Cancer Res Treat.
2019 Jan;51(1):252-266. 10.4143/crt.2017.613.
Tumor-Associated Macrophages Derived TGF-β‒Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer Cells through Smad2,3-4/Snail Signaling Pathway
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Colorectal and Anal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China. wxb113@126.com
- KMID: 2437617
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2017.613
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We investigated the role of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) on the epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) of colorectal cancer cells and determined the potential mechanism involved in the metastatic process.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In this study, flow cytometry was used to detect the expression of target proteins. We used transwell assay to evaluate the migration of cancer cells under specific conditions. Using real-time polymerase chain reaction, we examined the expressions of cytokines and EMT-related markers in mRNA level. Animal assay was performed for analysis in vivo and hematoxylin and eosin was used to visualize the effect of TAMs on tumor metastasis. We also used immunohistochemistry and Western blotting to detect the expression of target proteins.
RESULTS
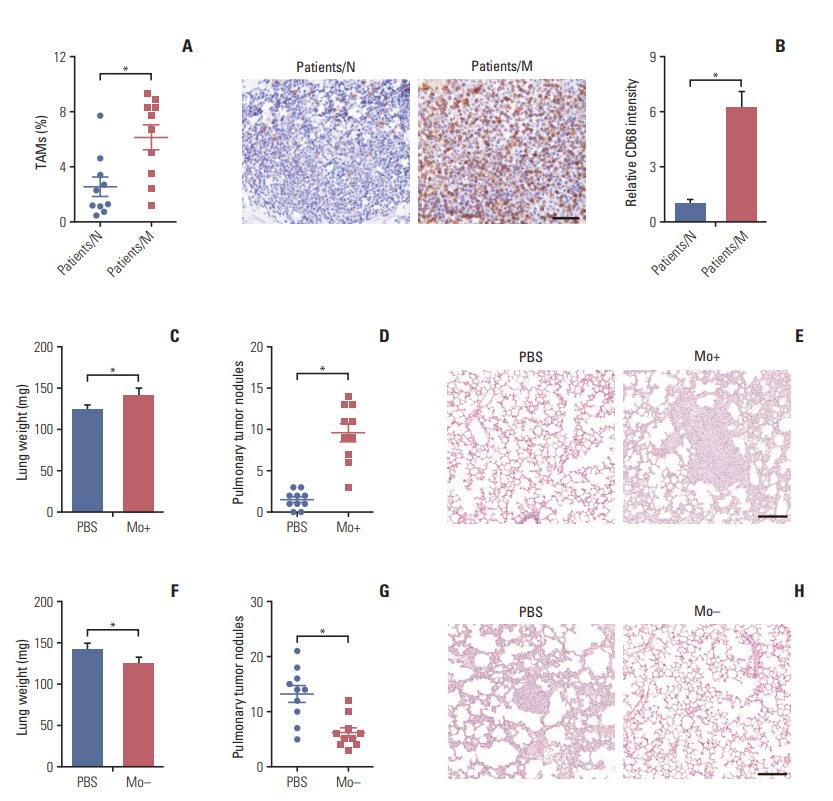
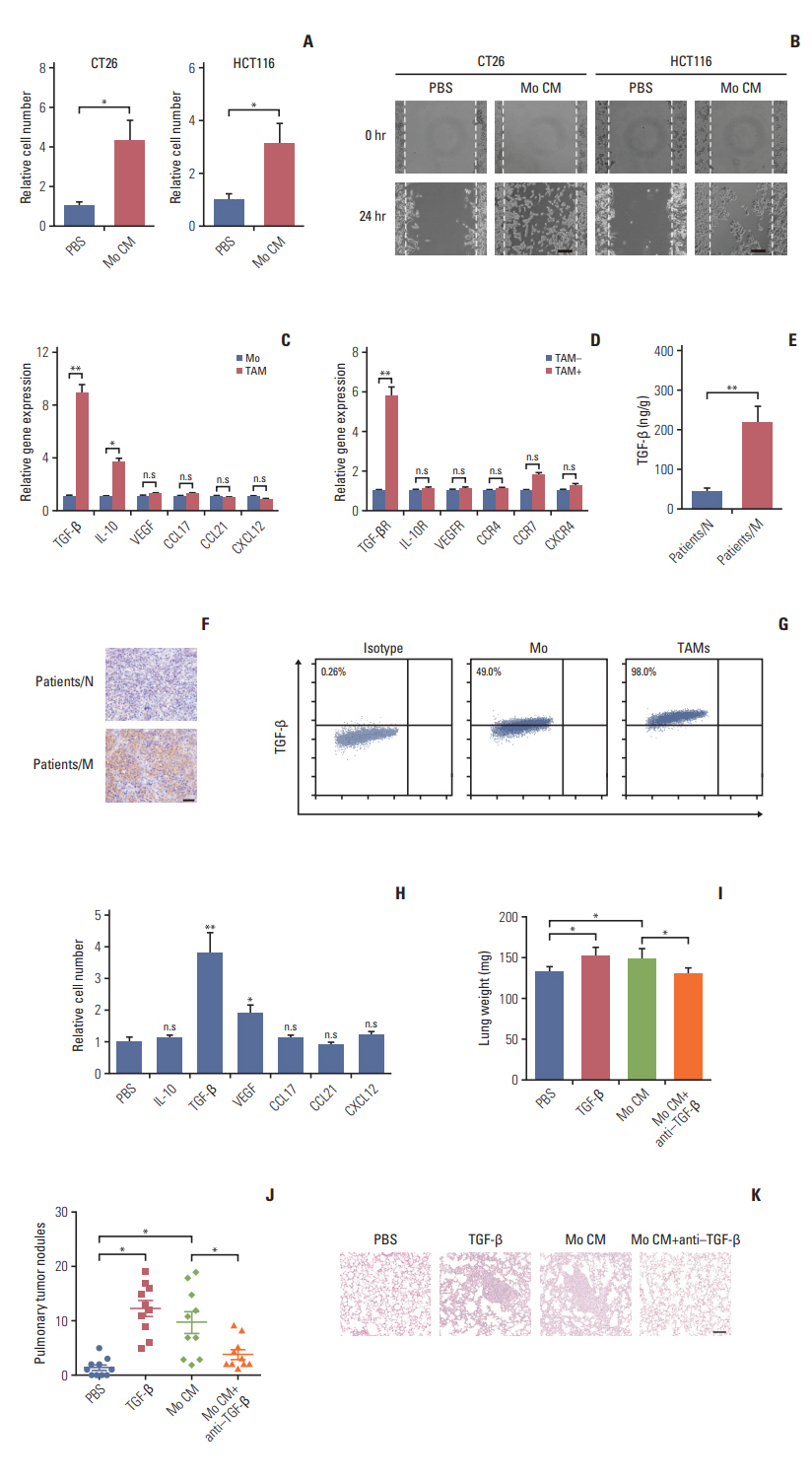
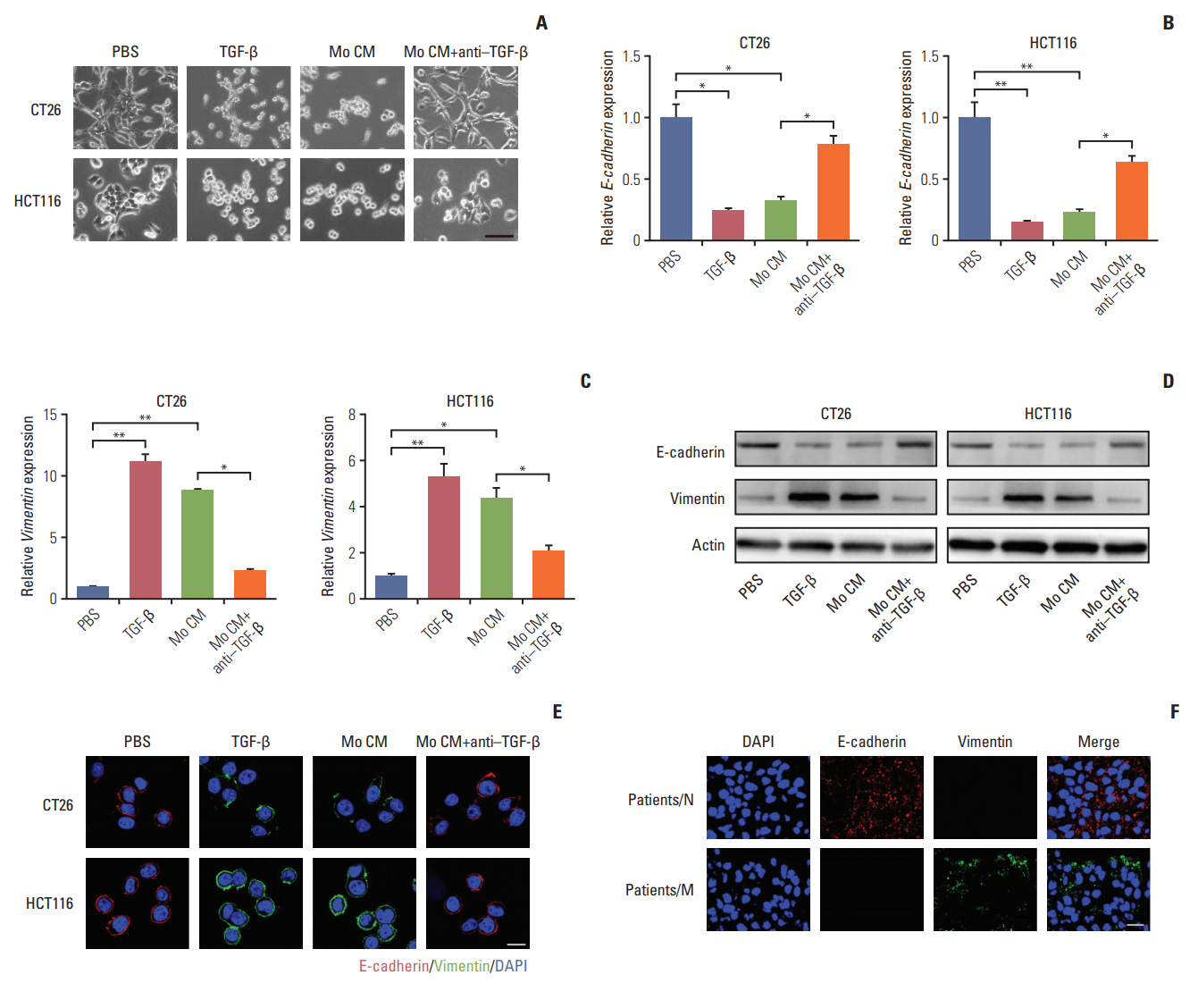
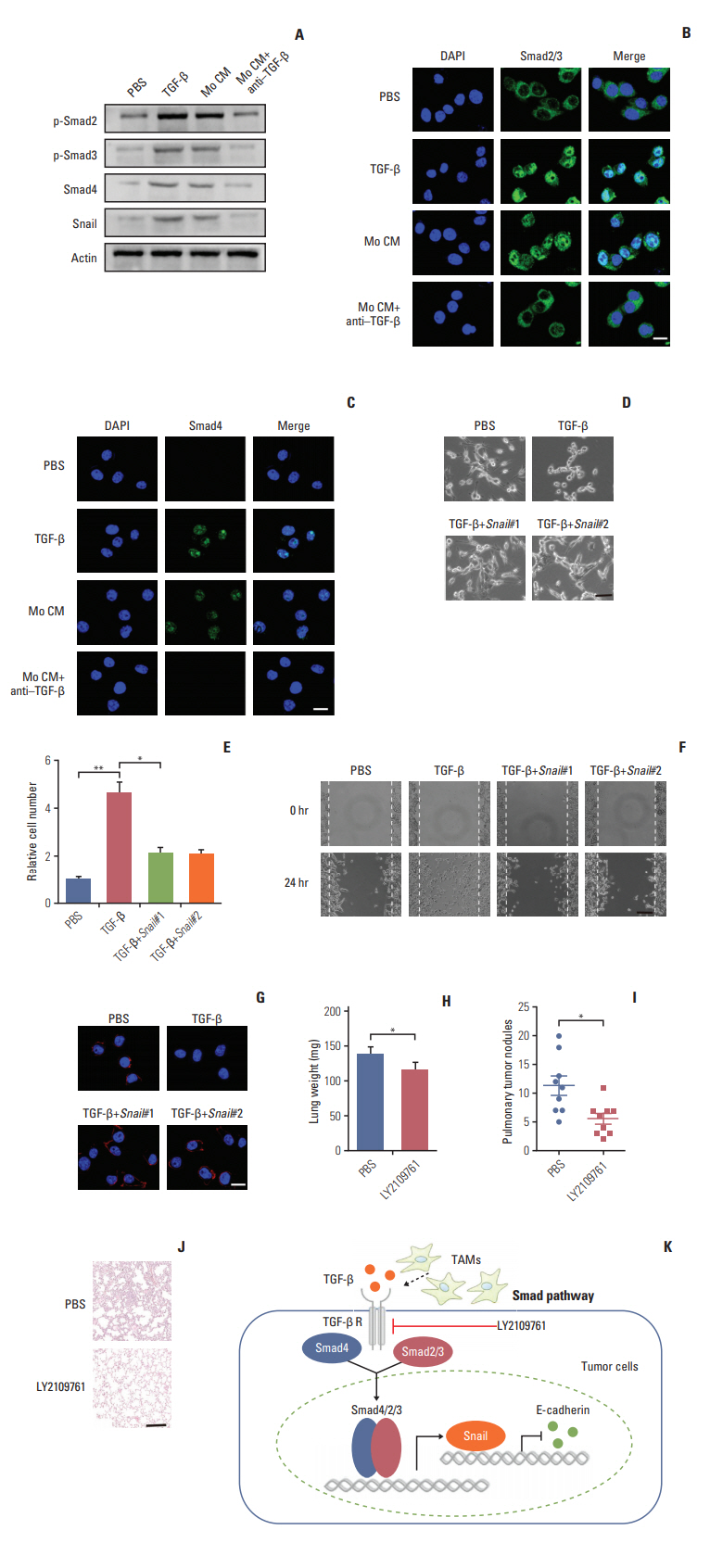
Here, we observed enrichment of TAMs in colorectal tumor tissues, resulting in high metastasis in clinical therapy. Moreover, those TAMs could facilitate the EMT progression of colorectal cancer cells, which is induced by the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) derived from TAMs, leading to the invasion and migration of cancer cells.
CONCLUSION
Our results demonstrated that TAMs contributed the EMT progression through a TGF-β/Smad2,3-4/Snail signaling pathway, and disrupting this pathway with TGF-β