Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2019 Jul;23(4):281-289. 10.4196/kjpp.2019.23.4.281.
Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-C and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Korea. syk@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biomedicine & Health Sciences, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Korea.
- 3Catholic Neuroscience Institute, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Korea.
- 4Institute of Aging and Metabolic Diseases, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Korea.
- 5Department of Anatomy, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Korea.
- KMID: 2450495
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2019.23.4.281
Abstract
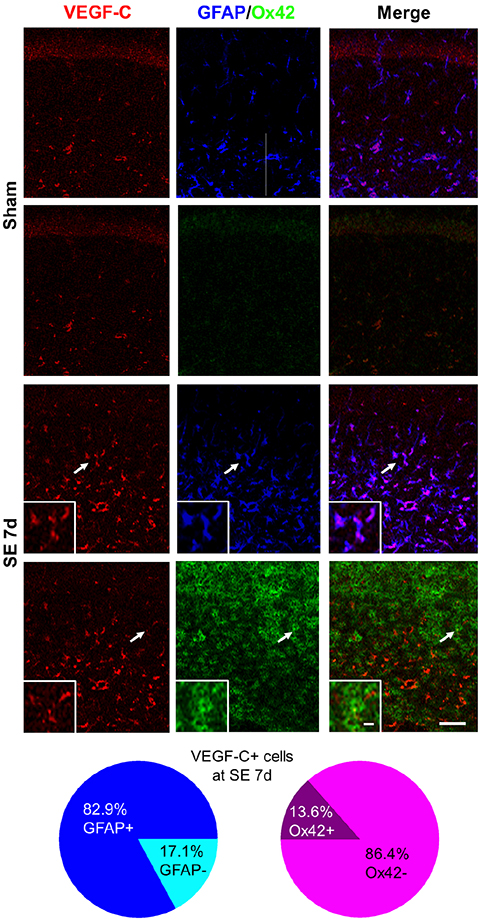
- Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C and its receptor, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-3, are responsible for lymphangiogenesis in both embryos and adults. In epilepsy, the expression of VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 was significantly upregulated in the human brains affected with temporal lobe epilepsy. Moreover, pharmacologic inhibition of VEGF receptors after acute seizures could suppress the generation of spontaneous recurrent seizures, suggesting a critical role of VEGF-related signaling in epilepsy. Therefore, in the present study, the spatiotemporal expression of VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 against pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus (SE) was investigated in C57BL/6N mice using immunohistochemistry. At 1 day after SE, hippocampal astrocytes and microglia were activated. Pyramidal neuronal death was observed at 4 days after SE. In the subpyramidal zone, VEGF-C expression gradually increased and peaked at 7 days after SE, while VEGFR-3 was significantly upregulated at 4 days after SE and began to decrease at 7 days after SE. Most VEGF-C/VEGFR-3-expressing cells were pyramidal neurons, but VEGF-C was also observed in some astrocytes in sham-manipulated animals. However, at 4 days and 7 days after SE, both VEGFR-3 and VEGF-C immunoreactivities were observed mainly in astrocytes and in some microglia of the stratum radiatum and lacunosum-moleculare of the hippocampus, respectively. These data indicate that VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 can be upregulated in hippocampal astrocytes and microglia after pilocarpine-induced SE, providing basic information about VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 expression patterns following acute seizures.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Animals
Astrocytes
Brain
Embryonic Structures
Epilepsy
Epilepsy, Temporal Lobe
Hippocampus
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Lymphangiogenesis
Mice*
Microglia
Pyramidal Cells
Receptors, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
Seizures
Status Epilepticus
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A*
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C*
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-3*
Receptors, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-3
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lehéricy S, Semah F, Hasboun D, Dormont D, Clémenceau S, Granat O, Marsault C, Baulac M. Temporal lobe epilepsy with varying severity: MRI study of 222 patients. Neuroradiology. 1997; 39:788–796.
Article2. Howe KL, Dimitri D, Heyn C, Kiehl TR, Mikulis D, Valiante T. Histologically confirmed hippocampal structural features revealed by 3T MR imaging: potential to increase diagnostic specificity of mesial temporal sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010; 31:1682–1689.
