Yonsei Med J.
2019 Dec;60(12):1195-1202. 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.12.1195.
Propofol Attenuates Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Apoptosis and Autophagy in HK-2 Cells by Inhibiting JNK Activation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Wuhan University Renmin Hospital, Wuhan, China. 45123915@qq.com
- KMID: 2463799
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.12.1195
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to investigate whether propofol could attenuate hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis and autophagy in human renal proximal tubular cells (HK-2) by inhibiting JNK activation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
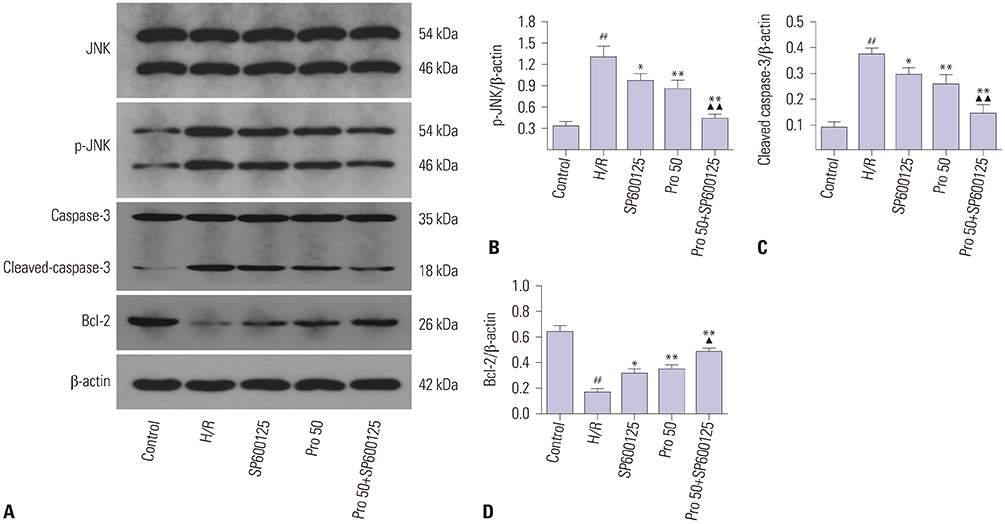
HK-2 cells were treated with or without propofol or JNK inhibitor SP600125 for 1 hour and then subjected to 15 hours of hypoxia and 2 hours of reoxygenation (H/R). Cell viability and LDH release were measured with commercial kits. Cell apoptosis was evaluated by flow cytometry. The expressions of p-JNK, cleaved-caspase-3, Bcl-2, and autophagy markers LC3 and p62 were measured by Western blot or immunofluorescence.
RESULTS
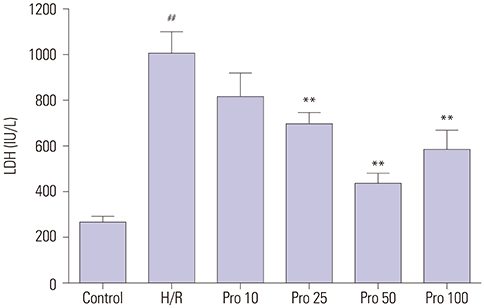
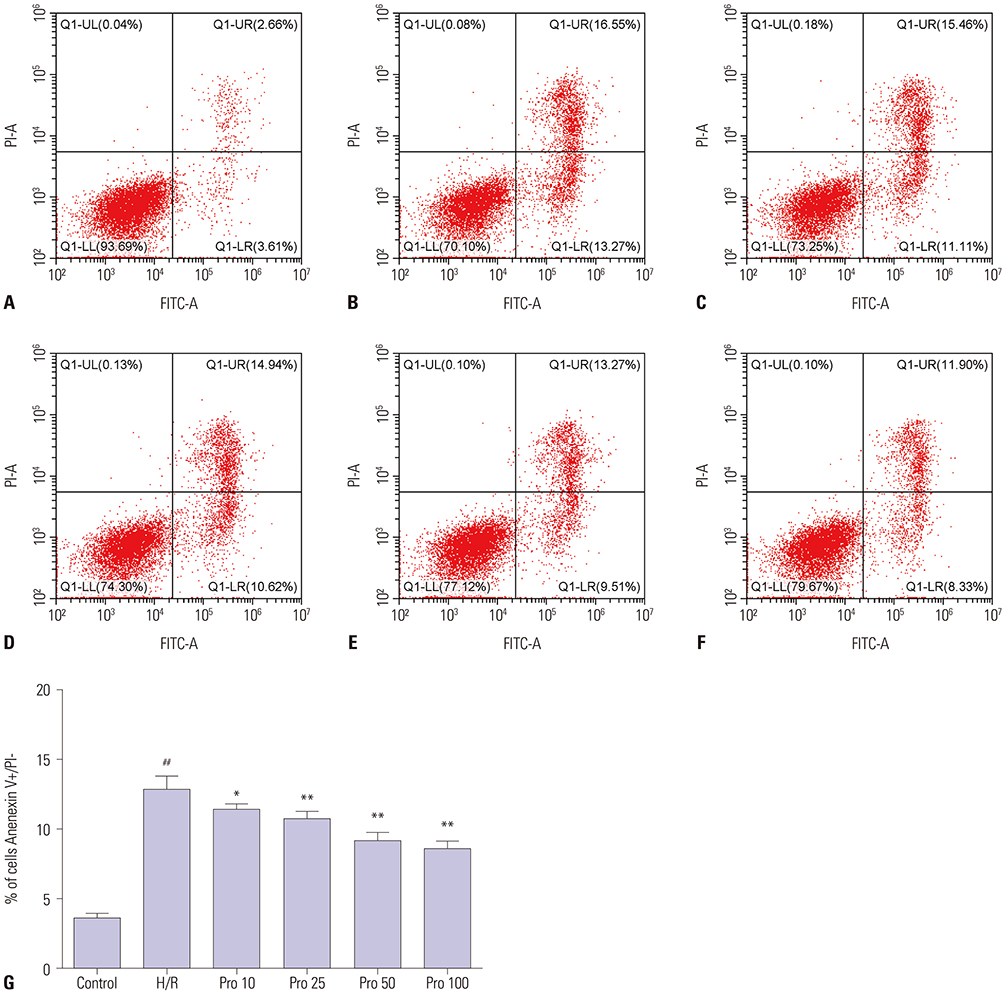
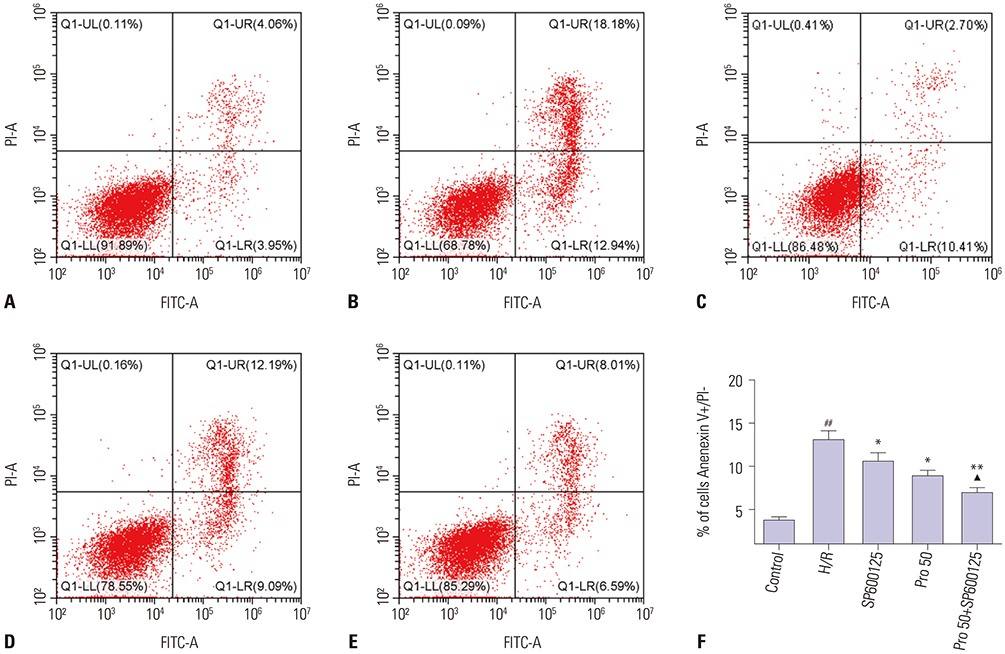
