Ann Lab Med.
2014 Jan;34(1):7-14. 10.3343/alm.2014.34.1.7.
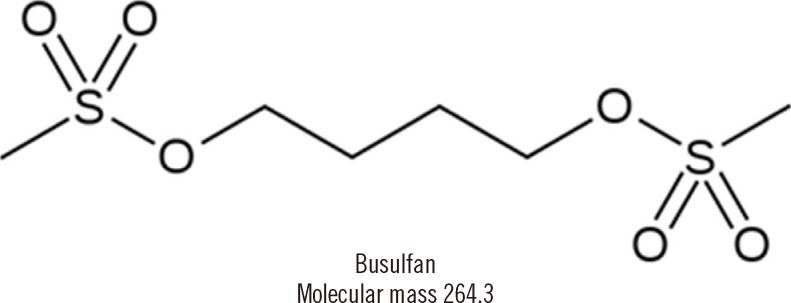
Quantification of Human Plasma-Busulfan Concentration by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. cloak21@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 1781353
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2014.34.1.7
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Busulfan, an alkylating agent administered prior to hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, has a narrow therapeutic range and wide variability in metabolism. We developed a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method for rapid and accurate quantification of plasma busulfan.
METHODS
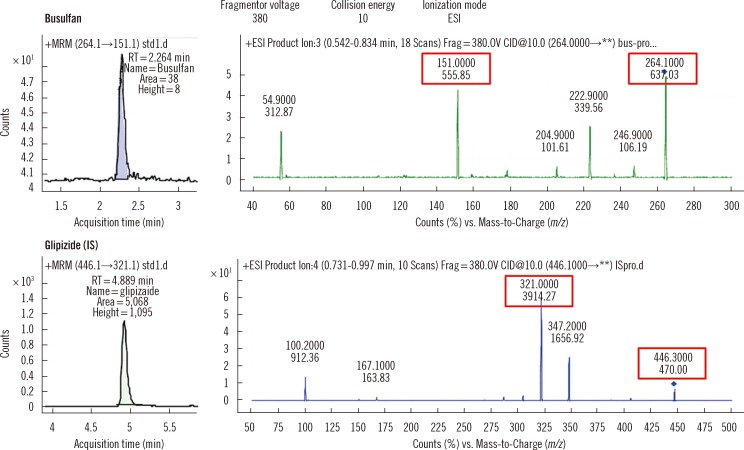
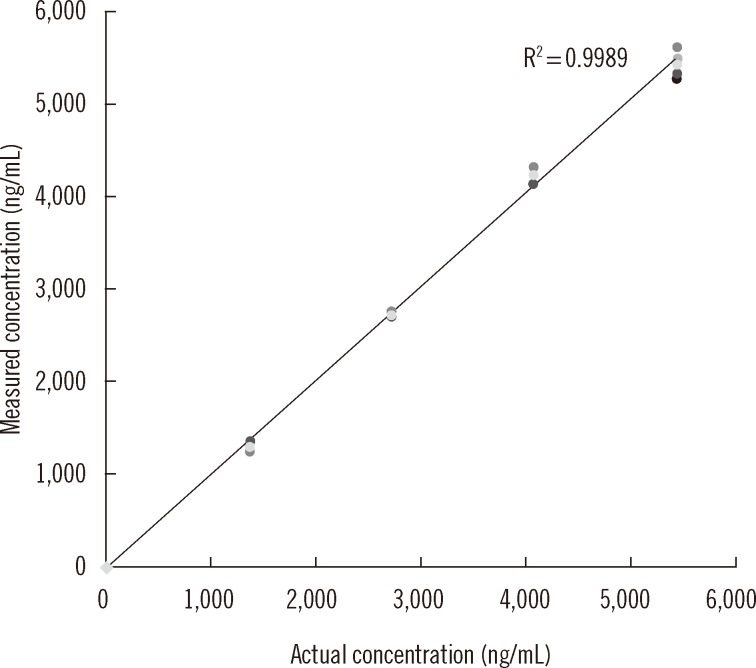
Busulfan was separated and detected using an LC system containing a C18 column equipped with MS/MS. The sample was eluted with a mobile phase gradient for a total run time of 10 min. Plasma busulfan concentration was quantified against a 6-point standard curve in a multiple reaction monitoring mode at mass-to-charge (m/z) 264.1 > 151.1. Precision, recovery, matrix effect, linearity, detection capability, carryover, and stability were evaluated. The range of plasma busulfan concentration was obtained by analyzing samples from 9 children receiving busulfan.
