J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Oct;22(5):862-867. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.5.862.
A Study on Altered Expression of Serine Palmitoyltransferase and Ceramidase in Psoriatic Skin Lesion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. nikim@khmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Medical Nutrition, Graduate School of East-West Medical Science, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1713294
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.5.862
Abstract
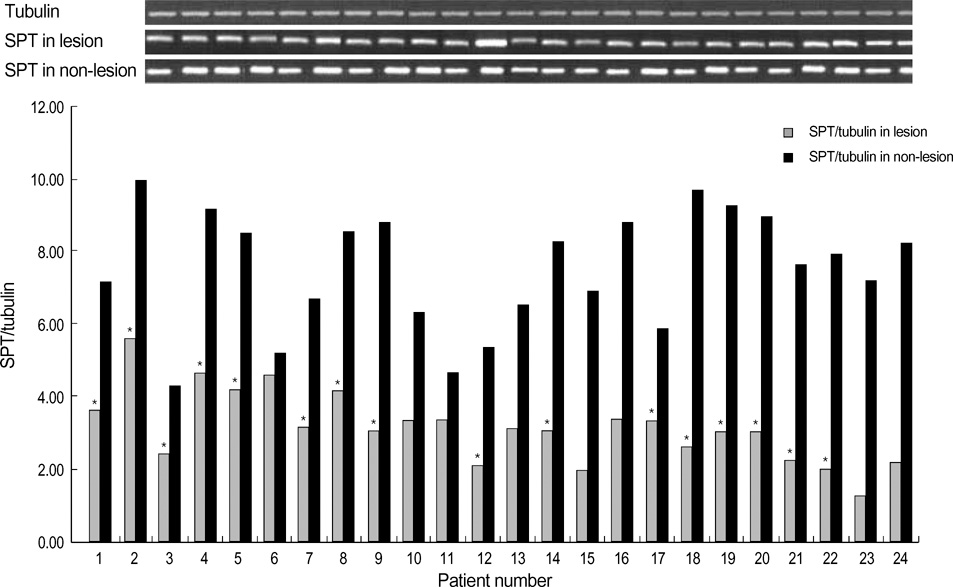
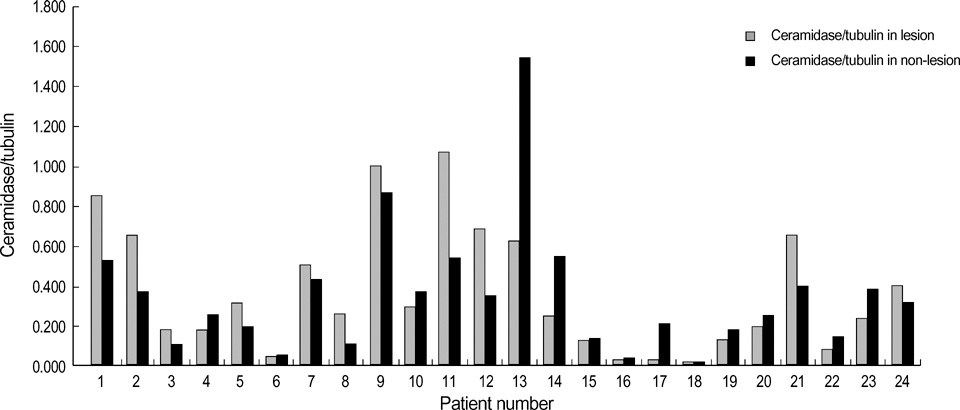
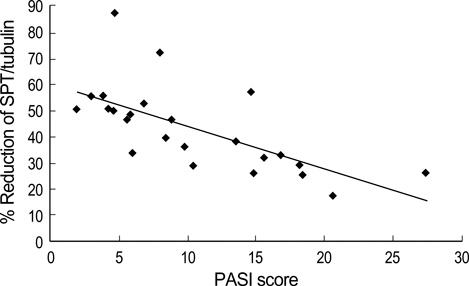
- Ceramides are the main lipid component maintaining the lamellae structure of stratum corneum, as well as lipid second messengers for the regulation of cellular proliferation and/or apoptosis. In our previous study, psoriatic skin lesions showed marked decreased levels of ceramides and signaling molecules, specially protein kinase C-alpha (PKC-alpha) and c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in proportion to the psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) scores, which suggested that the depletion of ceramide is responsible for epidermal hyperproliferation of psoriasis via downregulation of proapoptotic signal cascade such as PKC-alpha and JNK. In this study, we investigated the protein expression of serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) and ceramidase, two major ceramide metabolizing enzymes, in both psoriatic epidermis and non-lesional epidermis. The expression of SPT, the ceramide generating enzyme in the de novo synthesis in psoriatic epidermis, was significantly less than that of the non-lesional epidermis, which was inversely correlated with PASI score. However, the expression of ceramidase, the degradative enzyme of ceramides, showed no significant difference between the lesional epidermis and the non-lesional epidermis of psoriatic patients. This might suggest that decreased expression of SPT protein is one of the important causative factors for decreased ceramide levels in psoriasis.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Amidohydrolases/*biosynthesis/metabolism
Apoptosis
Cell Proliferation
Ceramidases
Ceramides/chemistry
Child
Epidermis/metabolism
Female
Humans
JNK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases/metabolism
Male
Models, Biological
Protein Kinase C-alpha/metabolism
Psoriasis/*blood/diagnosis
Serine C-Palmitoyltransferase/*biosynthesis
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Altered Levels of Sphingosine and Sphinganine in Psoriatic Epidermis
Sung-Hyuk Moon, Ju-Young Kim, Eun-Hwa Song, Min-Kyung Shin, Yun-Hi Cho, Nack-In Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2013;25(3):321-326. doi: 10.5021/ad.2013.25.3.321.