HK-2 cells exposed to H/R insult showed higher cell injury (detected by increased LDH release and decreased cell viability), increased cell apoptosis index and expression of cleaved-caspase-3, a decrease in the expression of Bcl-2 accompanied by increased expression of p-JNK and LC3II, and a decrease in expression of p62. All of these alterations were attenuated by propofol treatment. Similar effects were provoked upon treatment with the JNK inhibitor SP600125. Moreover, the protective effects were more obvious with the combination of propofol and SP600125.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that propofol could attenuate hypoxia/reoxygenation induced apoptosis and autophagy in HK-2 cells, probably through inhibiting JNK activation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Saat TC, van den Akker EK, IJzermans JN, Dor FJ, de Bruin RW. Improving the outcome of kidney transplantation by ameliorating renal ischemia reperfusion injury: lost in translation? J Transl Med. 2016; 14:20.
Article2. Chouchani ET, Pell VR, James AM, Work LM, Saeb-Parsy K, Frezza C, et al. A unifying mechanism for mitochondrial superoxide production during ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cell Metab. 2016; 23:254–263.
Article3. Hamzawy M, Gouda SAA, Rashed L, Morcos MA, Shoukry H, Sharawy N. 22-oxacalcitriol prevents acute kidney injury via inhibition of apoptosis and enhancement of autophagy. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2019; 23:43–55.
Article4. Smith SF, Hosgood SA, Nicholson ML. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in renal transplantation: 3 key signaling pathways in tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 2019; 95:50–56.
