Immune Netw.
2009 Dec;9(6):236-242. 10.4110/in.2009.9.6.236.
Selenium Inhibits Metastasis of Murine Melanoma Cells through the Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Death
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy and Research Center for Tumor Immunology, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan 614-735, Korea. dyhur@inje.ac.kr
- 2Department of LifeScience, Sookmyung Women's University, Seoul 140-742, Korea.
- 3Department of Anatomy and Cancer Immunology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-799, Korea.
- KMID: 2150651
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2009.9.6.236
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
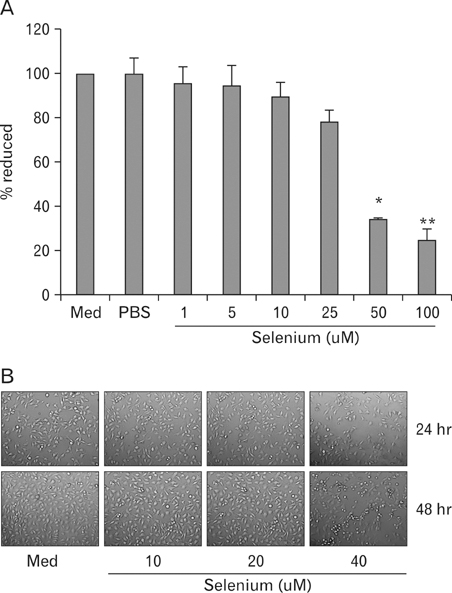
Melanoma is the most fatal form of skin cancer due to its rapid metastasis. Recently, several studies reported that selenium can induce apoptosis in melanoma cells. However, the precise mechanism remains to be elucidated. In this study, we investigated the effect of selenium on cell proliferation in murine melanoma and on tumor growth and metastasis in C57BL/6 mice. METHODS: Cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay in selenium-treated melanoma cells. Cell cycle distribution was analysized by staining DNA with propidum iodide (PI). mRNA and protein expression related to cell cycle arrest was measured by reverse transcription PCR and western blot. Tumor growth and metastasis was measured by in vivo model. RESULTS: Selenium was suppressed the proliferation of melanoma cells in a dose dependent manner. The growth inhibition of melanoma by selenium was associated with an arrest of cell cycle distribution at G0/G1 stage. The mRNA and protein level of CDK2/CDK4 was suppressed by treatment with selenium in a time-dependent manner. In vivo, tumor growth was not suppressed by selenium; however tumor metastasis was suppressed by selenium in mouse model. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that selenium might be a potent agent to inhibit proliferative activity of melanoma cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mancianti ML, Herlyn M. Tumor progression in melanoma: the biology of epidermal melanocytes in vitro. Carcinog Compr Surv. 1989. 11:369–386.2. Nagao N, Nakayama T, Etoh T, Saiki I, Miwa N. Tumor invasion is inhibited by phosphorylated ascorbate via enrichment of intracellular vitamin C and decreasing of oxidative stress. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2000. 126:511–518.
Article3. Roomi MW, Roomi N, Ivanov V, Kalinovsky T, Niedzwiecki A, Rath M. Inhibition of pulmonary metastasis of melanoma b16fo cells in C57BL/6 mice by a nutrient mixture consisting of ascorbic Acid, lysine, proline, arginine, and green tea extract. Exp Lung Res. 2006. 32:517–530.
Article4. Dua P, Ingle A, Gude RP. Suramin augments the antitumor and antimetastatic activity of pentoxifylline in B16F10 melanoma. Int J Cancer. 2007. 121:1600–1608.
Article5. Combs GF Jr, Gray WP. Chemopreventive agents: selenium. Pharmacol Ther. 1998. 79:179–192.6. Patrick L. Selenium biochemistry and cancer: a review of the literature. Altern Med Rev. 2004. 9:239–258.7. Han B, Wei W, Hua F, Cao T, Dong H, Yang T, Yang Y, Pan H, Xu C. Requirement for ERK activity in selenium-induced apoptosis of acute promyelocytic leukemia-derived NB4 cells. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. 40:196–204.
Article8. Kim EH, Sohn S, Kwon HJ, Kim SU, Kim MJ, Lee SJ, Choi KS. Selenium induces superoxide-mediated mitochondrial damage and subsequent autophagic cell death in malignant glioma cells. Cancer Res. 2007. 67:6314–6324.
Article9. Wang H, Yang X, Zhang Z, Xu H. Both calcium and ROS as common signals mediate Na(2)SeO(3)-induced apoptosis in SW480 human colonic carcinoma cells. J Inorg Biochem. 2003. 97:221–230.
Article10. Kramer GF, Ames BN. Mechanisms of mutagenicity and toxicity of selenium (Na2SeO3) in salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res. 1988. 201:169–180.
