J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2014 Dec;40(6):291-296. 10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.6.291.
Effect of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 on bisphosphonate-treated osteoblasts
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea. ssh8080@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Oral Anatomy and Cell Biology, School of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea.
- 3Department of Dentistry, Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1799563
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.6.291
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ) is a side effect of bisphophonate therapy that has been reported in recent years. Osteoclastic inactivity by bisphosphonate is the known cause of BRONJ. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) plays an important role in the development of bone. Recombinant human BMP-2 (rhBMP-2) is potentially useful as an activation factor for bone repair. We hypothesized that rhBMP-2 would enhance the osteoclast-osteoblast interaction related to bone remodeling.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Human fetal osteoblast cells (hFOB 1.19) were treated with 100 microM alendronate, and 100 ng/mL rhBMP-2 was added. Cells were incubated for a further 48 hours, and cell viability was measured using an MTT assay. Expression of the three cytokines from osteoblasts, receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand (RANKL), osteoprotegerin (OPG), and macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), were analyzed by real-time polymerase chain reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
RESULTS
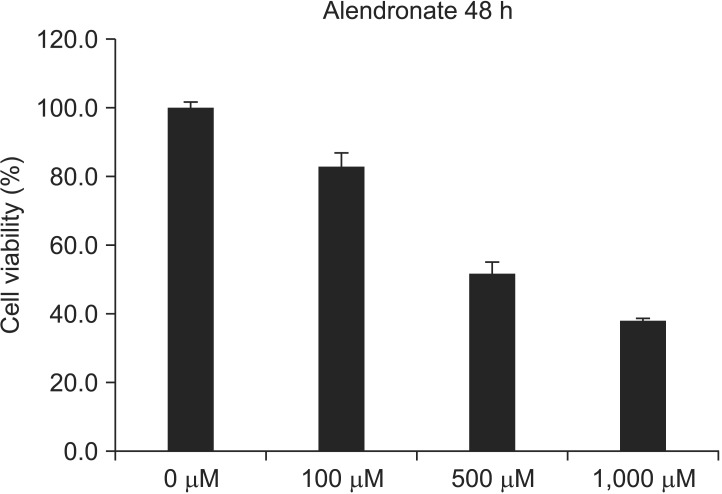
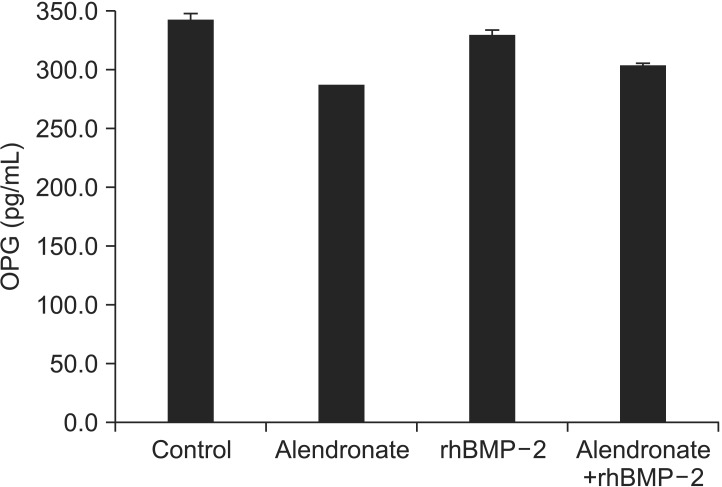
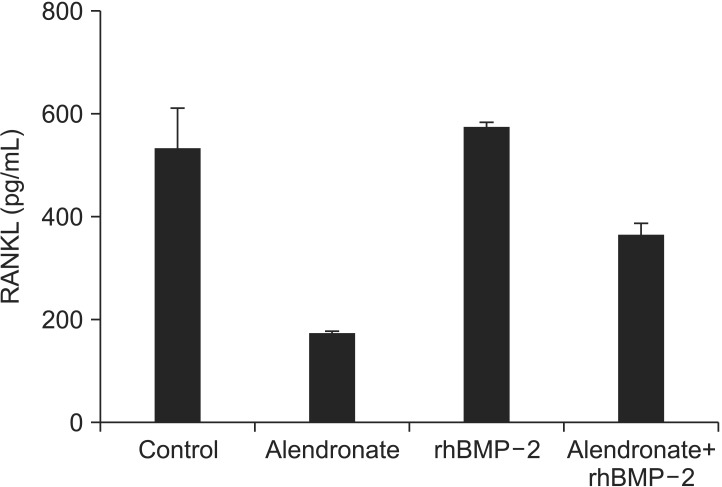
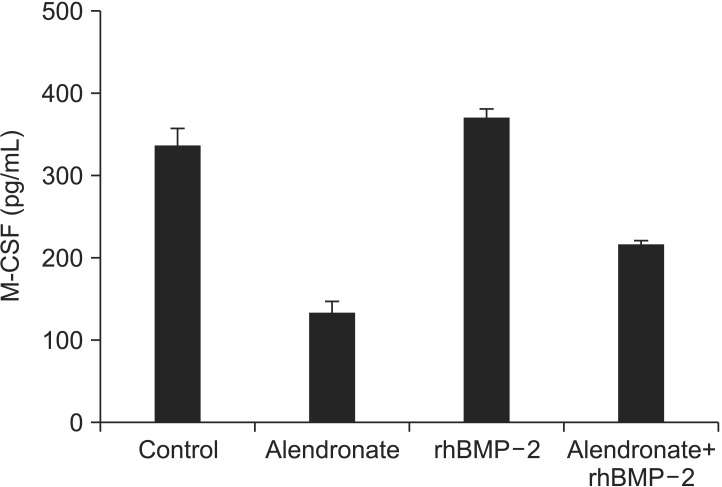
Cell viability was decreased to 82.75%+/-1.00% by alendronate and then increased to 110.43%+/-1.35% after treatment with rhBMP-2 (P<0.05, respectively). OPG, RANKL, and M-CSF expression were all decreased by alendronate treatment. RANKL and M-CSF expression were increased, but OPG was not significantly affected by rhBMP-2.
CONCLUSION
rhBMP2 does not affect OPG gene expression in hFOB, but it may increase RANKL and M-CSF gene expression.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Alendronate
Bisphosphonate-Associated Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Bone Remodeling
Cell Survival
Cytokines
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Gene Expression
Humans
Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
Osteoblasts*
Osteoclasts
Osteoprotegerin
RANK Ligand
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Alendronate
Cytokines
Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
Osteoprotegerin
RANK Ligand
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Combined effect of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 and low level laser irradiation on bisphosphonate-treated osteoblasts
Seok-Young Jeong, Ji-Un Hong, Jae Min Song, In Ryoung Kim, Bong Soo Park, Chul Hoon Kim, Sang Hun Shin
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;44(6):259-268. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2018.44.6.259.
Reference
-
1. Marx RE. Pamidronate (Aredia) and zoledronate (Zometa) induced avascular necrosis of the jaws: a growing epidemic. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 61:1115–1117. PMID: 12966493.
Article2. Kim HK, Kim JH, Abbas AA, Yoon TR. Alendronate enhances osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells: a preliminary study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:3121–3128. PMID: 18665432.
Article3. Aubin J, Liu F, Bilezikian J, Raisz L, Rodan G. Principles of bone biology. 2nd ed. San Diego: Academic Press;1996.5. Reddi AH. Bone and cartilage differentiation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994; 4:737–744. PMID: 7849513.
Article6. Reddi AH. Role of morphogenetic proteins in skeletal tissue engineering and regeneration. Nat Biotechnol. 1998; 16:247–252. PMID: 9528003.
Article7. Bostrom MP, Asnis P. Transforming growth factor beta in fracture repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; (355 Suppl):S124–S131. PMID: 9917633.
Article8. Barnes GL, Kostenuik PJ, Gerstenfeld LC, Einhorn TA. Growth factor regulation of fracture repair. J Bone Miner Res. 1999; 14:1805–1815. PMID: 10571679.
Article9. Bessa PC, Casal M, Reis RL. Bone morphogenetic proteins in tissue engineering: the road from the laboratory to the clinic, part I (basic concepts). J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2008; 2:1–13. PMID: 18293427.
Article10. Bessa PC, Casal M, Reis RL. Bone morphogenetic proteins in tissue engineering: the road from laboratory to clinic, part II (BMP delivery). J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2008; 2:81–96. PMID: 18383454.
Article11. Chen D, Zhao M, Mundy GR. Bone morphogenetic proteins. Growth Factors. 2004; 22:233–241. PMID: 15621726.
Article12. Marx RE. Clinical concerns of alendronate use. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 66:1322. PMID: 18486814.
