Immune Netw.
2010 Feb;10(1):15-25. 10.4110/in.2010.10.1.15.
Effects of IL-3 and SCF on Histamine Production Kinetics and Cell Phenotype in Rat Bone Marrow-derived Mast Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Korea University Graduate School, Seoul 136-705, Korea. csw0419@korea.ac.kr
- 2Division of Brain Korea 21 Projects for Biomedical Science, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul 136-705, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul 136-705, Korea.
- 4Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul 136-705, Korea.
- 5Department of Parasitology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul 136-705, Korea.
- KMID: 1456193
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2010.10.1.15
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
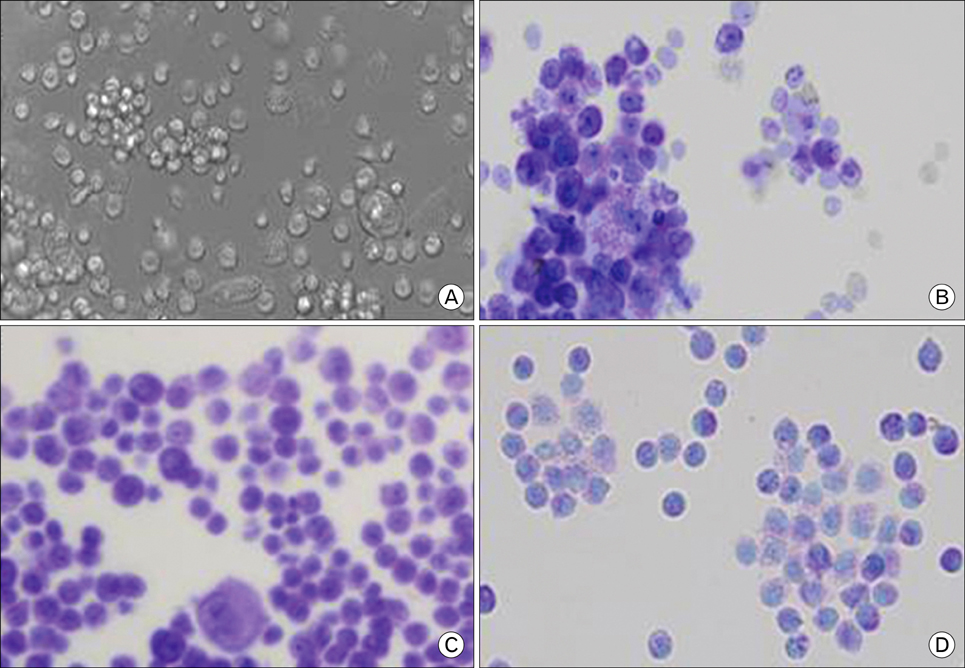
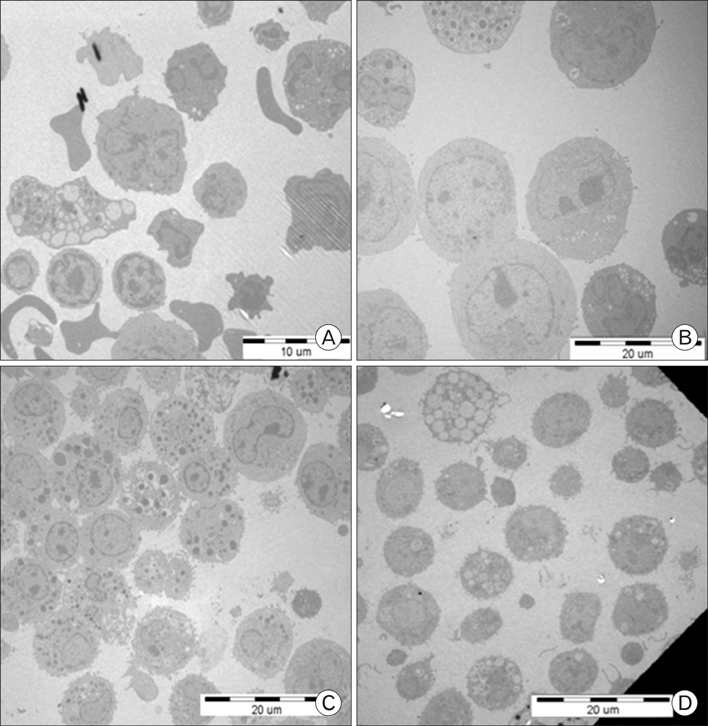
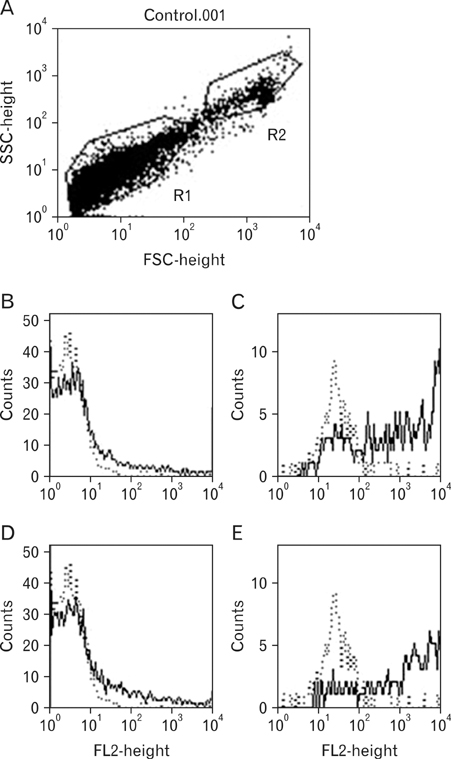
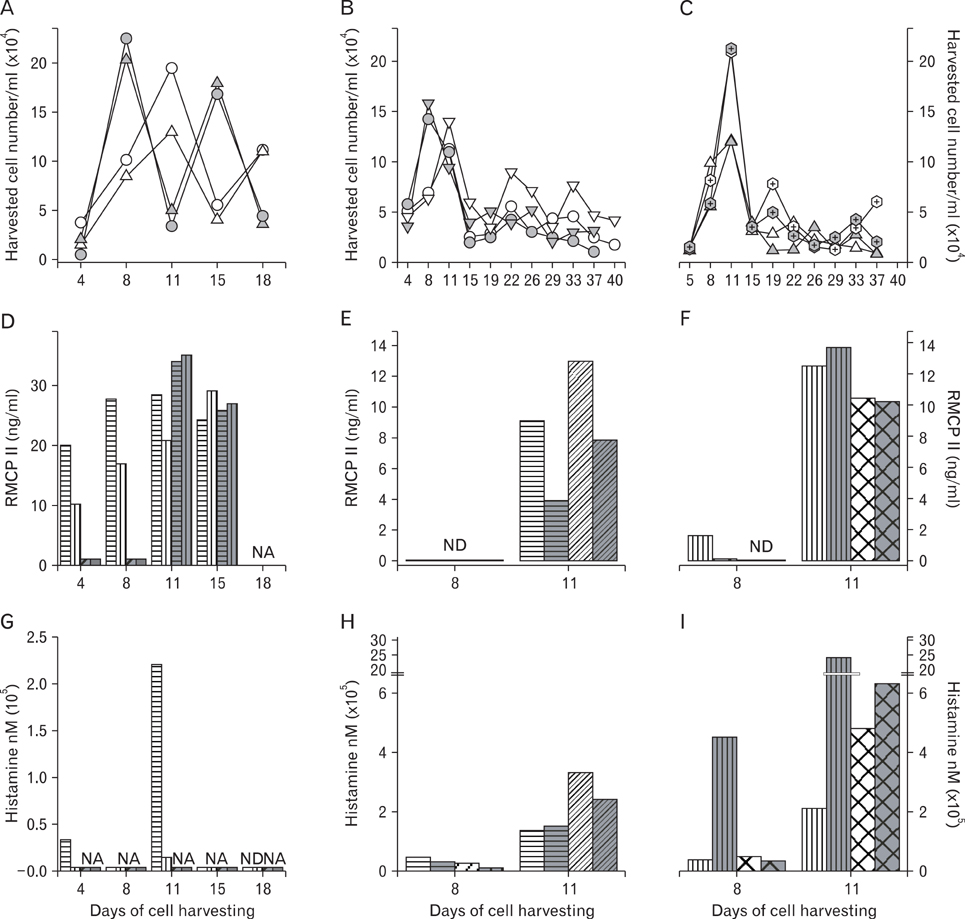
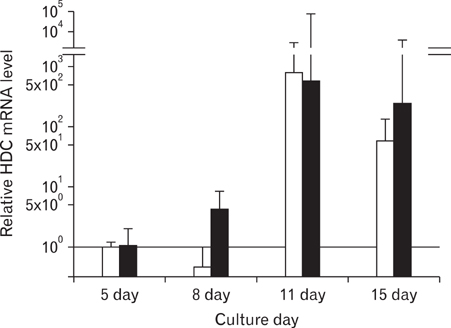
Rat mast cells were regarded as a good model for mast cell function in immune response. METHODS: Rat bone marrow mast cells (BMMC) were prepared both by recombinant rat IL-3 (rrIL-3) and by recombinant mouse stem cell factor (rmSCF), and investigated