Article5. Su M, Ren S, Zhong W, Han X. Impact of propofol on renal ischemia/ reperfusion endoplasmic reticulum stress. Acta Cir Bras. 2017; 32:533–539.
Article6. Decuypere JP, Pirenne J, Jochmans I. Autophagy in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury: friend or foe? Am J Transplant. 2014; 14:1464–1465.
Article7. Sun B, Ou H, Ren F, Huan Y, Zhong T, Gao M, et al. Propofol inhibited autophagy through Ca(2+)/CaMKKβ/AMPK/mTOR pathway in OGD/R-induced neuron injury. Mol Med. 2018; 24:58.
Article8. Zhu Y, Li S, Liu J, Wen Q, Yu J, Yu L, et al. Role of JNK signaling pathway in dexmedetomidine post-conditioning-induced reduction of the inflammatory response and autophagy effect of focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Inflammation. 2019; 08. 24. [Epub]. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-01082-2.
Article9. Jiang M, Fan J, Qu X, Li S, Nilsson SK, Sun YBY, et al. Combined blockade of Smad3 and JNK pathways ameliorates progressive fibrosis in folic acid nephropathy. Front Pharmacol. 2019; 10:880.
Article10. Ibrahim YF, Moussa RA, Bayoumi AMA, Ahmed AF. Tocilizumab attenuates acute lung and kidney injuries and improves survival in a rat model of sepsis via down-regulation of NF-κB/JNK: a possible role of P-glycoprotein. Inflammopharmacology. 2019; 08. 22. [Epub]. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-019-00628-y.
