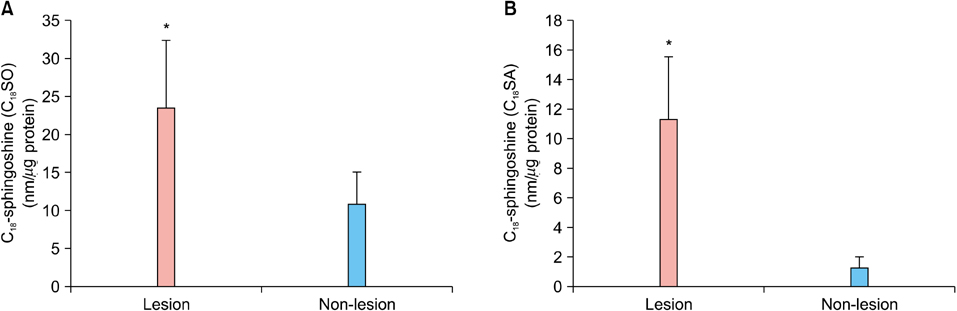
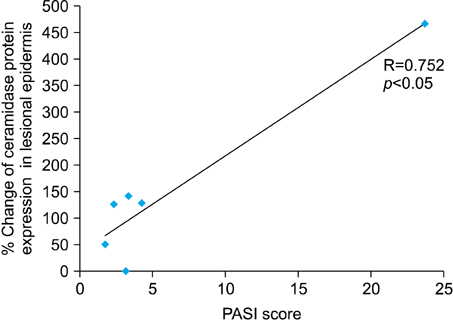
Levels of sphingosine and sphinganine in the lesional epidermis were significantly higher than those in the non-lesional epidermis. Although there was no altered ceramide synthase and ceramidase, there was a highly significant positive correlation between the % change of ceramidase, the degradative enzyme of ceramide into sphingosine, and the Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) score.
CONCLUSION
The levels of sphingosine and sphinganine were significantly increased in psoriatic epidermis and the % change of ceramidase was positively correlated with the clinical severity of psoriasis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Elias PM, Menon G. Structural and lipid biochemical correlates of the epidermal permeability barrier. In : Elias PM, editor. Skin lipid. Advances in lipid research. San Diego: Academic Press;1999. p. 24–26.2. Imokawa G, Abe A, Jin K, Higaki Y, Kawashima M, Hidano A. Decreased level of ceramides in stratum corneum of atopic dermatitis: an etiologic factor in atopic dry skin? J Invest Dermatol. 1991; 96:523–526.
Article3. Matsumoto M, Umemoto N, Sugiura H, Uehara M. Difference in ceramide composition between "dry" and "normal" skin in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1999; 79:246–247.
Article4. Chung S, Kong S, Seong K, Cho Y. Gamma-linolenic acid in borage oil reverses epidermal hyperproliferation in guinea pigs. J Nutr. 2002; 132:3090–3097.
Article5. Cho Y, Lew BL, Seong K, Kim NI. An inverse relationship between ceramide synthesis and clinical severity in patients with psoriasis. J Korean Med Sci. 2004; 19:859–863.
Article6. Lew BL, Cho Y, Kim J, Sim WY, Kim NI. Ceramides and cell signaling molecules in psoriatic epidermis: reduced levels of ceramides, PKC-alpha, and JNK. J Korean Med Sci. 2006; 21:95–99.
Article7. Aschrafi A, Franzen R, Shabahang S, Fabbro D, Pfeilschifter J, Huwiler A. Ceramide induces translocation of protein kinase C-alpha to the Golgi compartment of human embryonic kidney cells by interacting with the C2 domain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003; 1634:30–39.
Article8. Huwiler A, Fabbro D, Pfeilschifter J. Selective ceramide binding to protein kinase C-alpha and -delta isoenzymes in renal mesangial cells. Biochemistry. 1998; 37:14556–14562.
