Transl Clin Pharmacol.
2018 Jun;26(2):64-72. 10.12793/tcp.2018.26.2.64.
Determination of donepezil in human plasma using ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Pharmacy, Research Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 41566, Korea. kshin@knu.ac.kr
- 2Dong-A University Hospital, Busan 49201, Korea.
- 3Clinical Trials Center, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon 21565, Korea.
- KMID: 2413829
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2018.26.2.64
Abstract
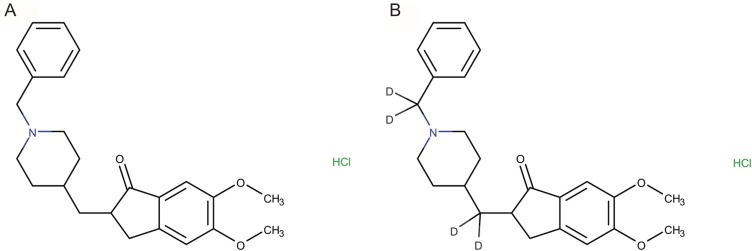
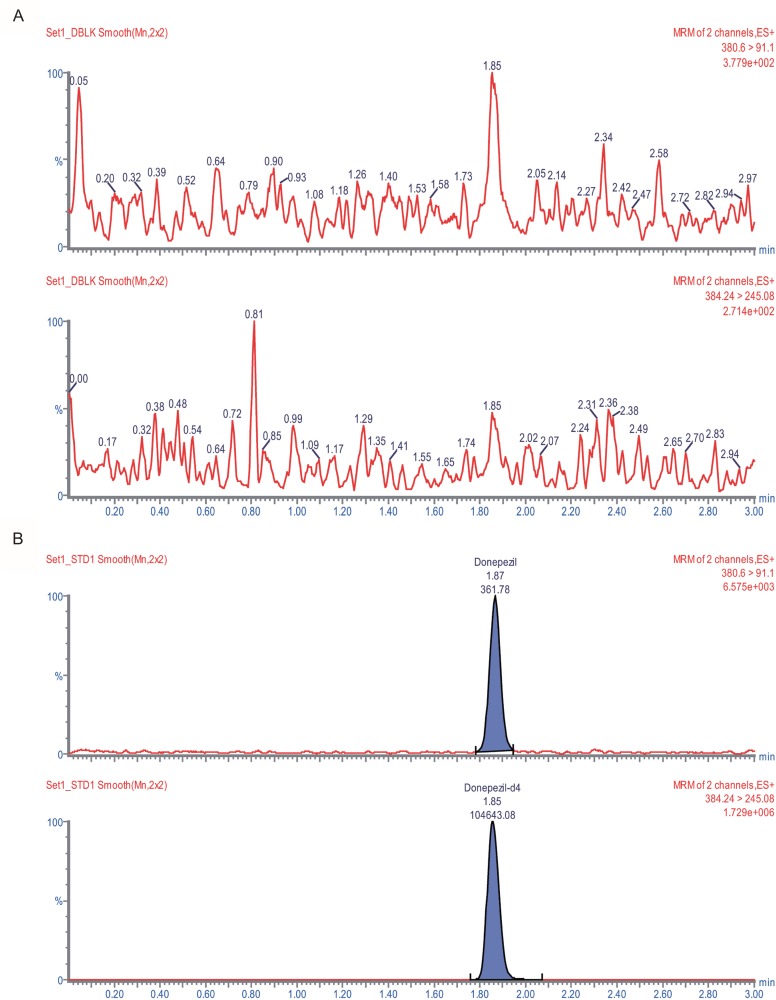
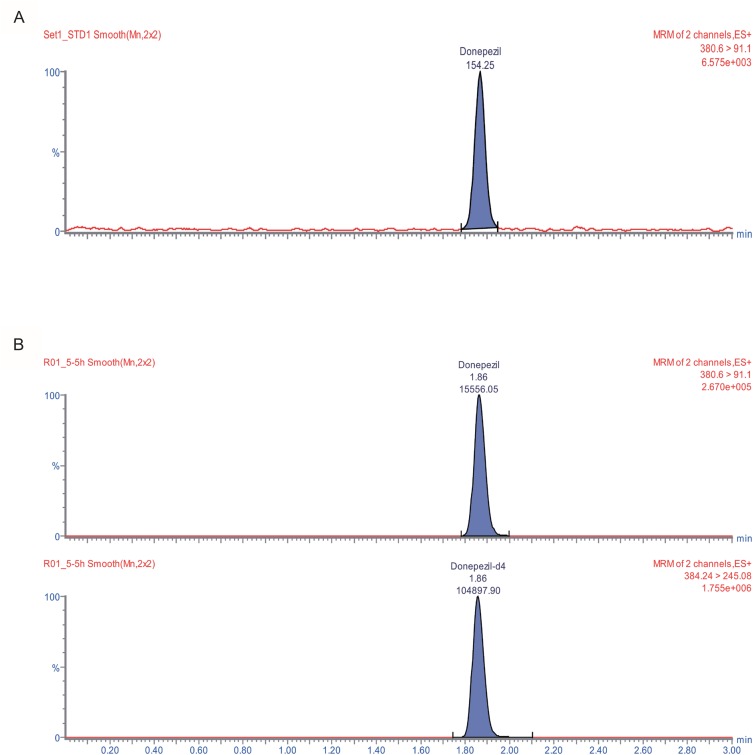
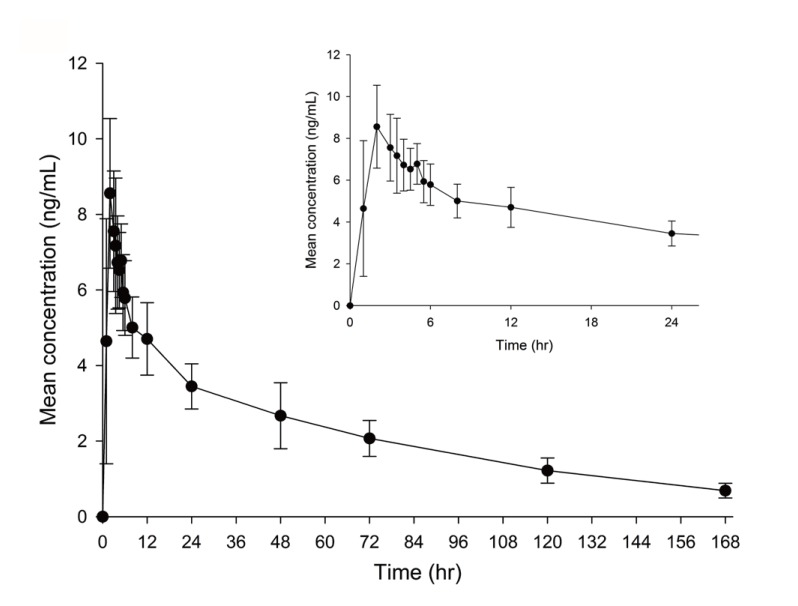
- An ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) method was developed and validated for the quantification of donepezil in human plasma. Donepezil and donepezil-D4 were extracted from human plasma by liquid-liquid extraction using a mixture of hexane and ethyl acetate (70:30 v/v). The extracted samples were analyzed using a Thermo Hypersil Gold C18 column with 5% acetic acid in 20 mM ammonium acetate buffer (pH 3.3) and 100% acetonitrile as a mobile phase with the 60:40 (v:v) isocratic method, at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min. The injection volume was 3 µL, and the total run time was 3 min. Inter- and intra-batch accuracies ranged from 98.0% to 110.0%, and the precision was below 8%. The developed method was successfully applied to the quantification of donepezil in human plasma. The mean (standard deviation) maximum concentration and the median (range) time to maximum concentration were 8.6 (2.0) ng/mL and 2.0 h (1.0~5.0 h), respectively, in healthy Koreans after oral administration of 5 mg donepezil.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Colović MB, Krstić DZ, Lazarević-Pašti TD, Bondžić AM, Vasić VM. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: pharmacology and toxicology. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2013; 11:315–335. DOI: 10.2174/1570159X11311030006. PMID: 24179466.2. Mangialasche F, Solomon A, Winblad B, Mecocci P, Kivipelto M. Alzheimer's disease: clinical trials and drug development. Lancet Neurol. 2010; 9:702–716. DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70119-8. PMID: 20610346.
Article3. Shigeta M, Homma A. Donepezil for Alzheimer's disease: pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic, and clinical profiles. CNS Drug Rev. 2001; 7:353–368. PMID: 11830754.
Article4. Yasui-Furukori N, Furuya R, Takahata T, Tateishi T. Determination of donepezil, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet absorbance detection. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2002; 768:261–265. DOI: 10.1016/S1570-0232(01)00592-X.
Article5. Rogers SL, Friedhoff LT. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of donepezil HCl following single oral doses. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998; 46(Suppl 1):1–6. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1998.0460s1001.x.