receptor inhibitor could suppress metastasis, readjusting our focus to the connection of TAMs and cancer metastasis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017; 67:7–30.
Article2. Kim IH, Lee JE, Yang JH, Jeong JW, Ro S, Oh ST, et al. Clinical significance of discordance between carcinoembryonic antigen levels and RECIST in metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2018; 50:283–92.
Article3. Loupakis F, Cremolini C, Masi G, Lonardi S, Zagonel V, Salvatore L, et al. Initial therapy with FOLFOXIRI and bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014; 371:1609–18.
Article4. O'Connell JB, Maggard MA, Ko CY. Colon cancer survival rates with the new American Joint Committee on Cancer sixth edition staging. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004; 96:1420–5.5. Simmonds PC, Primrose JN, Colquitt JL, Garden OJ, Poston GJ, Rees M. Surgical resection of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: a systematic review of published studies. Br J Cancer. 2006; 94:982–99.
Article6. Liu H, Radisky DC, Yang D, Xu R, Radisky ES, Bissell MJ, et al. MYC suppresses cancer metastasis by direct transcriptional silencing of alphav and beta3 integrin subunits. Nat Cell Biol. 2012; 14:567–74.7. Ma L, Young J, Prabhala H, Pan E, Mestdagh P, Muth D, et al. miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 2010; 12:247–56.
Article8. Tanaka H, Kono E, Tran CP, Miyazaki H, Yamashiro J, Shimomura T, et al. Monoclonal antibody targeting of N-cadherin inhibits prostate cancer growth, metastasis and castration resistance. Nat Med. 2010; 16:1414–20.
Article9. Yoo YA, Kang MH, Lee HJ, Kim BH, Park JK, Kim HK, et al. Sonic hedgehog pathway promotes metastasis and lymphangiogenesis via activation of Akt, EMT, and MMP-9 pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 2011; 71:7061–70.
Article10. Gilkes DM, Semenza GL, Wirtz D. Hypoxia and the extracellular matrix: drivers of tumour metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014; 14:430–9.