Reference
-
1. Elias PM, Menon G. Elias PM, editor. Structural and lipid biochemical correlates of the epidermal permeability barrier. Skin Lipid. Advances in Lipid Research. 1999. 24. San Diego: Academic Press;26.
Article2. Imokawa G, Abe A, Jin K, Higaki Y, Kawashima M, Hidano A. Decreased levels of ceramides in stratum corneum of atopic dermatitis: an etiological factor in atopic dry skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991. 96:523–526.3. Matsumoto M, Umemoto N, Sugiura H, Uehara M. Difference in ceramide composition between "dry" and normal skin in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol (Stockh). 1999. 79:246–247.4. Chung S, Kong S, Seong K, Cho Y. γ-Linolenic acid in borage oil reverses epidermal hyperproliferation in guinea pigs. J Nutr. 2002. 132:3090–3097.
Article5. Aschrafi A, Franzen R, Shabahang S, Fabbro D, Pfeilschifter J, Huwiler A. Ceramide induces translocation of protein kinase C-alpha to the Golgi compartment of human embryonic kidney cells by interacting with the C2 domain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003. 1634:30–39.6. Huwiler A, Fabbro D, Pfeilschifter J. Selective ceramide binding to protein kinase C-alpha and -delta isoenzymes in renal mesangial cells. Biochemistry. 1998. 37:14556–14562.7. Ruvolo PP. Ceramide regulates cellular homeostasis via diverse stress signaling pathways. Leukemia. 2001. 15:1153–1160.
Article8. Cho Y, Lew BL, Seong K, Kim NI. An inverse relationship between ceramide synthesis and clinical severity in patients with psoriasis. J Korean Med Sci. 2004. 19:859–863.
Article9. Lew BL, Cho Y, Kim J, Sim WY, Kim NI. Ceramides and cell signaling molecules in psoriatic epidermis: reduced levels of ceramides, PKC-alpha, and JNK. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:95–99.10. Macheleidt O, Kaiser HW, Sandhoff K. Deficiency of epidermal protein-bound ω-hydroxyceramides in atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2002. 119:166–173.
Article11. Lampe MA, Burlingame AL, Whitney J, Williams ML, Brown BE, Roitman E, Elias PM. Human stratum corneum lipids: characterization and regional variations. J Lipid Res. 1983. 24:120–130.
Article12. Hannun YA, Luberto C. Ceramide in the eukaryotic stress response. Trends Cell Biol. 2000. 10:73–80.
Article13. Perry DK. The role of de novo ceramide synthesis in chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. 905:91–96.
Article14. Huwiler A, Kolter T, Pfeilschifter J, Sandhoff K. Physiology and pathophysiology of sphingolipid metabolism and signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. 1485:63–99.
Article15. van Blitterswijk WJ, van der Luit AH, Veldman RJ, Verheij M, Borst J. Ceramide: second messenger or modulator of membrane structure and dynamics? Biochem J. 2003. 369:199–211.16. Merrill AH Jr, Jones DD. An update of the enzymology and regulation of sphingomyelin metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990. 1044:1–12.
Article17. Holleran WM, Williams ML, Gao WN, Elias PM. Serine palmitoyltransferase activity in cultured human keratinocytes. J Lipid Res. 1990. 31:1655–1661.18. Holleran WM, Gao WN, Feingold KR, Elias PM. Localization of epidermal sphingolipid synthesis and serine palmitoyltransferase activity: alterations imposed by permeability barrier requirements. Arch Dermatol Res. 1995. 287:254–258.19. Tardi PG, Mukherjee JJ, Choy PC. The quantitation of long-chain acyl-CoA in mammalian tissue. Lipids. 1992. 27:65–67.
Article20. Mangino MJ, Zografakis J, Murphy MK, Anderson CB. Improved and simplified tissue extraction method for quantitating long-chain acyl-coenzyme A thioesters with picomolar detection using high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1992. 577:157–162.
Article21. DeMar JC Jr, Anderson RE. Identification and quantitation of the fatty acids composing the CoA ester pool of bovine retina, heart, and liver. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:31362–31368.
Article22. Hanada K, Hara T, Nishijima M. Purification of the serine palmitoyltransferase complex responsible for sphingoid base synthesis by using affinity peptide chromatography techniques. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:8409–8415.
Article23. Ohnishi Y, Okino N, Ito M, Imayama S. Ceramidase activity in bacterial skin flora as a possible cause of ceramide deficiency in atopic dermatitis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1999. 6:101–104.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Altered Levels of Sphingosine and Sphinganine in Psoriatic Epidermis
- Interleukin-8 Expression in Psoriatic Skin of Different Disease Activities
- Comparative effect of dietary borage oil and safflower oil on anti-proliferation and ceramide metabolism in the epidermis of essential fatty acid deficient guinea pigs
- Dietary effect of red ginseng extracts mixed with torilis fructus and corni fructus on the epidermal levels of ceramides and ceramide related enzyme proteins in uv-induced hairless mice
- A Histopathologic Study of Early Psoriatic Lesions