Article3. Cronin J, Dudek FE. Chronic seizures and collateral sprouting of dentate mossy fibers after kainic acid treatment in rats. Brain Res. 1988; 474:181–184.
Article4. de Lanerolle NC, Kim JH, Robbins RJ, Spencer DD. Hippocampal interneuron loss and plasticity in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain Res. 1989; 495:387–395.
Article5. Sutula T, Cascino G, Cavazos J, Parada I, Ramirez L. Mossy fiber synaptic reorganization in the epileptic human temporal lobe. Ann Neurol. 1989; 26:321–330.
Article6. Maglóczky Z, Wittner L, Borhegyi Z, Halász P, Vajda J, Czirják S, Freund TF. Changes in the distribution and connectivity of interneurons in the epileptic human dentate gyrus. Neuroscience. 2000; 96:7–25.
Article7. Buckmaster PS, Haney MM. Factors affecting outcomes of pilocarpine treatment in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2012; 102:153–159.
Article8. Turski WA, Cavalheiro EA, Bortolotto ZA, Mello LM, Schwarz M, Turski L. Seizures produced by pilocarpine in mice: a behavioral, electroencephalographic and morphological analysis. Brain Res. 1984; 321:237–253.
Article9. Cavalheiro EA. The pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Ital J Neurol Sci. 1995; 16:33–37.
Article10. Turski WA, Cavalheiro EA, Schwarz M, Czuczwar SJ, Kleinrok Z, Turski L. Limbic seizures produced by pilocarpine in rats: behavioural, electroencephalographic and neuropathological study. Behav Brain Res. 1983; 9:315–335.
Article11. Borges K, Gearing M, McDermott DL, Smith AB, Almonte AG, Wainer BH, Dingledine R. Neuronal and glial pathological changes during epileptogenesis in the mouse pilocarpine model. Exp Neurol. 2003; 182:21–34.
Article12. Yamazaki Y, Morita T. Molecular and functional diversity of vascular endothelial growth factors. Mol Divers. 2006; 10:515–527.
Article13. Saharinen P, Tammela T, Karkkainen MJ, Alitalo K. Lymphatic vasculature: development, molecular regulation and role in tumor metastasis and inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2004; 25:387–395.
Article14. Oliver G. Lymphatic vasculature development. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004; 4:35–45.
Article15. Lagercrantz J, Farnebo F, Larsson C, Tvrdik T, Weber G, Piehl F. A comparative study of the expression patterns for vegf, vegf-b/vrf and vegf-c in the developing and adult mouse. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998; 1398:157–163.
Article16. Ward MC, Cunningham AM. Developmental expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 and vascular endothelial growth factor C in forebrain. Neuroscience. 2015; 303:544–557.
Article17. Choi JS, Shin YJ, Lee JY, Yun H, Cha JH, Choi JY, Chun MH, Lee MY. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 mRNA in the rat developing forebrain and retina. J Comp Neurol. 2010; 518:1064–1081.
Article18. Hou Y, Shin YJ, Han EJ, Choi JS, Park JM, Cha JH, Choi JY, Lee MY. Distribution of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3/Flt4 mRNA in adult rat central nervous system. J Chem Neuroanat. 2011; 42:56–64.
Article19. Shin YJ, Choi JS, Lee JY, Choi JY, Cha JH, Chun MH, Lee MY. Differential regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor-C and its receptor in the rat hippocampus following transient forebrain ischemia. Acta Neuropathol. 2008; 116:517–527.
Article20. Shin YJ, Choi JS, Choi JY, Hou Y, Cha JH, Chun MH, Lee MY. Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 mRNA in glial cells following focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neuroimmunol. 2010; 229:81–90.
Article21. Shin YJ, Choi JS, Choi JY, Cha JH, Chun MH, Lee MY. Enhanced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 in the subventricular zone of stroke-lesioned rats. Neurosci Lett. 2010; 469:194–198.