for both proliferation and differentiation in time course. Rat BMMC was induced by culture of rat bone marrow cells (BMCs) in the presence of both rrIL-3 (5 ng/ml) and rmSCF (5 ng/ml). Culture media were changed 2 times per week with the cell number condition of 5x10(4)/ml in 6 well plate. Proliferation was analyzed by cell number and cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) and differentiation was by rat mast cell protease (RMCP) II and histamine. RESULTS: Cell proliferation rates reached a maximum at 8 or 11 days of culture and decreased thereafter. However, both RMCP II production and histamine synthesis peaked after 11 days of culture. By real time RT-PCR, the level of histidine decarboxylase mRNA was more than 500 times higher on culture day 11 than on culture day 5. By transmission electron microscopy, the cells were heterogeneous in size and contained cytoplasmic granules. Using gated flow cytometry, we showed that cultured BMCs expressed high levels of FcepsilonRI and the mast cell antigen, ganglioside, on culture day 11. CONCLUSION: These results indicate that rat BMMCs were generated by culturing BMCs in the presence of rrIL-3 and rmSCF and that the BMMCs have the characteristics of mucosal mast cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Bone Marrow
Bone Marrow Cells
Cell Count
Cell Proliferation
Culture Media
Cytoplasmic Granules
Flow Cytometry
Histamine
Histidine Decarboxylase
Interleukin-3
Kinetics
Mast Cells
Mice
Microscopy, Electron, Transmission
Phenotype
Rats
RNA, Messenger
Stem Cell Factor
Culture Media
Histamine
Histidine Decarboxylase
Interleukin-3
RNA, Messenger
Stem Cell Factor
Figure
Reference
-
1. Galli SJ, Nakae S, Tsai M. Mast cells in the development of adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2005. 6:135–142.
Article2. Marshall JS. Mast-cell responses to pathogens. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004. 4:787–799.
Article3. Bonnefoy JY, Gauchat JF, Life P, Graber P, Mazzei G, Aubry JP. Pairs of surface molecules involved in human IgE regulation: CD23-CD21 and CD40-CD40L. Eur Respir J Suppl. 1996. 22:63s–66s.4. Galli SJ, Grimbaldeston M, Tsai M. Immunomodulatory mast cells: negative, as well as positive, regulators of immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008. 8:478–486.
Article5. McLachlan JB, Shelburne CP, Hart JP, Pizzo SV, Goyal R, Brooking-Dixon R, Staats HF, Abraham SN. Mast cell activators: a new class of highly effective vaccine adjuvants. Nat Med. 2008. 14:536–541.