Article6. Nakashima K, Itoh K, Kono M, Nakashima MN, Wada M. Determination of donepezil hydrochloride in human and rat plasma, blood and brain microdialysates by HPLC with a short C30 column. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2006; 41:201–206. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2005.10.017. PMID: 16321494.
Article7. Ponnayyan Sulochana S, Sharma K, Mullangi R, Sukumaran SK. Review of the validated HPLC and LC-MS/MS methods for determination of drugs used in clinical practice for Alzheimer's disease Bioanalytical methods for quantitation of drugs to treat Alzheimer's. Biomed Chromatogr. 2014; 28:1431–1490. DOI: 10.1002/bmc.3116. PMID: 24515838.8. Korfmacher WA. Foundation review: Principles and applications of LC-MS in new drug discovery. Drug Discov Today. 2005; 10:1357–1367. DOI: 10.1016/S1359-6446(05)03620-2. PMID: 16253874.
Article9. Nováková L, Matysová L, Solich P. Advantages of application of UPLC in pharmaceutical analysis. Talanta. 2006; 68:908–918. DOI: 10.1016/j.talanta.2005.06.035. PMID: 18970409.
Article10. Vogeser M, Seger C. A decade of HPLC-MS/MS in the routine clinical laboratory — Goals for further developments. Clin Biochem. 2008; 41:649–662. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2008.02.017. PMID: 18374660.
Article11. FDA. Bioanalytical Method Validation, Guidance for Industry. Accessed 6 September 2017. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidances/ucm368107.pdf/.12. MFDS. Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation. Accessed 6 September 2017. http://nifds.go.kr/_custom/nifds/_common/board/download.jsp?attach_no=18470/.13. Park EJ, Lee HW, Ji HY, Kim HY, Lee MH, Park ES, et al. Hydrophilic interaction chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry of donepezil in human plasma: Application to a pharmacokinetic study of donepezil in volunteers. Arch Pharm Res. 2008; 31:1205–1211. DOI: 10.1007/s12272-001-1290-6. PMID: 18806965.
Article14. Shah HJ, Kundlik ML, Pandya A, Prajapati S, Subbaiah G, Patel CN, et al. A rapid and specific approach for direct measurement of donepezil concentration in human plasma by LC-MS/MS employing solid-phase extraction. Biomed Chromatogr. 2009; 23:141–151. DOI: 10.1002/bmc.1095. PMID: 18823072.
Article15. Bhateria M, Ramakrishna R, Pakala DB, Bhatta RS. Development of an LC–MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of memantine and donepezil in rat plasma and its application to pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015; 1001:131–139. DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.07.042.
Article16. Pilli NR, Inamadugu JK, Kondreddy N, Karra VK, Damaramadugu R, Rao JV. A rapid and sensitive LC-MS/MS method for quantification of donepezil and its active metabolite, 6-o-desmethyl donepezil in human plasma and its pharmacokinetic application. Biomed Chromatogr. 2011; 25:943–951. DOI: 10.1002/bmc.1552. PMID: 21154884.
Article17. Nováková L, Vlčková H. A review of current trends and advances in modern bio-analytical methods: chromatography and sample preparation. Anal Chim Acta. 2009; 656:8–35. DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2009.10.004. PMID: 19932811.
Article18. Pavlovič DM, Babič S, Horvat AJM, Kaštelan-Macan M. Sample preparation in analysis of pharmaceuticals. Trac-Trends Anal Chem. 2007; 26:1062–1075. DOI: 10.1016/j.trac.2007.09.010.19. Dejaegher B, Mangelings D, Vander Heyden Y. Method development for HILIC assays. J Sep Sci. 2008; 31:1438–1448. DOI: 10.1002/jssc.200700680. PMID: 18461571.
Article20. Katakam P, Kalakuntla RR, Adiki SK, Chandu BR. Development and validation of a liquid chromatography mass spectrometry method for the determination of donepezil in human plasma. J Pharm Res. 2013; 7:720–726. DOI: 10.1016/j.jopr.2013.08.021.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrafast liquid chromatographytandem mass spectrometry determination of donepezil in human plasma: application to a bioequivalence study
- Development and validation of analytical method for the determination of radotinib in human plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- Quantification of apixaban in human plasma using ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry
- Bioanalytical methods for the detection of duloxetine and thioctic acid in plasma using ultra performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS)
- Simultaneous Screening of 177 Drugs of Abuse in Urine Using Ultra-performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Drug-intoxicated Patients