Article11. Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell. 2010; 141:52–67.
Article12. Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 2011; 331:1559–64.
Article13. Ye X, Brabletz T, Kang Y, Longmore GD, Nieto MA, Stanger BZ, et al. Upholding a role for EMT in breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2017; 547:E1–3.
Article14. Steidl C, Lee T, Shah SP, Farinha P, Han G, Nayar T, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages and survival in classic Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:875–85.
Article15. Franklin RA, Liao W, Sarkar A, Kim MV, Bivona MR, Liu K, et al. The cellular and molecular origin of tumor-associated macrophages. Science. 2014; 344:921–5.
Article16. Ye XZ, Xu SL, Xin YH, Yu SC, Ping YF, Chen L, et al. Tumorassociated microglia/macrophages enhance the invasion of glioma stem-like cells via TGF-beta1 signaling pathway. J Immunol. 2012; 189:444–53.17. Erreni M, Mantovani A, Allavena P. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) and inflammation in colorectal cancer. Cancer Microenviron. 2011; 4:141–54.
Article18. Ikushima H, Miyazono K. TGFbeta signalling: a complex web in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010; 10:415–24.19. Chaudhury A, Hussey GS, Ray PS, Jin G, Fox PL, Howe PH. TGF-beta-mediated phosphorylation of hnRNP E1 induces EMT via transcript-selective translational induction of Dab2 and ILEI. Nat Cell Biol. 2010; 12:286–93.20. Chen J, Yao Y, Gong C, Yu F, Su S, Chen J, et al. CCL18 from tumor-associated macrophages promotes breast cancer metastasis via PITPNM3. Cancer Cell. 2011; 19:541–55.
Article21. Sica A, Schioppa T, Mantovani A, Allavena P. Tumour-associated macrophages are a distinct M2 polarised population promoting tumour progression: potential targets of anti-cancer therapy. Eur J Cancer. 2006; 42:717–27.
Article22. Braun J, Hoang-Vu C, Dralle H, Huttelmaier S. Downregulation of microRNAs directs the EMT and invasive potential of anaplastic thyroid carcinomas. Oncogene. 2010; 29:4237–44.
Article23. Zhang H, Liu L, Wang Y, Zhao G, Xie R, Liu C, et al. KLF8 involves in TGF-beta-induced EMT and promotes invasion and migration in gastric cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013; 139:1033–42.
Article24. Padua D, Massague J. Roles of TGFbeta in metastasis. Cell Res. 2009; 19:89–102.25. Kudo-Saito C, Shirako H, Takeuchi T, Kawakami Y. Cancer metastasis is accelerated through immunosuppression during Snail-induced EMT of cancer cells. Cancer Cell. 2009; 15:195–206.
Article26. Mulholland DJ, Kobayashi N, Ruscetti M, Zhi A, Tran LM, Huang J, et al. Pten loss and RAS/MAPK activation cooperate to promote EMT and metastasis initiated from prostate cancer stem/progenitor cells. Cancer Res. 2012; 72:1878–89.
Article27. Feng XH, Derynck R. Specificity and versatility in tgf-beta signaling through Smads. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005; 21:659–93.28. Qian BZ. Inflammation fires up cancer metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2017; 47:170–6.
Article29. David CJ, Huang YH, Chen M, Su J, Zou Y, Bardeesy N, et al. TGF-beta tumor suppression through a lethal EMT. Cell. 2016; 164:1015–30.30. Seguin L, Desgrosellier JS, Weis SM, Cheresh DA. Integrins and cancer: regulators of cancer stemness, metastasis, and drug resistance. Trends Cell Biol. 2015; 25:234–40.
Article31. Qian BZ, Pollard JW. Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell. 2010; 141:39–51.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Trefoil Factor 1 Suppresses Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition through Inhibition of TGF-beta Signaling in Gastric Cancer Cells
- Parthenolide inhibits transforming growth factor β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cells
- Inhibitory Effects of Resveratrol on Airway Remodeling by Transforming Growth Factor-β/Smad Signaling Pathway in Chronic Asthma Model
- Inhibition of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Expression in Smoke-Exposed Alveolar Type II Epithelial Cells Attenuates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
- Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions of Bile Duct Epithelial Cells in Primary Hepatolithiasis