J Adv Prosthodont.
2014 Jun;6(3):157-164. 10.4047/jap.2014.6.3.157.
Magnesium vs. machined surfaced titanium - osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Republic of Korea. verycutebear@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2118225
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2014.6.3.157
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study focused on in vitro cell differentiation and surface characteristics in a magnesium coated titanium surface implanted on using a plasma ion source.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
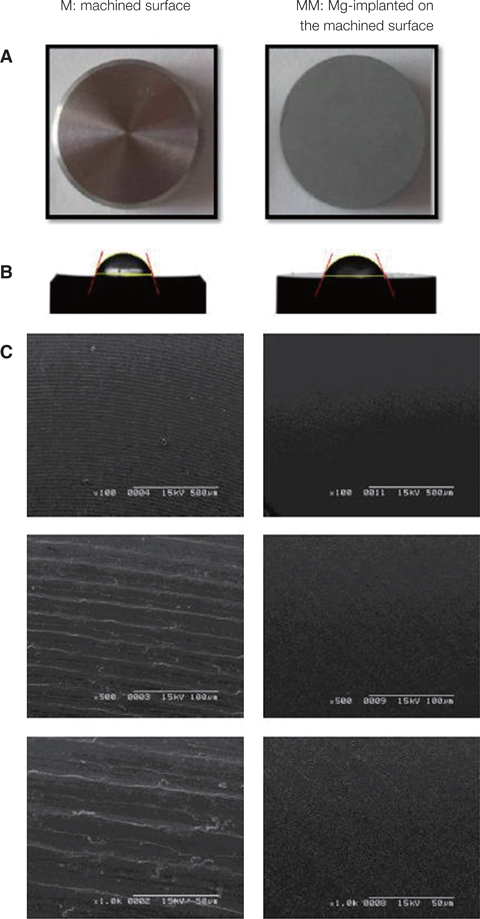
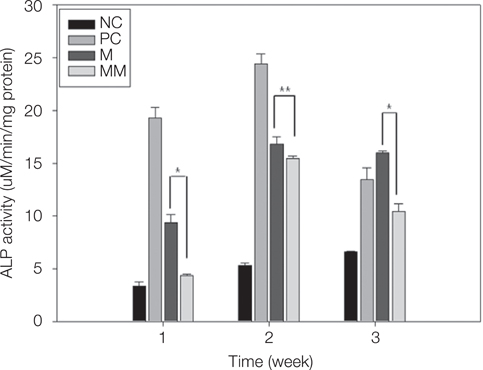
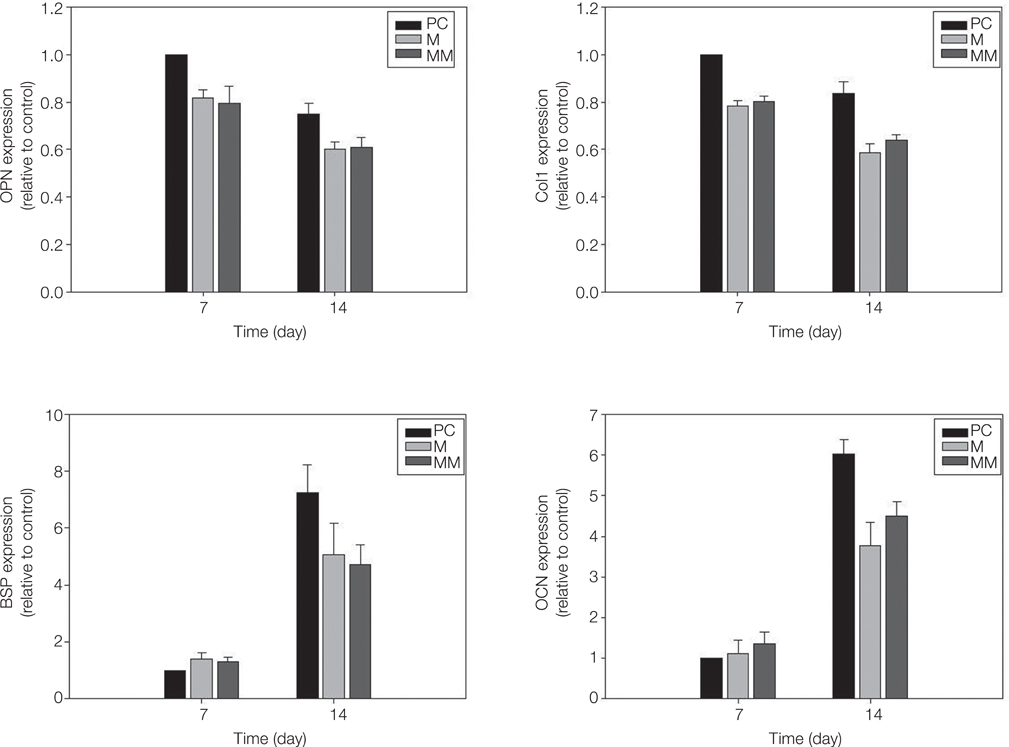
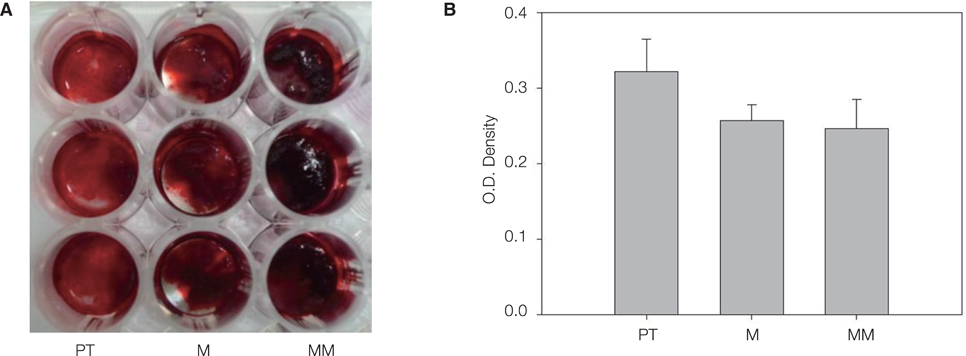
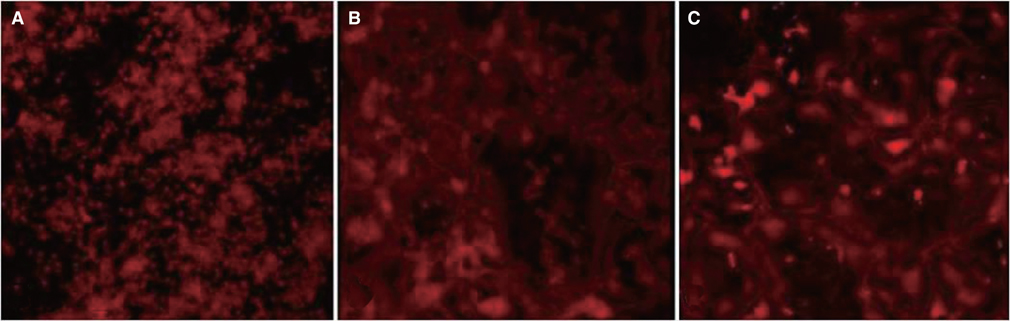
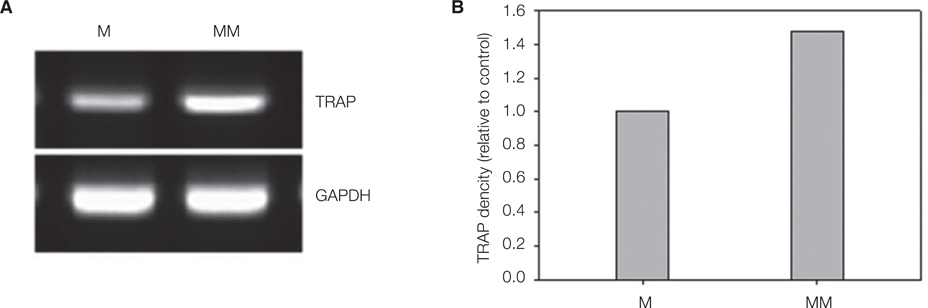
40 commercially made pure titanium discs were prepared to produce Ti oxide machined surface (M) and Mg-incorporated Ti oxide machined surface (MM). Surface properties were analyzed using a scanning electron microscopy (SEM). On each surface, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, alizarin red S staining for mineralization of MC3T3-E1 cells, and quantitative analysis of osteoblastic gene expression, were evaluated. Actin ring formation assay and gene expression analysis of TRAP and GAPDH performing RT-PCR were performed to characterize osteoclast differentiation on mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMMs).
RESULTS
MM showed similar surface morphology and surface roughness with M, but was slightly smoother after ion implantation at the micron scale. M was more hydrophobic than MM. No significant difference between surfaces on ALP activity at 7 and 14 days were observed. Real-time PCR analyses showed similar levels of mRNA expression of the osteoblast phenotype genes; osteopontin (OPN), osteocalcin (OCN), bone sialoprotein (BSP), and collagen 1 (Col 1) in cell grown on MM at 7, 14 and 21 days. Alizarin red S staining at 21 days showed no significant difference. BMMs differentiation increased in M and MM. Actin ring formation assay and gene expression analysis of TRAP showed osteoclast differentiation to be more active on MM.