RESULTS
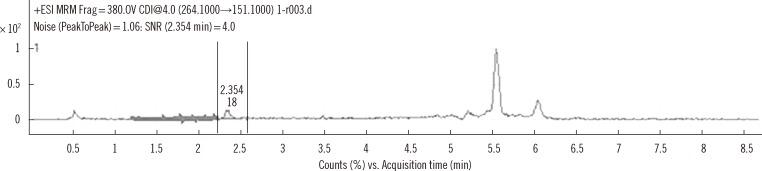
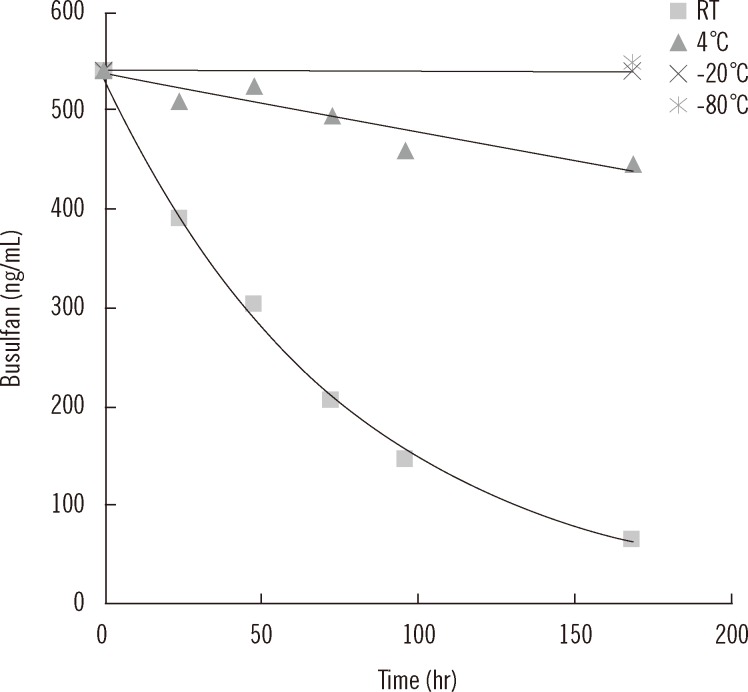
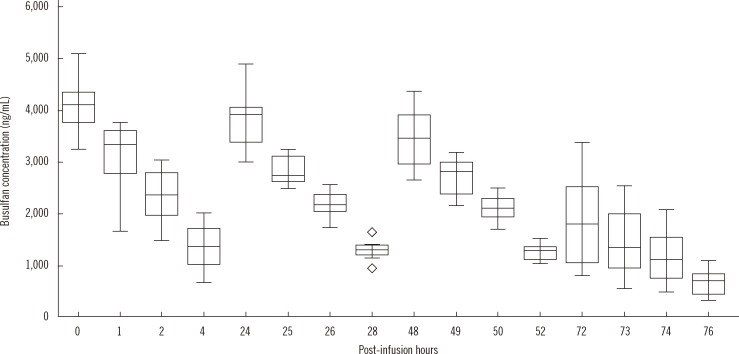
The coefficients of variation of within-run and within-laboratory precision were all below 5%. Recoveries were all within the range of 100-105%. Linearity was verified from 0 to 5,000 ng/mL. Limit of detection and limit of quantification were 1.56 and 25 ng/mL, respectively. Carryover rate was within allowable limits. Plasma busulfan concentration was stable for 2 weeks at -20degrees C and -80degrees C, but decreased by 25% when the plasma was stored for 24 hr at room temperature, and by <5% in 24 hr at 4degrees C. The plasma busulfan concentrations were between 347 ng/mL and 5,076 ng/mL.