Article6. Metz M, Maurer M. Mast cells -- key effector cells in immune responses. Trends Immunol. 2007. 28:234–241.
Article7. Humphries DE, Wong GW, Friend DS, Gurish MF, Qiu WT, Huang C, Sharpe AH, Stevens RL. Heparin is essential for the storage of specific granule proteases in mast cells. Nature. 1999. 400:769–772.
Article8. Soucek L, Lawlor ER, Soto D, Shchors K, Swigart LB, Evan GI. Mast cells are required for angiogenesis and macroscopic expansion of Myc-induced pancreatic islet tumors. Nat Med. 2007. 13:1211–1218.
Article9. Haig DM, McKee TA, Jarrett EE, Woodbury R, Miller HR. Generation of mucosal mast cells is stimulated in vitro by factors derived from T cells of helminth-infected rats. Nature. 1982. 300:188–190.
Article10. McCloskey MA, Fan Y, Luther S. Chemotaxis of rat mast cells toward adenine nucleotides. J Immunol. 1999. 163:970–977.11. Razin E. Culture of bone marrow-derived mast cells: a model for studying oxidative metabolism of arachidonic acid and synthesis of other molecules derived from membrane phospholipids. Methods Enzymol. 1990. 187:514–520.12. Nakano N, Nishiyama C, Kanada S, Niwa Y, Shimokawa N, Ushio H, Nishiyama M, Okumura K, Ogawa H. Involvement of mast cells in IL-12/23 p40 production is essential for survival from polymicrobial infections. Blood. 2007. 109:4846–4855.
Article13. Quan FS, Matsumoto T, Lee JB, Timothy O, Kim TS, Joo KH, Lee JS. Immunization with Trichinella spiralis Korean isolate larval excretory-secretory antigen induces protection and lymphocyte subset changes in rats. Immunol Invest. 2004. 33:15–26.
Article14. Rim HJ. Clonorchiasis: an update. J Helminthol. 2005. 79:269–281.
Article15. Cho SW, Lee HN. Immune reactions and allergy in experimental anisakiasis. Korean J Parasitol. 2006. 44:271–283.
Article16. McCloskey MA, Qian YX. Selective expression of potassium channels during mast cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1994. 269:14813–14819.
Article17. Dy M, Schneider E. Histamine-cytokine connection in immunity and hematopoiesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004. 15:393–410.
Article18. Jiang W, Kreis ME, Eastwood C, Kirkup AJ, Humphrey PP, Grundy D. 5-HT(3) and histamine H(1) receptors mediate afferent nerve sensitivity to intestinal anaphylaxis in rats. Gastroenterology. 2000. 119:1267–1275.
Article19. Cohen DR, Hapel AJ, Young IG. Cloning and expression of the rat interleukin-3 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986. 14:3641–3658.
Article20. Zsebo KM, Wypych J, McNiece IK, Lu HS, Smith KA, Karkare SB, Sachdev RK, Yuschenkoff VN, Birkett NC, Williams LR, et al. Identification, purification, and biological characterization of hematopoietic stem cell factor from buffalo rat liver--conditioned medium. Cell. 1990. 63:195–201.
Article21. Basciano LK, Berenstein EH, Kmak L, Siraganian RP. Monoclonal antibodies that inhibit IgE binding. J Biol Chem. 1986. 261:11823–11831.
Article22. Jamur MC, Grodzki AC, Moreno AN, de Fatima CdM, Pastor MV, Berenstein EH, Siraganian RP, Oliver C. Identification and isolation of rat bone marrow-derived mast cells using the mast cell-specific monoclonal antibody AA4. J Histochem Cytochem. 2001. 49:219–228.
Article23. Ishih A, Uchikawa R. Immunoglobulin E and mast cell responses are related to worm biomass but not expulsion of Hymenolepis diminuta during low dose infection in rats. Parasite Immunol. 2000. 22:561–566.