CONCLUSION
Both M and MM have a good effect on osteoblastic cell differentiation, but MM may speed the bone remodeling process by activating on osteoclast differentiation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Actins
Alkaline Phosphatase
Animals
Bone Remodeling
Cell Differentiation
Collagen
Gene Expression
Integrin-Binding Sialoprotein
Macrophages
Magnesium*
Mice
Microscopy, Electron, Scanning
Osteoblasts*
Osteocalcin
Osteoclasts*
Osteopontin
Phenotype
Plasma
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA, Messenger
Surface Properties
Titanium*
Actins
Alkaline Phosphatase
Collagen
Integrin-Binding Sialoprotein
Magnesium
Osteocalcin
Osteopontin
RNA, Messenger
Titanium
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sul YT, Johansson C, Albrektsson T. Which surface properties enhance bone response to implants? Comparison of oxidized magnesium, TiUnite, and Osseotite implant surfaces. Int J Prosthodont. 2006; 19:319–328.2. Zreiqat H, Howlett CR, Zannettino A, Evans P, Schulze-Tanzil G, Knabe C, Shakibaei M. Mechanisms of magnesium-stimulated adhesion of osteoblastic cells to commonly used orthopaedic implants. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002; 62:175–184.3. Sul YT, Johansson P, Chang BS, Byon ES, Jeong Y. Bone tissue responses to Mg-incorporated oxidized implants and machine-turned implantsin the rabbit femur. J Appl Biomater Biomech. 2005; 3:18–28.4. Sul YT, Johansson CB, Kang Y, Jeon DG, Albrektsson T. Bone reactions to oxidized titanium implants with electrochemical anion sulphuric acid and phosphoric acid incorporation. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2002; 4:78–87.5. Maitz MF, Poon RW, Liu XY, Pham MT, Chu PK. Bioactivity of titanium following sodium plasma immersion ion implantation and deposition. Biomaterials. 2005; 26:5465–5473.6. Sul YT, Johansson C, Byon E, Albrektsson T. The bone response of oxidized bioactive and non-bioactive titanium implants. Biomaterials. 2005; 26:6720–6730.7. Cho LR, Kim DG, Kim JH, Byon ES, Jeong YS, Park CJ. Bone response of Mg ion-implanted clinical implants with the plasma source ion implantation method. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010; 21:848–856.8. Sammons RL, Lumbikanonda N, Gross M, Cantzler P. Comparison of osteoblast spreading on microstructured dental implant surfaces and cell behaviour in an explant model of osseointegration. A scanning electron microscopic study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005; 16:657–666.9. Park JW, Kim YJ, Jang JH, Song H. Osteoblast response to magnesium ion-incorporated nanoporous titanium oxide surfaces. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010; 21:1278–1287.10. Takebe J, Itoh S, Okada J, Ishibashi K. Anodic oxidation and hydrothermal treatment of titanium results in a surface that causes increased attachment and altered cytoskeletal morphology of rat bone marrow stromal cells in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000; 51:398–407.11. Samee N, Geoffroy V, Marty C, Schiltz C, Vieux-Rochas M, Levi G, de Vernejoul MC. Dlx5, a positive regulator of osteoblastogenesis, is essential for osteoblast-osteoclast coupling. Am J Pathol. 2008; 173:773–780.12. Tadic T, Dodig M, Erceg I, Marijanovic I, Mina M, Kalajzic Z, Velonis D, Kronenberg MS, Kosher RA, Ferrari D, Lichtler AC. Overexpression of Dlx5 in chicken calvarial cells accelerates osteoblastic differentiation. J Bone Miner Res. 2002; 17:1008–1014.13. Ajroud K, Sugimori T, Goldmann WH, Fathallah DM, Xiong JP, Arnaout MA. Binding Affinity of Metal Ions to the CD11b A-domain Is Regulated by Integrin Activation and Ligands. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:25483–25488.14. Zreiqat H, Valenzuela SM, Nissan BB, Roest R, Knabe C, Radlanski RJ, Renz H, Evans PJ. The effect of surface chemistry modification of titanium alloy on signalling pathways in human osteoblasts. Biomaterials. 2005; 26:7579–7586.15. Olivares-Navarrete R, Raz P, Zhao G, Chen J, Wieland M, Cochran DL, Chaudhri RA, Ornoy A, Boyan BD, Schwartz Z. Integrin alpha2beta1 plays a critical role in osteoblast response to micron-scale surface structure and surface energy of titanium substrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105:15767–15772.16. Keselowsky BG, Wang L, Schwartz Z, Garcia AJ, Boyan BD. Integrin alpha(5) controls osteoblastic proliferation and differentiation responses to titanium substrates presenting different roughness characteristics in a roughness independent manner. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007; 80:700–710.17. Wilson SR, Peters C, Saftig P, Brömme D. Cathepsin K activity-dependent regulation of osteoclast actin ring formation and bone resorption. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284:2584–2592.18. Flanagan AM, Massey HM, Wilson C, Vellodi A, Horton MA, Steward CG. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor and receptor activator NF-kappaB ligand fail to rescue osteoclastpoor human malignant infantile osteopetrosis in vitro. Bone. 2002; 30:85–90.19. Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003; 423:337–342.20. Burgess TL, Qian Y, Kaufman S, Ring BD, Van G, Capparelli C, Kelley M, Hsu H, Boyle WJ, Dunstan CR, Hu S, Lacey DL. The ligand for osteoprotegerin (OPGL) directly activates mature osteoclasts. J Cell Biol. 1999; 145:527–538.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Osteoblast adhesion and differentiation on magnesium titanate surface
- Inhibition of Osteoclast differentiation based on precipitation time of titanium surfaces immersed in modified simulated body fluid
- A study on the biological characteristics of modified titanium surface
- Effect of titanium surface roughness on cell adhesion of human osteoblast-like cells (MG63)
- The biological effects of fibronectin typeIII 7-10 to MC3T3-E1 osteoblast