CONCLUSIONS
Our method using LC-MS/MS enables highly accurate, reproducible, and rapid busulfan monitoring with minimal sample preparation. The method may also enable safe and proper dosage.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Recommendations for the Use of Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry in the Clinical Laboratory: Part I. Implementation and Management
Kyunghoon Lee, Soo Young Moon, Serim Kim, Hyun-Jung Choi, Sang-Guk Lee, Hyung-Doo Park, Soo-Youn Lee, Sang Hoon Song,
Lab Med Online. 2020;10(1):1-9. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2020.10.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Nath CE, Shaw PJ. Busulphan in blood and marrow transplantation: dose, route, frequency and role of therapeutic drug monitoring. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2007; 2:75–91. PMID: 18690856.2. Ciurea SO, Andersson BS. Busulfan in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009; 15:523–536. PMID: 19361744.
Article3. Russell JA, Kangarloo SB. Therapeutic drug monitoring of busulfan in transplantation. Curr Pharm Des. 2008; 14:1936–1949. PMID: 18691105.
Article4. Dean RM, Pohlman B, Sweetenham JW, Sobecks RM, Kalaycio ME, Smith SD, et al. Superior survival after replacing oral with intravenous busulfan in autologous stem cell transplantation for non-Hodgkin lymphoma with busulfan, cyclophosphamide and etoposide. Br J Haematol. 2010; 148:226–234. PMID: 19821828.
Article5. Lee JW, Kang HJ, Lee SH, Yu KS, Kim NH, Yuk YJ, et al. Highly variable pharmacokinetics of once-daily intravenous busulfan when combined with fludarabine in pediatric patients: phase I clinical study for determination of optimal once-daily busulfan dose using pharmacokinetic modeling. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012; 18:944–950. PMID: 22155501.
Article6. Gaziev J, Nguyen L, Puozzo C, Mozzi AF, Casella M, Perrone Donnorso M, et al. Novel pharmacokinetic behavior of intravenous busulfan in children with thalassemia undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a prospective evaluation of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile with therapeutic drug monitoring. Blood. 2010; 115:4597–4604. PMID: 20237319.
Article7. Paci A, Vassal G, Moshous D, Dalle JH, Bleyzac N, Neven B, et al. Pharmacokinetic behavior and appraisal of intravenous busulfan dosing in infants and older children: the results of a population pharmacokinetic study from a large pediatric cohort undergoing hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Ther Drug Monit. 2012; 34:198–208. PMID: 22406655.8. Méresse V, Hartmann O, Vassal G, Benhamou E, Valteau-Couanet D, Brugieres L, et al. Risk factors for hepatic veno-occlusive disease after high-dose busulfan-containing regimens followed by autologous bone marrow transplantation: a study in 136 children. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1992; 10:135–141. PMID: 1525602.9. Carreras E, Rosiñol L, Terol MJ, Alegre A, de Arriba F, García-Laraña J, et al. Veno-occlusive disease of the liver after high-dose cytoreductive therapy with busulfan and melphalan for autologous blood stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007; 13:1448–1454. PMID: 18022574.
Article10. Chen TL, Grochow LB, Hurowitz LA, Brundrett RB. Determination of busulfan in human plasma by gas chromatography with electron-capture detection. J Chromatogr. 1988; 425:303–309. PMID: 3372644.
Article11. Quernin MH, Poonkuzhali B, Montes C, Krishnamoorthy R, Dennison D, Srivastava A, et al. Quantification of busulfan in plasma by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry following derivatization with tetrafluorothiophenol. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 1998; 709:47–56. PMID: 9653925.
Article12. Bleyzac N, Barou P, Aulagner G. Rapid and sensitive high-performance liquid chromatographic method for busulfan assay in plasma. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 2000; 742:427–432. PMID: 10901148.
Article13. Peris JE, Latorre JA, Castel V, Verdeguer A, Esteve S, Torres-Molina F. Determination of busulfan in human plasma using high-performance liquid chromatography with pre-column derivatization and fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 1999; 730:33–40. PMID: 10437669.