Article13. Sahni M, Guenther HL, Fleisch H, Collin P, Martin TJ. Bisphosphonates act on rat bone resorption through the mediation of osteoblasts. J Clin Invest. 1993; 91:2004–2011. PMID: 8486770.
Article14. García-Moreno C, Serrano S, Nacher M, Farré M, Díez A, Mariñoso ML, et al. Effect of alendronate on cultured normal human osteoblasts. Bone. 1998; 22:233–239. PMID: 9580147.
Article15. Koch FP, Merkel C, Ziebart T, Smeets R, Walter C, Al-Nawas B. Influence of bisphosphonates on the osteoblast RANKL and OPG gene expression in vitro. Clin Oral Investig. 2012; 16:79–86.
Article16. Sudhoff H, Jung JY, Ebmeyer J, Faddis BT, Hildmann H, Chole RA. Zoledronic acid inhibits osteoclastogenesis in vitro and in a mouse model of inflammatory osteolysis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2003; 112:780–786. PMID: 14535562.
Article17. Kwak HB, Kim JY, Kim KJ, Choi MK, Kim JJ, Kim KM, et al. Risedronate directly inhibits osteoclast differentiation and inflammatory bone loss. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009; 32:1193–1198. PMID: 19571384.
Article18. Idris AI, Rojas J, Greig IR, Van't Hof RJ, Ralston SH. Aminobisphosphonates cause osteoblast apoptosis and inhibit bone nodule formation in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int. 2008; 82:191–201. PMID: 18259679.
Article19. Suh DY, Boden SD, Louis-Ugbo J, Mayr M, Murakami H, Kim HS, et al. Delivery of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 using a compression-resistant matrix in posterolateral spine fusion in the rabbit and in the non-human primate. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:353–360. PMID: 11840099.
Article20. Kübler NR, Würzler KK, Reuther JF, Sieber E, Kirchner T, Sebald W. Effect of different factors on the bone forming properties of recombinant BMPs. Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir. 2000; (4 Suppl 2):S465–S469. PMID: 11094517.21. Uludag H, D'Augusta D, Palmer R, Timony G, Wozney J. Characterization of rhBMP-2 pharmacokinetics implanted with biomaterial carriers in the rat ectopic model. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999; 46:193–202. PMID: 10379997.
Article22. Linde A, Hedner E. Recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-2 enhances bone healing, guided by osteopromotive e-PTFE membranes: an experimental study in rats. Calcif Tissue Int. 1995; 56:549–553. PMID: 7648485.
Article23. Yamamoto M, Takahashi Y, Tabata Y. Controlled release by biodegradable hydrogels enhances the ectopic bone formation of bone morphogenetic protein. Biomaterials. 2003; 24:4375–4383. PMID: 12922150.
Article24. Toth JM, Boden SD, Burkus JK, Badura JM, Peckham SM, McKay WF. Short-term osteoclastic activity induced by locally high concentrations of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in a cancellous bone environment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:539–550. PMID: 19240666.
Article25. Kanatani M, Sugimoto T, Kaji H, Kobayashi T, Nishiyama K, Fukase M, et al. Stimulatory effect of bone morphogenetic protein-2 on osteoclast-like cell formation and bone-resorbing activity. J Bone Miner Res. 1995; 10:1681–1690. PMID: 8592944.
Article26. Kaneko H, Arakawa T, Mano H, Kaneda T, Ogasawara A, Nakagawa M, et al. Direct stimulation of osteoclastic bone resorption by bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2 and expression of BMP receptors in mature osteoclasts. Bone. 2000; 27:479–486. PMID: 11033442.
Article27. Itoh K, Udagawa N, Katagiri T, Iemura S, Ueno N, Yasuda H, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 2 stimulates osteoclast differentiation and survival supported by receptor activator of nuclear factorkappaB ligand. Endocrinology. 2001; 142:3656–3662. PMID: 11459815.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Combined effect of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 and low level laser irradiation on bisphosphonate-treated osteoblasts
- Combined effect of bisphosphonate and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 on bone healing of rat calvarial defects
- Spinal Fusion Based on Ex Vivo Gene Therapy Using Recombinant Human BMP Adenoviruses
- Regenerative effect of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2/absorbable collagen sponge (rhBMP-2/ACS) after sequestrectomy of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ)
- Development of Refolding Process to Obtain Active Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 and its Osteogenic Efficacy on Oral Stem Cells