Article9. Ruvolo PP. Ceramide regulates cellular homeostasis via diverse stress signaling pathways. Leukemia. 2001; 15:1153–1160.
Article10. Bibel DJ, Aly R, Shinefield HR. Topical sphingolipids in antisepsis and antifungal therapy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1995; 20:395–400.
Article11. Ohnishi Y, Okino N, Ito M, Imayama S. Ceramidase activity in bacterial skin flora as a possible cause of ceramide deficiency in atopic dermatitis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1999; 6:101–104.
Article12. Arikawa J, Ishibashi M, Kawashima M, Takagi Y, Ichikawa Y, Imokawa G. Decreased levels of sphingosine, a natural antimicrobial agent, may be associated with vulnerability of the stratum corneum from patients with atopic dermatitis to colonization by Staphylococcus aureus. J Invest Dermatol. 2002; 119:433–439.
Article13. Aburai K, Yoshino S, Sakai K, Sakai H, Abe M, Loiseau N, et al. Physicochemical analysis of liposome membranes consisting of model lipids in the stratum corneum. J Oleo Sci. 2011; 60:197–202.
Article14. Macheleidt O, Kaiser HW, Sandhoff K. Deficiency of epidermal protein-bound omega-hydroxyceramides in atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2002; 119:166–173.
Article15. Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951; 193:265–275.
Article16. Ruwisch L, Schäfer-Korting M, Kleuser B. An improved high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of sphingosine-1-phosphate in complex biological materials. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2001; 363:358–363.
Article17. Min JK, Yoo HS, Lee EY, Lee WJ, Lee YM. Simultaneous quantitative analysis of sphingoid base 1-phosphates in biological samples by o-phthalaldehyde precolumn derivatization after dephosphorylation with alkaline phosphatase. Anal Biochem. 2002; 303:167–175.
Article18. Yoon HT, Yoo HS, Shin BK, Lee WJ, Kim HM, Hong SP, et al. Improved fluorescent determination method of cellular sphingoid bases in high-performance liquid chromatography. Arch Pharm Res. 1999; 22:294–299.
Article19. Rogers J, Harding C, Mayo A, Banks J, Rawlings A. Stratum corneum lipids: the effect of ageing and the seasons. Arch Dermatol Res. 1996; 288:765–770.
Article20. Gray GM, White RJ, Williams RH, Yardley HJ. Lipid composition of the superficial stratum corneum cells of pig epidermis. Br J Dermatol. 1982; 106:59–63.
Article21. Hedberg CL, Wertz PW, Downing DT. The time course of lipid biosynthesis in pig epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1988; 91:169–174.
Article22. Grubauer G, Feingold KR, Harris RM, Elias PM. Lipid content and lipid type as determinants of the epidermal permeability barrier. J Lipid Res. 1989; 30:89–96.
Article23. Wertz PW, Cho ES, Downing DT. Effect of essential fatty acid deficiency on the epidermal sphingolipids of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983; 753:350–355.
Article24. Coderch L, López O, de la Maza A, Parra JL. Ceramides and skin function. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003; 4:107–129.
Article25. Kobayashi T, Shinnoh N, Goto I. Metabolism of free sphingoid bases in murine tissues and in cultured human fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1989; 186:493–499.
Article26. Hong KK, Cho HR, Ju WC, Cho Y, Kim NI. A study on altered expression of serine palmitoyltransferase and ceramidase in psoriatic skin lesion. J Korean Med Sci. 2007; 22:862–867.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Enhanced Expression of Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen in Psoriatic Epidermis
- Dietary effect of silk protein on epidermal levels of free sphingoid bases and phosphate metabolites in NC/Nga mice
- Analysis of ceramide metabolites in differentiating epidermal keratinocytes treated with calcium or vitamin C
- Fumonisin B1-Induced Toxicity Was Not Exacerbated in Glutathione Peroxidase-1/Catalase Double Knock Out Mice
- A Study on Altered Expression of Serine Palmitoyltransferase and Ceramidase in Psoriatic Skin Lesion