J Bacteriol Virol.
2018 Dec;48(4):130-136. 10.4167/jbv.2018.48.4.130.
Gene Expression Profiles of Th1-type Chemokines in Whole Blood of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis-Infected Cattle
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, Research Institute of Life Science, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 2Department of Infectious Diseases, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. yoohs@snu.ac.kr
- 3National Institute of Animal Science, Rural Development Administration, Wanju, Korea.
- 4Institute of Green Bio Science and Technology, Seoul National University, Pyeongchang, Korea.
- KMID: 2452065
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2018.48.4.130
Abstract
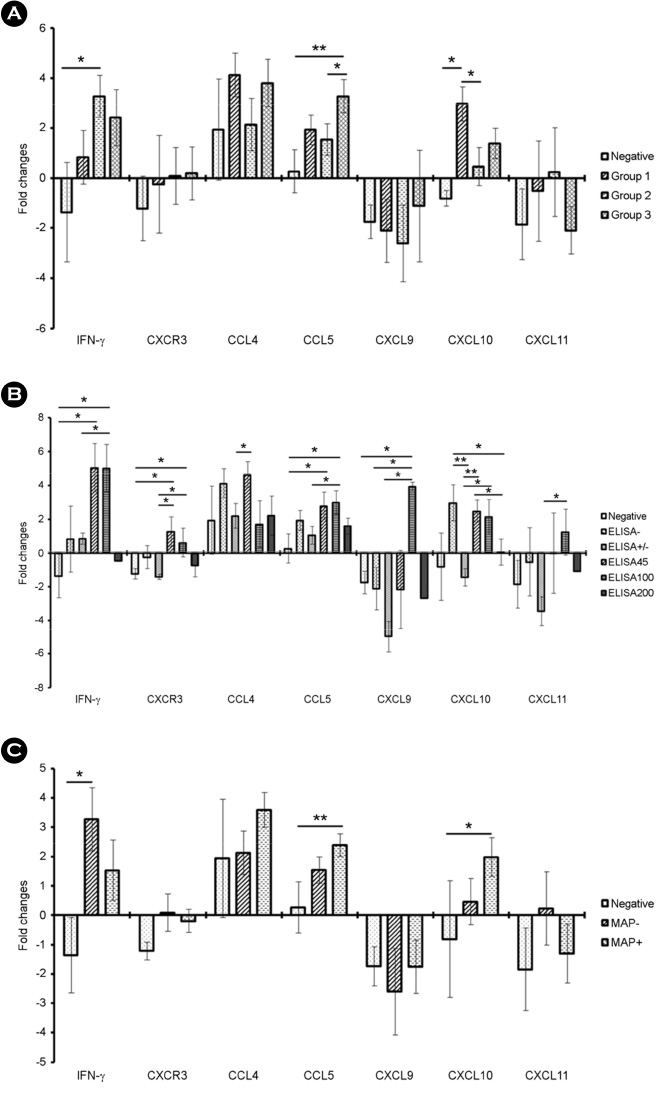
- Johne's disease (JD) is a chronic, debilitating disease of ruminants including cows, and is caused by Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP). MAP is not only important in animal husbandry, but also in public health as it is associated with the onset of Crohn's disease, a chronic inflammatory bowel disease in humans. JD, like other mycobacterial diseases including tuberculosis, is classified into different stages based on the progression of infection. In addition, development of diagnostic assays that can distinguish between subclinical and clinical stages of JD is essential to control mycobacterial infection by providing an effective treatment. For the development of novel diagnostic methods of JD, it is important to investigate and understand the mRNA expression of the various immune markers in individuals at each stage of infection. In this study, we measured the levels of Th1-type chemokines, CXCR3, CCL4, CCL5, CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11 in MAP-infected bovine blood by interferon (IFN)-γ release assay (IGRA) using IFN-γ as an alternative biomarker. The association of mRNA expression patterns of these chemokines with the MAP infection stages was analyzed and IFN-γ, CCL5, and CXCL10 were found to be significantly upregulated compared to IFN-γ, the biomarker used in IGRA. Our results further indicate that IFN-γ levels significantly increased in individuals with MAP-specific antibody, and CCL5 and CXCL10 levels significantly increased in those with MAP DNA. In particular, CCL5 was significantly upregulated in individuals, in which both MAP-specific antibody and MAP DNA were detected, but the expression of CXCL10 was specifically elevated in MAP DNA-detected individuals without MAP-specific antibody.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animal Husbandry
Animals
Biomarkers
Cattle*
Chemokines*
Crohn Disease
DNA
Gene Expression*
Humans
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Interferons
Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis
Mycobacterium avium*
Mycobacterium*
Paratuberculosis
Public Health
RNA, Messenger
Ruminants
Transcriptome*
Tuberculosis
Biomarkers
Chemokines
DNA
Interferons
RNA, Messenger
Figure
Reference
-
1. Motiwala AS, Janagama HK, Paustian ML, Zhu X, Bannantine JP, Kapur V, et al. Comparative transcriptional analysis of human macrophages exposed to animal and human isolates of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis with diverse genotypes. Infect Immun. 2006; 74:6046–6056.
