Lab Anim Res.
2013 Jun;29(2):63-69. 10.5625/lar.2013.29.2.63.
Ferulic acid regulates the AKT/GSK-3beta/CRMP-2 signaling pathway in a middle cerebral artery occlusion animal model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, College of Veterinary Medicine, Research Institute of Life Science, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. pokoh@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Division of Life Science and Applied Life Science (Brain Korea 21), Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 1431333
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2013.29.2.63
Abstract
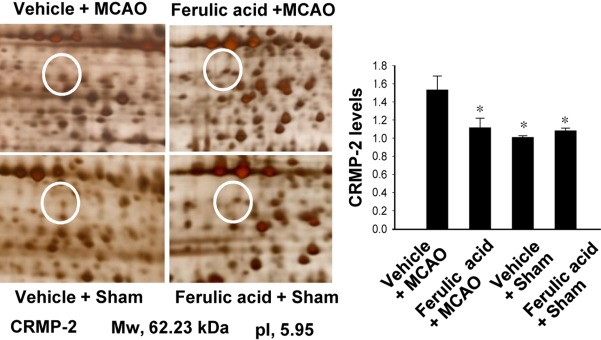
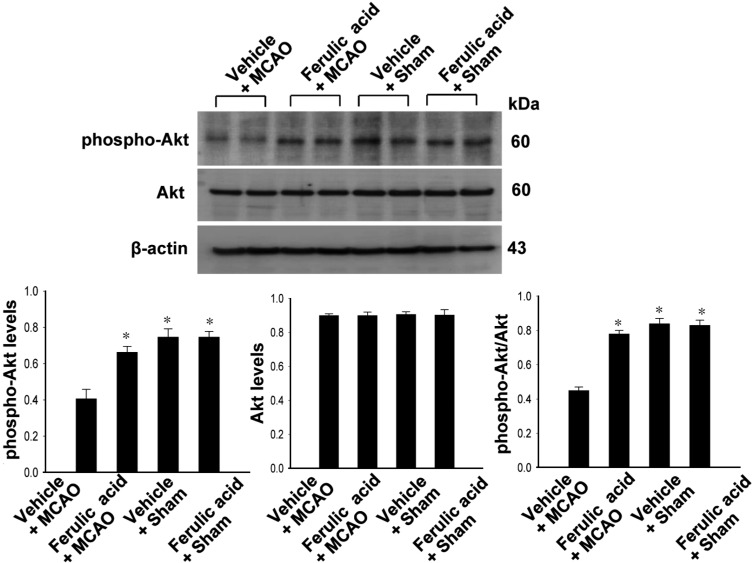
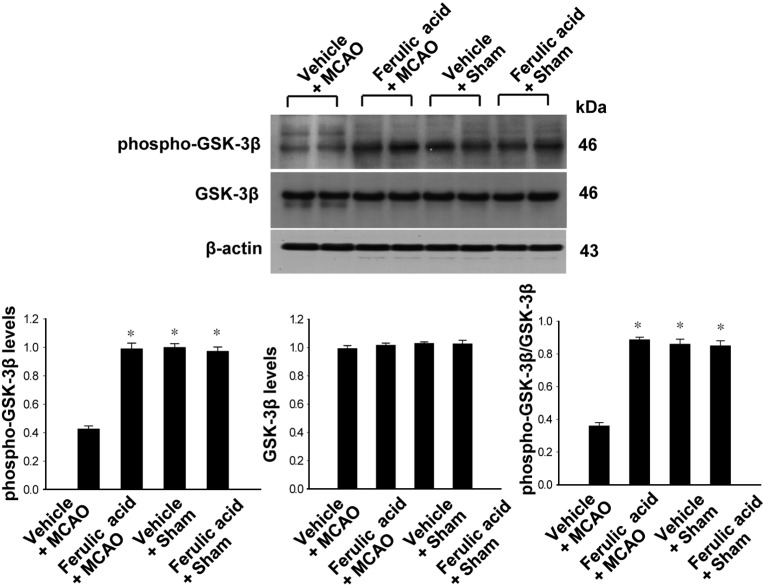
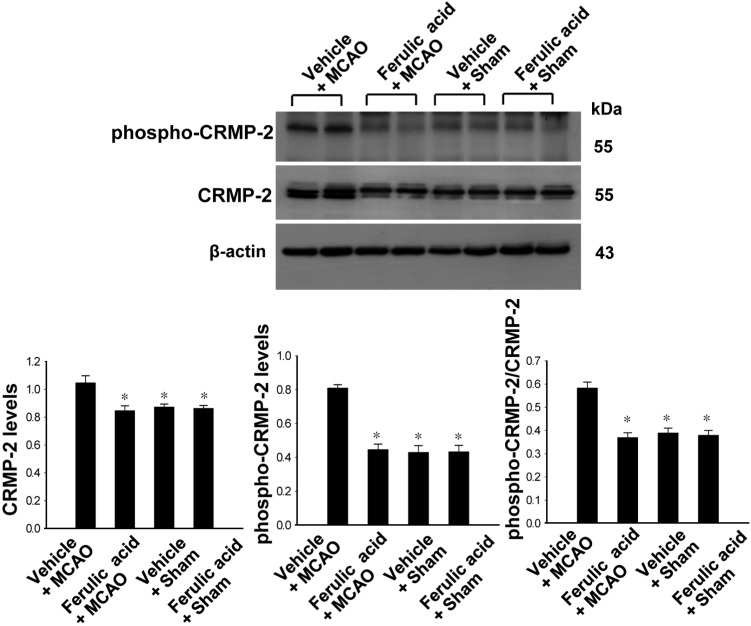
- Ferulic acid, a component of the plants Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels and Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort, exerts a neuroprotective effect by regulating various signaling pathways. This study showed that ferulic acid treatment prevents the injury-induced increase of collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP-2) in focal cerebral ischemia. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta) regulates CRMP-2 function through phosphorylation of CRMP-2. Moreover, the pro-apoptotic activity of GSK-3beta is inactivated by phosphorylation by Akt. This study investigated whether ferulic acid modulates the expression of CRMP-2 and its upstream targets, Akt and GSK-3beta, in focal cerebral ischemia. Male rats were treated immediately with ferulic acid (100 mg/kg, i.v.) or vehicle after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), and then cerebral cortices were collected 24 hr after MCAO. MCAO resulted in decreased levels of phospho-Akt and phospho-GSK-3beta, while ferulic acid treatment prevented the decrease in the levels of these proteins. Moreover, phospho-CRMP-2 and CRMP-2 levels increased during MCAO, whereas ferulic acid attenuated these injury-induced increases. These results demonstrate that ferulic acid regulates the Akt/GSK-3beta/CRMP-2 signaling pathway in focal cerebral ischemic injury, thereby protecting against brain injury.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Angelica sinensis
Animals
Brain Injuries
Brain Ischemia
Cerebral Cortex
Coumaric Acids
Glycogen Synthase
Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3
Humans
Infarction, Middle Cerebral Artery
Ligusticum
Male
Middle Cerebral Artery
Neuroprotective Agents
Phosphorylation
Proteins
Rats
Semaphorin-3A
Coumaric Acids
Glycogen Synthase
Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3
Neuroprotective Agents
Proteins
Semaphorin-3A
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Ferulic acid prevents the injury-induced decrease of γ-enolase expression in brain tissue and HT22 cells
Sang-A Gim, Phil-Ok Koh
Lab Anim Res. 2014;30(1):8-13. doi: 10.5625/lar.2014.30.1.8.
Reference
-
1. Sultana R, Ravagna A, Mohmmad-Abdul H, Calabrese V, Butterfield DA. Ferulic acid ethyl ester protects neurons against amyloid beta-peptide(1-42)-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity: relationship to antioxidant activity. J Neurochem. 2005; 92(4):749–758. PMID: 15686476.2. Srinivasan M, Sudheer AR, Pillai KR, Kumar PR, Sudhakaran PR, Menon VP. Influence of ferulic acid on gamma-radiation induced DNA damage, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in primary culture of isolated rat hepatocytes. Toxicology. 2006; 228(2-3):249–258. PMID: 17049709.3. Srinivasan M, Sudheer AR, Menon VP. Ferulic Acid: therapeutic potential through its antioxidant property. Ferulic Acid: therapeutic potential through its antioxidant property. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2007; 40(2):92–100. PMID: 18188410.4. Kawabata K, Yamamoto T, Hara A, Shimizu M, Yamada Y, Matsunaga K, Tanaka T, Mori H. Modifying effects of ferulic acid on azoxymethane-induced colon carcinogenesis in F344 rats. Cancer Lett. 2000; 157(1):15–21. PMID: 10893437.
Article5. Ohnishi M, Matuo T, Tsuno T, Hosoda A, Nomura E, Taniguchi H, Sasaki H, Morishita H. Antioxidant activity and hypoglycemic effect of ferulic acid in STZ-induced diabetic mice and KK-Ay mice. Biofactors. 2004; 21(1-4):315–319. PMID: 15630218.6. Cheng CY, Ho TY, Lee EJ, Su SY, Tang NY, Hsieh CL. Ferulic acid reduces cerebral infarct through its antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects following transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Am J Chin Med. 2008; 36(6):1105–1119. PMID: 19051339.
Article7. Cheng CY, Su SY, Tang NY, Ho TY, Chiang SY, Hsieh CL. Ferulic acid provides neuroprotection against oxidative stress-related apoptosis after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ICAM-1 mRNA expression in rats. Brain Res. 2008; 1209:136–150. PMID: 18400211.
Article8. Koh PO. Ferulic acid prevents the cerebral ischemic injury-induced decrease of Akt and Bad phosphorylation. Neurosci Lett. 2012; 507(2):156–160. PMID: 22200499.
Article9. Koh PO. Ferulic acid prevents the cerebral ischemic injury-induced decreases of astrocytic phosphoprotein PEA-15 and its two phosphorylated forms. Neurosci Lett. 2012; 511(2):101–105. PMID: 22306184.