Article24. Taurog JD, Mendoza GR, Hook WA, Siraganian RP, Metzger H. Noncytotoxic IgE-mediated release of histamine and serotonin from murine mastocytoma cells. J Immunol. 1977. 119:1757–1761.25. Cho SW, Kilmon MA, Studer EJ, van der Putten H, Conrad DH. B cell activation and Ig, especially IgE, production is inhibited by high CD23 levels in vivo and in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1997. 180:36–46.
Article26. Defranco AL, Raveche ES, Asofsk R, Paul WE. Frequency of B lymphocytes responsive to anti-immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1982. 155:1523–1536.
Article27. Bazin H, Querinjean P, Beckers A, Heremans JF, Dessy F. Transplantable immunoglobulin-secreting tumours in rats. IV. Sixty-three IgE-secreting immunocytoma tumours. Immunology. 1974. 26:713–723.28. Conrad DH, Studer E, Gervasoni J, Mohanakumar T. Properties of two monoclonal antibodies directed against the Fc and Fab' regions of rat IgE. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1983. 70:352–360.
Article29. Cho TH, Park HY, Cho S, Sohn J, Yoon YW, Cho JE, Cho SW. The time course of biological and immunochemical allergy states induced by Anisakis simplex larvae in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. 143:203–208.
Article30. Ortega Soto E, Pecht I. A monoclonal antibody that inhibits secretion from rat basophilic leukemia cells and binds to a novel membrane component. J Immunol. 1988. 141:4324–4332.31. Watanabe T, Ohtsu H. L-histidine decarboxylase as a probe in studies on histamine. Chem Rec. 2002. 2:369–376.
Article32. Tippens AS, Davis SV, Hayes JR, Bryda EC, Green TL, Gruetter CA. Detection of histidine decarboxylase in rat aorta and cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Inflamm Res. 2004. 53:390–395.
Article33. Kitamura Y, Das AK, Murata Y, Maeyama K, Dev S, Wakayama Y, Kalubi B, Takeda N, Fukui H. Dexamethasone suppresses histamine synthesis by repressing both transcription and activity of HDC in allergic rats. Allergol Int. 2006. 55:279–286.
Article34. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001. 25:402–408.
Article35. Kim SH, Cho YA, Park CH, Uhm CS. The ultrastructural changes of tendon axonal profiles of medial rectus muscles according to duration in patients with intermittent exotropia. Eye (Lond). 2008. 22:1076–1081.
Article36. Kulka M, Fukuishi N, Rottem M, Mekori YA, Metcalfe DD. Mast cells, which interact with Escherichia coli, up-regulate genes associated with innate immunity and become less responsive to Fc(epsilon)RI-mediated activation. J Leukoc Biol. 2006. 79:339–350.
Article37. Rottem M, Barbieri S, Kinet JP, Metcalfe DD. Kinetics of the appearance of FcεRI-bearing cells in interleukin-3-dependent mouse bone marrow cultures: correlation with histamine content and mast cell maturation. Blood. 1992. 79:972–980.
Article38. Haig DM, Jarrett EE, Tas J. In vitro studies on mast cell proliferation in N. brasiliensis infection. Immunology. 1984. 51:643–651.39. Haig DM, McMenamin C, Gunneberg C, Woodbury R, Jarrett EE. Stimulation of mucosal mast cell growth in normal and nude rat bone marrow cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983. 80:4499–4503.
Article40. Haig DM, McMenamin C, Redmond J, Brown D, Young IG, Cohen SD, Hapel AJ. Rat IL-3 stimulates the growth of rat mucosal mast cells in culture. Immunology. 1988. 65:205–211.41. Haig DM, Huntley JF, MacKellar A, Newlands GF, Inglis L, Sangha R, Cohen D, Hapel A, Galli SJ, Miller HR. Effects of stem cell factor (kit-ligand) and interleukin-3 on the growth and serine proteinase expression of rat bone-marrow-derived or serosal mast cells. Blood. 1994. 83:72–83.