Article2. Coussens PM. Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and the bovine immune system. Anim Health Res Rev. 2001; 2:141–161.3. Sechi LA, Scanu AM, Molicotti P, Cannas S, Mura M, Dettori G, et al. Detection and isolation of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis from intestinal mucosal biopsies of patients with and without Crohn's disease in Sardinia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:1529–1536.
Article4. Shin AR, Kim HJ, Cho SN, Collins MT, Manning EJ, Naser SA, et al. Identification of seroreactive proteins in the culture filtrate antigen of Mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis human isolates to sera from Crohn's disease patients. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2010; 58:128–137.
Article5. Bögli-Stuber K, Kohler C, Seitert G, Glanemann B, Antognoli MC, Salman MD, et al. Detection of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis in Swiss dairy cattle by real-time PCR and culture: a comparison of the two assays. J Appl Microbiol. 2005; 99:587–597.
Article6. Leite FL, Stokes KD, Robbe-Austerman S, Stabel JR. Comparison of fecal DNA extraction kits for the detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis by polymerase chain reaction. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2013; 25:27–34.
Article7. Lalvani A, Pathan AA, McShane H, Wilkinson RJ, Latif M, Conlon CP, et al. Rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by enumeration of antigen-specific T cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 163:824–828.
Article8. Kim S, Lee H, Kim H, Kim Y, Cho JE, Jin H, et al. Diagnostic performance of a cytokine and IFN-gamma-induced chemokine mRNA assay after Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific antigen stimulation in whole blood from infected individuals. J Mol Diagn. 2015; 17:90–99.
Article9. Park HT, Shin M-K, Sung KY, Park H-E, Cho Y-I, Yoo HS. Effective DNA extraction method to improve detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in bovine feces. Korean J Vet Res. 2014; 54:55–57.
Article10. Cortes Y, Ojeda M, Araya D, Dueñas F, Fernández MS, Peralta OA. Isolation and multilineage differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from abattoir-derived bovine fetuses. BMC Vet Res. 2013; 9:133.
Article11. Yakes BJ, Lipert RJ, Bannantine JP, Porter MD. Detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis by a sonicate immunoassay based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008; 15:227–234.
Article12. Shin MK, Park HT, Shin SW, Jung M, Im YB, Park HE, et al. Whole-blood gene-expression profiles of cows infected with Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis reveal changes in immune response and lipid metabolism. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015; 25:255–267.
Article13. Magombedze G, Eda S, Ganusov VV. Competition for antigen between Th1 and Th2 responses determines the timing of the immune response switch during Mycobaterium avium subspecies paratuberulosis infection in ruminants. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014; 10:e1003414.14. Park HE, Shin MK, Park HT, Jung M, Cho YI, Yoo HS. Gene expression profiles of putative biomarker candidates in Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis-infected cattle. Pathog Dis. 2016; 74:ftw022.15. Park HE, Park HT, Jung YH, Yoo HS. Establishment a real-time reverse transcription PCR based on host biomarkers for the detection of the subclinical cases of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. PloS One. 2017; 12:e0178336.16. Yu Y, Zhang Y, Hu S, Jin D, Chen X, Jin Q, et al. Different patterns of cytokines and chemokines combined with IFN-gamma production reflect Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and disease. PloS One. 2012; 7:e44944.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of vaccines to Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection
- Tactics of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis for intracellular survival in mononuclear phagocytes
- Potential biomarkers as an indicator of vertical transmission of Johne's disease in a Korean native cattle farm
- Effective DNA extraction method to improve detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in bovine feces
- Immunohistochemical localization of galectin-3 in the granulomatous lesions of paratuberculosis-infected bovine intestine