Article10. Jin Y, Yan EZ, Fan Y, Guo XL, Zhao YJ, Zong ZH, Liu Z. Neuroprotection by sodium ferulate against glutamate-induced apoptosis is mediated by ERK and PI3 kinase pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007; 28(12):1881–1890. PMID: 18031600.
Article11. Datta SR, Brunet A, Greenberg ME. Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev. 1999; 13(22):2905–2907. PMID: 10579998.
Article12. Brazil DP, Yang ZZ, Hemmings BA. Advances in protein kinase B signalling: AKTion on multiple fronts. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004; 29(5):233–242. PMID: 15130559.
Article13. Janelidze S, Hu BR, Siesjö P, Siesjö BK. Alterations of Akt1 (PKBalpha) and p70(S6K) in transient focal ischemia. Neurobiol Dis. 2001; 8(1):147–154. PMID: 11162248.14. Noshita N, Lewén A, Sugawara T, Chan PH. Evidence of phosphorylation of Akt and neuronal survival after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001; 21(12):1442–1450. PMID: 11740206.
Article15. Shibata M, Yamawaki T, Sasaki T, Hattori H, Hamada J, Fukuuchi Y, Okano H, Miura M. Upregulation of Akt phosphorylation at the early stage of middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Brain Res. 2002; 942(1-2):1–10. PMID: 12031847.
Article16. Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M, Hemmings BA. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature. 1995; 378(6559):785–789. PMID: 8524413.
Article17. Brywe KG, Mallard C, Gustavsson M, Hedtjärn M, Leverin AL, Wang X, Blomgren K, Isgaard J, Hagberg H. IGF-I neuroprotection in the immature brain after hypoxia-ischemia, involvement of Akt and GSK3beta? Eur J Neurosci. 2005; 21(6):1489–1502. PMID: 15845077.18. Brown M, Jacobs T, Eickholt B, Ferrari G, Teo M, Monfries C, Qi RZ, Leung T, Lim L, Hall C. Alpha2-chimaerin, cyclin-dependent Kinase 5/p35, and its target collapsin response mediator protein-2 are essential components in semaphorin 3A-induced growth-cone collapse. J Neurosci. 2004; 24(41):8994–9004. PMID: 15483118.19. Cole AR, Knebel A, Morrice NA, Robertson LA, Irving AJ, Connolly CN, Sutherland C. GSK-3 phosphorylation of the Alzheimer epitope within collapsin response mediator proteins regulates axon elongation in primary neurons. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279(48):50176–50180. PMID: 15466863.
Article20. Yoshimura T, Kawano Y, Arimura N, Kawabata S, Kikuchi A, Kaibuchi K. GSK-3beta regulates phosphorylation of CRMP-2 and neuronal polarity. Cell. 2005; 120(1):137–149. PMID: 15652488.21. Zumbrunn J, Kinoshita K, Hyman AA, Näthke IS. Binding of the adenomatous polyposis coli protein to microtubules increases microtubule stability and is regulated by GSK3 beta phosphorylation. Curr Biol. 2001; 11(1):44–49. PMID: 11166179.22. Fukata Y, Itoh TJ, Kimura T, Ménager C, Nishimura T, Shiromizu T, Watanabe H, Inagaki N, Iwamatsu A, Hotani H, Kaibuchi K. CRMP-2 binds to tubulin heterodimers to promote microtubule assembly. Nat Cell Biol. 2002; 4(8):583–591. PMID: 12134159.
Article23. Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989; 20(1):84–91. PMID: 2643202.
Article24. Gu Y, Hamajima N, Ihara Y. Neurofibrillary tangle-associated collapsin response mediator protein-2 (CRMP-2) is highly phosphorylated on Thr-509, Ser-518, and Ser-522. Biochemistry. 2000; 39(15):4267–4275. PMID: 10757975.
Article25. Inagaki N, Chihara K, Arimura N, Ménager C, Kawano Y, Matsuo N, Nishimura T, Amano M, Kaibuchi K. CRMP-2 induces axons in cultured hippocampal neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2001; 4(8):781–782. PMID: 11477421.
Article26. Chen A, Liao WP, Lu Q, Wong WS, Wong PT. Upregulation of dihydropyrimidinase-related protein 2, spectrin alpha II chain, heat shock cognate protein 70 pseudogene 1 and tropomodulin 2 after focal cerebral ischemia in rats--a proteomics approach. Neurochem Int. 2007; 50(7-8):1078–1086. PMID: 17196711.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Resveratrol modulates the Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway in a middle cerebral artery occlusion animal model
- Ferulic acid modulates nitric oxide synthase expression in focal cerebral ischemia
- Ferulic acid prevents the injury-induced decrease of gamma-enolase expression in brain tissue and HT22 cells
- Chlorogenic acid alleviates the reduction of Akt and Bad phosphorylation and of phospho-Bad and 14-3-3 binding in an animal model of stroke
- Phosphorylation of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3beta(S9) Induced Neuronal Cell Survival by Sulindac in the Rat Retina