Article22. Shin YJ, Park JM, Cho JM, Cha JH, Kim SY, Lee MY. Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 expression in perivascular cells of the ischemic core following focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Acta Histochem. 2013; 115:170–177.
Article23. Zhang CQ, Shu HF, Yin Q, An N, Xu SL, Yin JB, Song YC, Liu SY, Yang H. Expression and cellular distribution of vascular endothelial growth factor-C system in cortical tubers of the tuberous sclerosis complex. Brain Pathol. 2012; 22:205–218.
Article24. Sun FJ, Wei YJ, Li S, Guo W, Chen X, Liu SY, He JJ, Yin Q, Yang H, Zhang CQ. Elevated expression of VEGF-C and its receptors, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3, in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. J Mol Neurosci. 2016; 59:241–250.
Article25. Castañeda-Cabral JL, Beas-Zárate C, Rocha-Arrieta LL, Orozco-Suárez SA, Alonso-Vanegas M, Guevara-Guzmán R, Ureña-Guerrero ME. Increased protein expression of VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C and their receptors in the temporal neocortex of pharmacoresistant temporal lobe epilepsy patients. J Neuroimmunol. 2019; 328:68–72.
Article26. Benini R, Roth R, Khoja Z, Avoli M, Wintermark P. Does angiogenesis play a role in the establishment of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy? Int J Dev Neurosci. 2016; 49:31–36.
Article27. Jeong KH, Lee KE, Kim SY, Cho KO. Upregulation of Krüppel-like factor 6 in the mouse hippocampus after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Neuroscience. 2011; 186:170–178.
Article28. Jang HJ, Kim JE, Jeong KH, Lim SC, Kim SY, Cho KO. The neuroprotective effect of hericium erinaceus extracts in mouse hippocampus after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20:859.
Article29. Kim JE, Cho KO. The pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy and EEG monitoring using radiotelemetry system in mice. J Vis Exp. 2018; (132):56831.
Article30. Racine RJ. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1972; 32:281–294.
Article31. Hou Y, Choi JS, Shin YJ, Cha JH, Choi JY, Chun MH, Lee MY. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 mRNA in the developing rat cerebellum. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2011; 31:7–16.
Article32. Tammela T, Zarkada G, Wallgard E, Murtomäki A, Suchting S, Wirzenius M, Waltari M, Hellström M, Schomber T, Peltonen R, Freitas C, Duarte A, Isoniemi H, Laakkonen P, Christofori G, Ylä-Herttuala S, Shibuya M, Pytowski B, Eichmann A, Betsholtz C, et al. Blocking VEGFR-3 suppresses angiogenic sprouting and vascular network formation. Nature. 2008; 454:656–660.
Article33. Han J, Calvo CF, Kang TH, Baker KL, Park JH, Parras C, Levittas M, Birba U, Pibouin-Fragner L, Fragner P, Bilguvar K, Duman RS, Nurmi H, Alitalo K, Eichmann AC, Thomas JL. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 controls neural stem cell activation in mice and humans. Cell Rep. 2015; 10:1158–1172.
Article34. Calvo CF, Fontaine RH, Soueid J, Tammela T, Makinen T, Alfaro-Cervello C, Bonnaud F, Miguez A, Benhaim L, Xu Y, Barallobre MJ, Moutkine I, Lyytikkä J, Tatlisumak T, Pytowski B, Zalc B, Richardson W, Kessaris N, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alitalo K, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 directly regulates murine neurogenesis. Genes Dev. 2011; 25:831–844.
Article35. Le Bras B, Barallobre MJ, Homman-Ludiye J, Ny A, Wyns S, Tammela T, Haiko P, Karkkainen MJ, Yuan L, Muriel MP, Chatzopoulou E, Bréant C, Zalc B, Carmeliet P, Alitalo K, Eichmann A, Thomas JL. VEGF-C is a trophic factor for neural progenitors in the vertebrate embryonic brain. Nat Neurosci. 2006; 9:340–348.
Article36. Kranich S, Hattermann K, Specht A, Lucius R, Mentlein R. VEGFR-3/Flt-4 mediates proliferation and chemotaxis in glial precursor cells. Neurochem Int. 2009; 55:747–753.