Article11. Kim T, Jung U, Cho DY, CHung AS. Se-methylselencysteine induces apoptosis through caspase activation in HL-60 cells. carcinogenesis. 2001. 22:559–565.
Article12. Jung U, Zheng X, Yoon SO, Chung AS. Se-methylselenocysteine induces apoptosis mediated by reactive oxygen species in HL-60 cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2001. 31:479–489.
Article13. Sherr CJ. cancer cell cycles revisited. Cancer Res. 2000. 60:3689–3695.14. Kaeck M, Lu J, Strange R, Ip C, Ganther HE, Thompson HJ. Differential induction of growth arrest inducible genes by selenium compounds. BioChemical Pharmacology. 1997. 53:921–926.
Article15. Rudolf E, Rudolf K, Cervinka M. Selenium activates p53 and p38 pathways and induces caspase-independent cell death in cervical cancer cells. Cell biol Toxicol. 2008. 24:123–241.
Article16. Vermeulen K, Van Bockstaele DR, Berneman ZN. The cell cycle: a review of regulation, deregulation and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 2003. 36:131–149.
Article17. Albino AP, Juan G, Traganos F, Reinhart L, Connolly J, Rose DP, Darzynkiewicz Z. Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of melanoma cells by docosahexaenoic acid: association with decreased pRb phosphorylation. Cancer Res. 2000. 60:4139–4145.18. Tsai J, Lee JT, Wang W, Zhang J, Cho H, Mamo S, Bremer R, Gillette S, Kong J, Haass NK, Sproesser K, Li L, Smalley KS, Fong D, Zhu YL, Marimuthu A, Nguyen H, Lam B, Liu J, Cheung I, Rice J, Suzuki Y, Luu C, Settachatgul C, Shellooe R, Cantwell J, Kim SH, Schlessinger J, Zhang KY, West BL, Powell B, Habets G, Zhang C, Ibrahim PN, Hirth P, Artis DR, Herlyn M, Bollag G. Discovery of a selective inhibitor of oncogenic B-Raf kinase with potent antimelanoma activity. PNAS. 2008. 105:3041–3046.
Article19. Wang CC, Chiang YM, Sung SC, Hsu YL, Chang JK, Kuo PL. Plumbagin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through reactive oxygen species/c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathways in human melanoma A375.S2 cells. Cancer Letters. 2008. 259:82–98.
Article20. An WW, Wang MW, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Ikejima T. Mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent apoptosis in norcan-tharidin-treated A375-S2 cells is proceeded by the activation of protein kinase C. Chin Med J (Engl). 2005. 118:198–203.21. Mhaidat NM, Zhang XD, Allen J, Avery-Kiejda KA, Scott RJ, Hersey P. Temozolomide induces senescence but not apoptosis in human melanoma cells. Br J Cancer. 2007. 97:1225–1233.
Article22. Kagawa S, Fujiwara T, Hizuta A, Yasuda T, Zhang WW, Roth JA, Tanaka N. p53 expression overcomes p21WAF1/CIP1-mediated G1 arrest and induces apoptosis in human cancer cells. Oncogene. 1997. 15:1903–1909.
Article23. Jiang C, Hu H, Malewiez B, Wang Z, Lü J. Selenite-induced p53 Ser-15 phosphorylation and caspase-mediated apoptosis in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004. 3:877–884.24. Traynor NJ, McKenzie RC, Beckett GJ, Gibbs NK. Selenomethionine inhibits ultraviolet radiation-induced p53 transactivation. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2006. 22:297–303.
Article25. Hahm E, Jin DH, Kang JS, Kim YI, Hong SW, Lee SK, Kim HN, Jung da J, Kim JE, Shin DH, Hwang YI, Kim YS, Hur DY, Yang Y, Cho D, Lee MS, Lee WJ. The Molecular Mechanisms of Vitamin C on Cell Cycle Regulation in B16F10 Murine Melanoma. J Cell Biochem. 2007. 102:1002–1010.
Article26. Deeds L, Teodorescu S, Chu M, Yu Q, Chen C. A p53-independent G1 cell cycle checkpoint induced by the suppression of protein kinase C alpha and theta isoforms. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:39782–39793.
Article27. Peter M, Herskowitz I. Joining the complex: Cyclindependent kinase inhibitory proteins and the cell cycle. Cell. 1994. 9:181–184.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of combination therapy of docetaxel with selenium on the human breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7
- Mechanism Underlying NaF-induced Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest on G361 Human Melanoma Cell Line
- Kaempferol induced the apoptosis via cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer MDA-MB-453 cells
- Heme Oxygenase-1 Induced by Aprotinin Inhibits Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation Through Cell Cycle Arrest in Hypertensive Rats
- S Phase Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis is Induced by Eugenol in G361 Human Melanoma Cells