Article14. Courtney JB, Harney R, Li Y, Lundell G, McMillin GA, Agarwal G, et al. Determination of busulfan in human plasma using an ELISA format. Ther Drug Monit. 2009; 31:489–494. PMID: 19494794.
Article15. Mürdter TE, Coller J, Claviez A, Schönberger F, Hofmann U, Dreger P, et al. Sensitive and rapid quantification of busulfan in small plasma volumes by liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 2001; 47:1437–1442. PMID: 11468234.16. Quernin MH, Duval M, Litalien C, Vilmer E, Aigrain EJ. Quantification of busulfan in plasma by liquid chromatography-ion spray mass spectrometry. Application to pharmacokinetic studies in children. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 2001; 763:61–69. PMID: 11710584.17. Kellogg MD, Law T, Sakamoto M, Rifai N. Tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of serum busulfan. Ther Drug Monit. 2005; 27:625–629. PMID: 16175136.
Article18. dos Reis EO, Vianna-Jorge R, Suarez-Kurtz G, Lima EL, Azevedo Dde A. Development of a rapid and specific assay for detection of busulfan in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2005; 19:1666–1674. PMID: 15912469.
Article19. Bunch DR, Heideloff C, Ritchie JC, Wang S. A fast and simple assay for busulfan in serum or plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry using turbulent flow online extraction technology. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2010; 878:3255–3258.
Article20. Ansari M, Uppugunduri CR, Déglon J, Théorêt Y, Versace F, Gumy-Pause F, et al. A simplified method for busulfan monitoring using dried blood spot in combination with liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2012; 26:1437–1446. PMID: 22592987.
Article21. Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical method validation. Rockville, MD: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research;2001.22. Clinical and Laboraotry Standards Institute. EP15-A2. User verification of performance for precision and trueness; Approved guideline. 2nd ed. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboraotry Standards Institute;2005.23. Matuszewski BK, Constanzer ML, Chavez-Eng CM. Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal Chem. 2003; 75:3019–3030. PMID: 12964746.
Article24. NCCLS. NCCLS document EP6-A. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures: a statistical approach; approved guideline. Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;2003.25. International Conference on Harmonization. Q2B: validation of analytical procedures: methodology. US FDA Federal Register. 1997; 62:27463–27467.26. Lee HJ, Kim SY, Lee SM, Heo J, Kim HH, Chang CL, et al. Elecsys hepatitis B surface antigen quantitative assay: performance evaluation and correlation with hepatitis B virus DNA during 96 weeks of follow-up in chronic hepatitis B patients. Ann Lab Med. 2012; 32:420–425. PMID: 23130341.
Article27. Snyder ML, Ritchie JC. Quantification of busulfan in plasma using liquid chromatography electrospray tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS/MS). Methods Mol Biol. 2010; 603:129–136. PMID: 20077065.
Article28. Oechtering D, Boos J, Hempel G. Monitoring of N,N-dimethylacetamide in children during i.v.-busulfan therapy by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2006; 838:129–134.
Article29. Hempel G, Oechtering D, Lanvers-Kaminsky C, Klingebiel T, Vormoor J, Gruhn B, et al. Cytotoxicity of dimethylacetamide and pharmacokinetics in children receiving intravenous busulfan. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:1772–1778. PMID: 17470868.
Article30. Cooper AJ, Younis IR, Niatsetskaya ZV, Krasnikov BF, Pinto JT, Petros WP, et al. Metabolism of the cysteine S-conjugate of busulfan involves a beta-lyase reaction. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008; 36:1546–1552. PMID: 18474673.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Determination of donepezil in human plasma using ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- Development and validation of analytical method for the determination of radotinib in human plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- Quantification of apixaban in human plasma using ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry
- Development and Validation of a Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of epsilon-Acetamidocaproic Acid in Rat Plasma
- A Novel Simultaneous Determination of Sarpogrelate and its Active Metabolite (M-1) in Human Plasma, Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Clinical Application