Article42. MacDonald AJ, Thornton EM, Newlands GF, Galli SJ, Moqbel R, Miller HR. Rat bone marrow-derived mast cells co-cultured with 3T3 fibroblasts in the absence of T-cell derived cytokines require stem cell factor for their survival and maintain their mucosal mast cell-like phenotype. Immunology. 1996. 88:375–383.
Article43. Carlos D, Sá-Nunes A, de Paula L, Matias-Peres C, Jamur MC, Oliver C, Serra MF, Martins MA, Faccioli LH. Histamine modulates mast cell degranulation through an indirect mechanism in a model IgE-mediated reaction. Eur J Immunol. 2006. 36:1494–1503.
Article44. Yanagida M, Fukamachi H, Ohgami K, Kuwaki T, Ishii H, Uzumaki H, Amano K, Tokiwa T, Mitsui H, Saito H, Iikura Y, Ishizaka T, Nakahata T. Effects of T-helper 2-type cytokines, interleukin-3 (IL-3), IL-4, IL-5, and IL-6 on the survival of cultured human mast cells. Blood. 1995. 86:3705–3714.
Article45. Karimi K, Redegeld FA, Blom R, Nijkamp FP. Stem cell factor and interleukin-4 increase responsiveness of mast cells to substance P. Exp Hematol. 2000. 28:626–634.
Article46. Saito H, Ebisawa M, Tachimoto H, Shichijo M, Fukagawa K, Matsumoto K, Iikura Y, Awaji T, Tsujimoto G, Yanagida M, Uzumaki H, Takahashi G, Tsuji K, Nakahata T. Selective growth of human mast cells induced by Steel factor, IL-6, and prostaglandin E2 from cord blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1996. 157:343–350.47. Jayawardana ST, Ushio H, Niyonsaba F, Gondokaryono SP, Takenaka H, Ikeda S, Okumura K, Ogawa H. Monomeric IgE and lipopolysaccharide synergistically prevent mast-cell apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. 365:137–142.
Article48. Razin E, Cordon-Cardo C, Good RA. Growth of a pure population of mouse mast cells in vitro with conditioned medium derived from concanavalin A-stimulated splenocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981. 78:2559–2561.
Article49. Vonakis BM, Gibbons SP Jr, Rotté MJ, Brothers EA, Kim SC, Chichester K, MacDonald SM. Regulation of rat basophilic leukemia-2H3 mast cell secretion by a constitutive Lyn kinase interaction with the high affinity IgE receptor (FcepsilonRI). J Immunol. 2005. 175:4543–4554.
Article50. Rottem M, Goff JP, Albert JP, Metcalfe DD. The effects of stem cell factor on the ultrastructure of Fc epsilon RI+ cells developing in IL-3-dependent murine bone marrow-derived cell cultures. J Immunol. 1993. 151:4950–4963.51. Tsuji K, Zsebo KM, Ogawa M. Murine mast cell colony formation supported by IL-3, IL-4, and recombinant rat stem cell factor, ligand for c-kit. J Cell Physiol. 1991. 148:362–369.
Article52. Melendez AJ, Harnett MM, Pushparaj PN, Wong WSF, Tay HK, McSharry CP, Harnett W. Inhibition of Fc epsilon RI-mediated mast cell responses by ES-62, a product of parasitic filarial nematodes. Nat Med. 2007. 13:1375–1381.
Article53. Melendez AJ, Khaw AK. Dichotomy of Ca2+ signals triggered by different phospholipid pathways in antigen stimulation of human mast cells. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:17255–17262.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of Stem Cell Factors in Granulation Recovery on Mast Cells of Rat
- Effect of Nitric Oxide on the Viability of Bone Marrow - Derived Cultured Mast Cells
- Effect of Interleukin-9 on Cell Proliferation and Histamine Release of Cord Blood-derived Human Mast Cells
- In Vitro Culture of Mast Cells from Human Umbilical Cord Blood Cells
- Immune Characterization of Bone Marrow-Derived Models of Mucosal and Connective Tissue Mast Cells