Article37. Morimoto K, Fahnestock M, Racine RJ. Kindling and status epilepticus models of epilepsy: rewiring the brain. Prog Neurobiol. 2004; 73:1–60.
Article38. Scorza FA, Arida RM, Naffah-Mazzacoratti Mda G, Scerni DA, Calderazzo L, Cavalheiro EA. The pilocarpine model of epilepsy: what have we learned. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2009; 81:345–365.
Article39. Fabene PF, Merigo F, Galiè M, Benati D, Bernardi P, Farace P, Nicolato E, Marzola P, Sbarbati A. Pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in rats involves ischemic and excitotoxic mechanisms. PLoS One. 2007; 2:e1105.
Article40. Cavalheiro EA, Leite JP, Bortolotto ZA, Turski WA, Ikonomidou C, Turski L. Long-term effects of pilocarpine in rats: structural damage of the brain triggers kindling and spontaneous recurrent seizures. Epilepsia. 1991; 32:778–782.41. Zhao T, Zhao W, Meng W, Liu C, Chen Y, Gerling IC, Weber KT, Bhattacharya SK, Kumar R, Sun Y. VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 pathway promotes myocyte hypertrophy and survival in the infarcted myocardium. Am J Transl Res. 2015; 7:697–709.42. Hsu M, Rayasam A, Kijak JA, Choi YH, Harding JS, Marcus SA, Karpus WJ, Sandor M, Fabry Z. Neuroinflammation-induced lymphangiogenesis near the cribriform plate contributes to drainage of CNS-derived antigens and immune cells. Nat Commun. 2019; 10:229.
Article43. Cho KO, Lybrand ZR, Ito N, Brulet R, Tafacory F, Zhang L, Good L, Ure K, Kernie SG, Birnbaum SG, Scharfman HE, Eisch AJ, Hsieh J. Aberrant hippocampal neurogenesis contributes to epilepsy and associated cognitive decline. Nat Commun. 2015; 6:6606.
Article44. Bhuiyan MI, Kim JC, Hwang SN, Lee MY, Kim SY. Ischemic tolerance is associated with VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 signaling in the mouse hippocampus. Neuroscience. 2015; 290:90–102.
Article45. Auer RN, Siesjö BK. Biological differences between ischemia, hypoglycemia, and epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 1988; 24:699–707.
Article46. Antila S, Karaman S, Nurmi H, Airavaara M, Voutilainen MH, Mathivet T, Chilov D, Li Z, Koppinen T, Park JH, Fang S, Aspelund A, Saarma M, Eichmann A, Thomas JL, Alitalo K. Development and plasticity of meningeal lymphatic vessels. J Exp Med. 2017; 214:3645–3667.
Article47. Louveau A, Smirnov I, Keyes TJ, Eccles JD, Rouhani SJ, Peske JD, Derecki NC, Castle D, Mandell JW, Lee KS, Harris TH, Kipnis J. Structural and functional features of central nervous system lymphatic vessels. Nature. 2015; 523:337–341.
Article48. Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, Plogg BA, Peng W, Gundersen GA, Benveniste H, Vates GE, Deane R, Goldman SA, Nagelhus EA, Nedergaard M. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid β. Sci Transl Med. 2012; 4:147ra111.
Article49. Smith AJ, Yao X, Dix JA, Jin BJ, Verkman AS. Test of the ‘glymphatic’ hypothesis demonstrates diffusive and aquaporin-4-independent solute transport in rodent brain parenchyma. Elife. 2017; 6:e27679.
Article50. van Vliet EA, Aronica E, Gorter JA. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction, seizures and epilepsy. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015; 38:26–34.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Zerumbone, Sesquiterpene Photochemical from Ginger, Inhibits Angiogenesis
- Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor : Clinical Implications in Cervical Neoplasia
- Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Peritumoral Brain Edema in Intracranial Meningiomas
- Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Human Trohoblast Cell Line
- Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Astrocytic Tumors: Correlation to Peritumoral Brain Edema and Microvasculature