Article11. Moonen L, D'Haese PC, Vervaet BA. Epithelial cell cycle behaviour in the injured kidney. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19:E2038.
Article12. Granger DN, Kvietys PR. Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: the evolution of a concept. Redox Biol. 2015; 6:524–551.
Article13. Ha SD, Solomon O, Akbari M, Sener A, Kim SO. Histone deacetylase 8 protects human proximal tubular epithelial cells from hypoxia-mimetic cobalt- and hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced mitochondrial fission and cytotoxicity. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:11332.
Article14. Lu J, Yi Y, Pan R, Zhang C, Han H, Chen J, et al. Berberine protects HK-2 cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation induced apoptosis via inhibiting SPHK1 expression. J Nat Med. 2018; 72:390–398.
Article15. Yoo YC, Yoo KJ, Lim BJ, Jun JH, Shim JK, Kwak YL. Propofol attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury aggravated by hyperglycemia. J Surg Res. 2013; 183:783–791.
Article16. Li Y, Zhong D, Lei L, Jia Y, Zhou H, Yang B. Propofol prevents renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibiting the oxidative stress pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015; 37:14–26.
Article17. Hiraoka H, Yamamoto K, Miyoshi S, Morita T, Nakamura K, Kadoi Y, et al. Kidneys contribute to the extrahepatic clearance of propofol in humans, but not lungs and brain. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005; 60:176–182.
Article18. Kanto J, Gepts E. Pharmacokinetic implications for the clinical use of propofol. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1989; 17:308–326.
Article19. Wu Q, Wu W, Fu B, Shi L, Wang X, Kuca K. JNK signaling in cancer cell survival. Med Res Rev. 2019; 39:2082–2104.
Article20. Zhang J, Xia Y, Xu Z, Deng X. Propofol suppressed hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in HBVSMC by regulation of the expression of Bcl-2, Bax, Caspase3, Kir6.1, and p-JNK. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016; 2016:1518738.
Article21. Wang D, Chen T, Liu F. Betulinic acid alleviates myocardial hypoxia/ reoxygenation injury via inducing Nrf2/HO-1 and inhibiting p38 and JNK pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018; 838:53–59.
Article22. Yan R, Zhang L, Xia N, Liu Q, Sun H, Guo H. Knockdown of augmenter of liver regeneration in HK-2 cells inhibits inflammation response via the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Inflamm Res. 2015; 64:453–462.
Article23. Xie Y, Xiao J, Fu C, Zhang Z, Ye Z, Zhang X. Ischemic preconditioning promotes autophagy and alleviates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biomed Res Int. 2018; 2018:8353987.
Article24. Ren H, Fu K, Mu C, Li B, Wang D, Wang G. DJ-1, a cancer and Parkinson's disease associated protein, regulates autophagy through JNK pathway in cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010; 297:101–108.
Article25. Lin CW, Lo S, Perng DS, Wu DB, Lee PH, Chang YF, et al. Complete activation of autophagic process attenuates liver injury and improves survival in septic mice. Shock. 2014; 41:241–249.
Article26. Li H, Zhang X, Tan J, Sun L, Xu LH, Jiang YG, et al. Propofol postconditioning protects H9c2 cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inducing autophagy via the SAPK/JNK pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018; 17:4573–4580.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Protective Effect of Propofol against Hypoxia-reoxygenation Injury in HaCaT Human Keratinocytes
- Requirement of ERK Activation in Hypoxia Induced Caspase Activation and Apoptosis of Cultured Tubular Cells
- Propofol Post-conditioning Protects against COS-7 Cells in Hypoxia/reoxygenation Injury by Induction of Intracellular Autophagy
- Effect of Propofol on Kupffer Cell Superoxide Dismutase Activities and Cytoprotections during Hypoxia-Reoxygenation
- The Influence of Propofol on Cell Viability after Reoxygenation in Rat Embryonic Heart H9c2 Cells