Cancer Res Treat.
2018 Apr;50(2):599-613. 10.4143/crt.2016.357.
Crizotinib in Combination with Everolimus Synergistically Inhibits Proliferation of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase‒Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. ssysmc@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2411148
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2016.357
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) is a rare aggresive non-Hodgkin lymphoma, of which over 50% of cases have an aberrant nucleophosmin (NPM)"’anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) fusion protein. Both mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor everolimus and ALK inhibitor crizotinib have shown promising antitumor activity in ALK-positive cancer cell lines. However, their combined effect has not yet been investigated.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We evaluated the anti-proliferative effects of everolimus and/or crizotinib in ALK-positive ALCL cell lines, Karpas 299 and SU-DHL-1, and lung adenocarcinoma cell line, NCI-H2228.
RESULTS
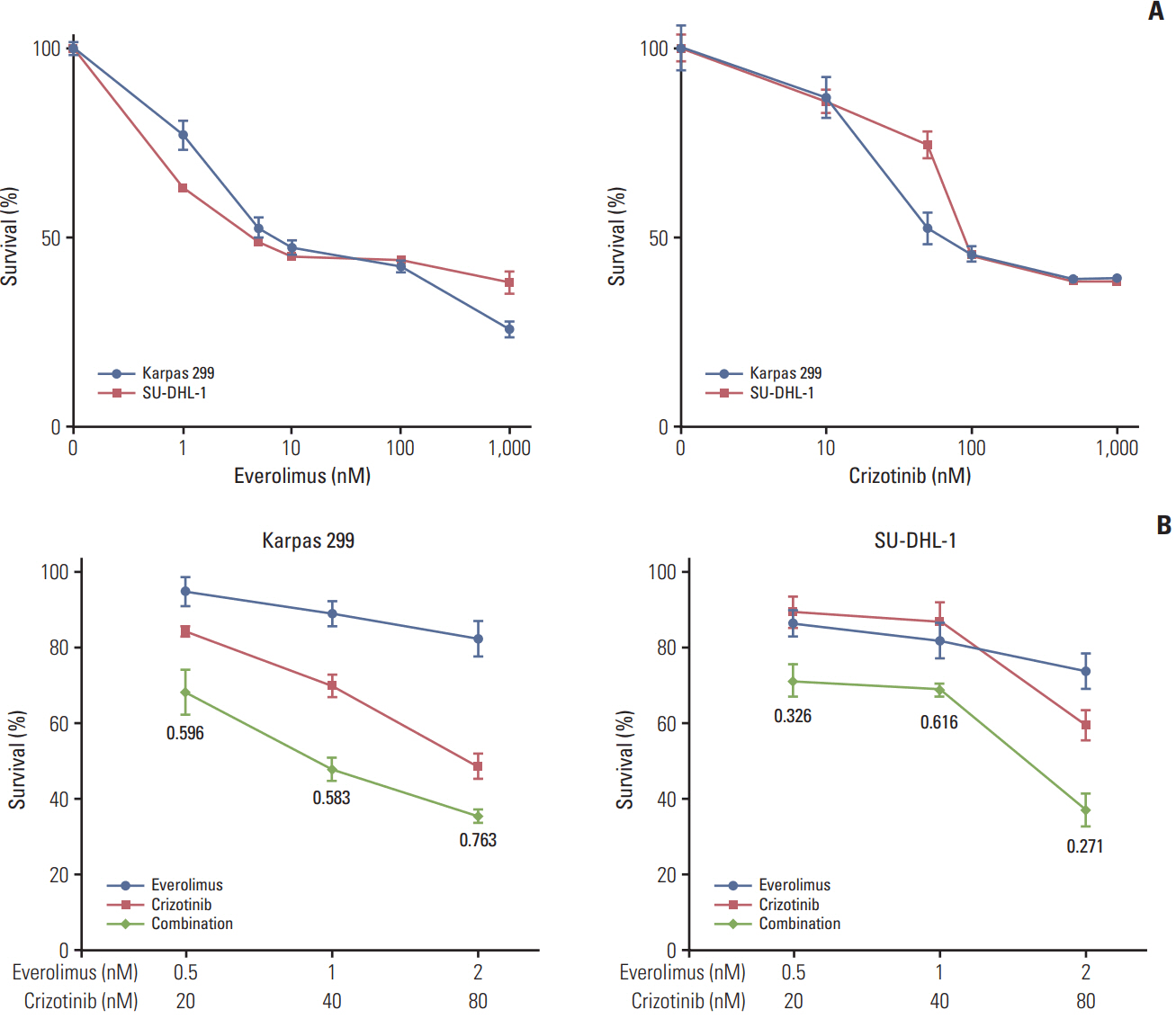
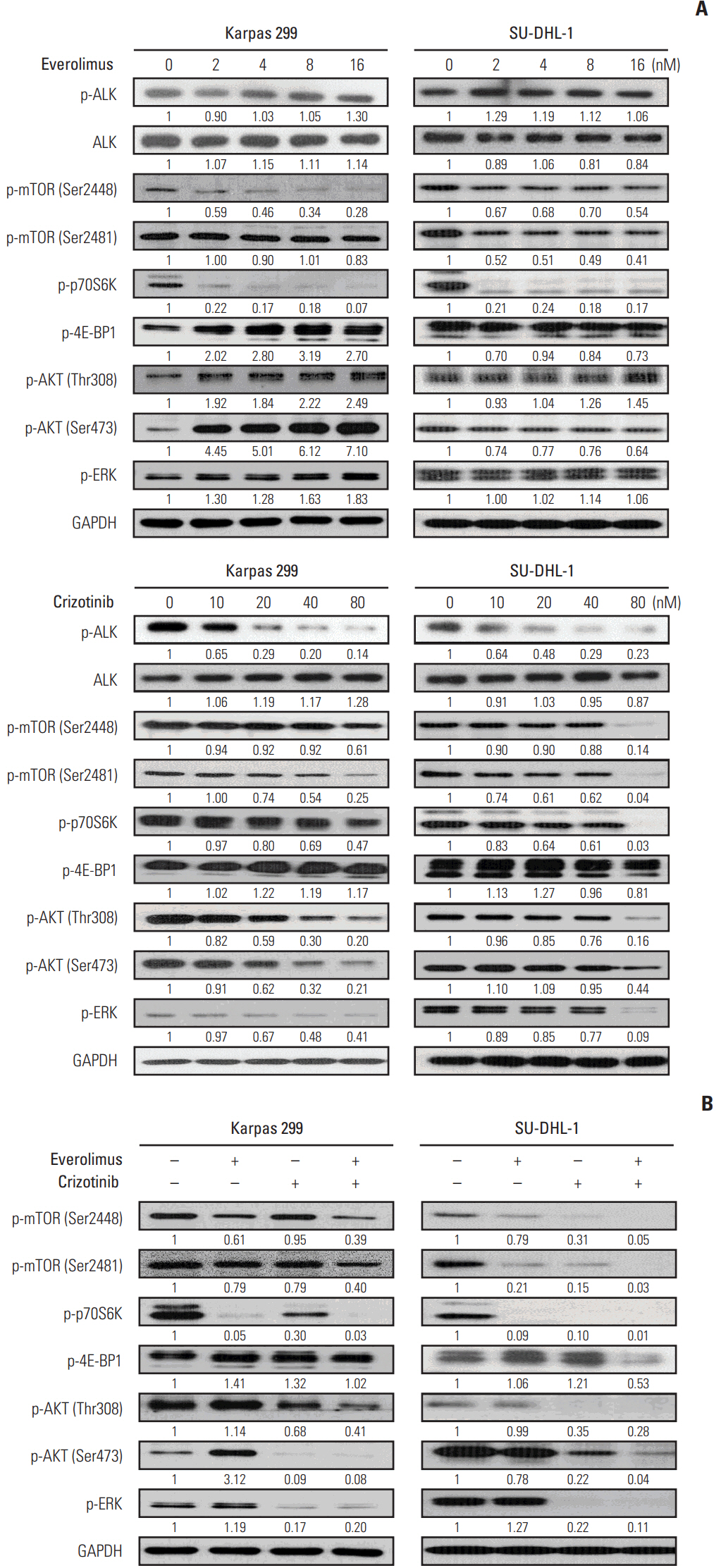
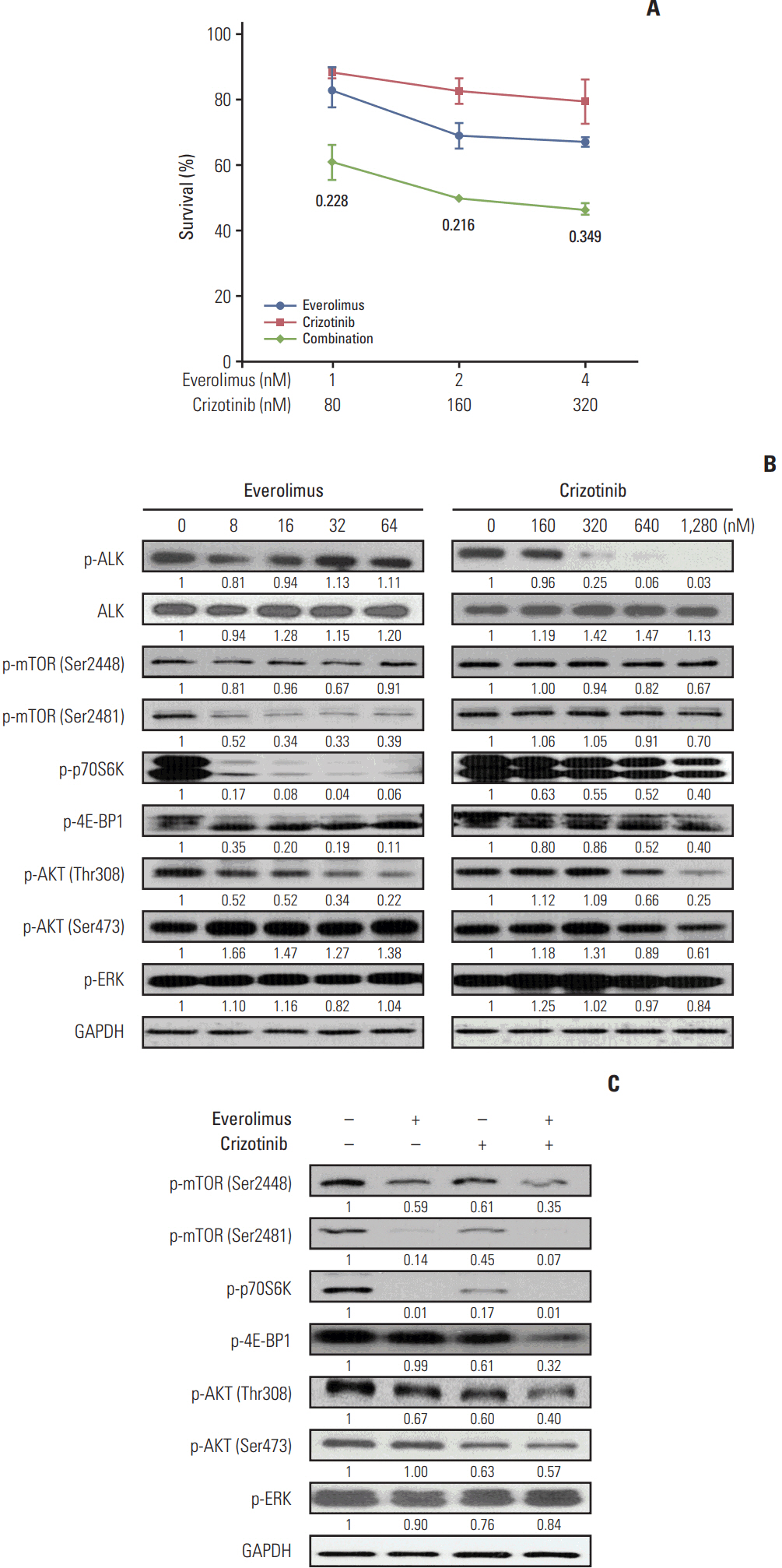
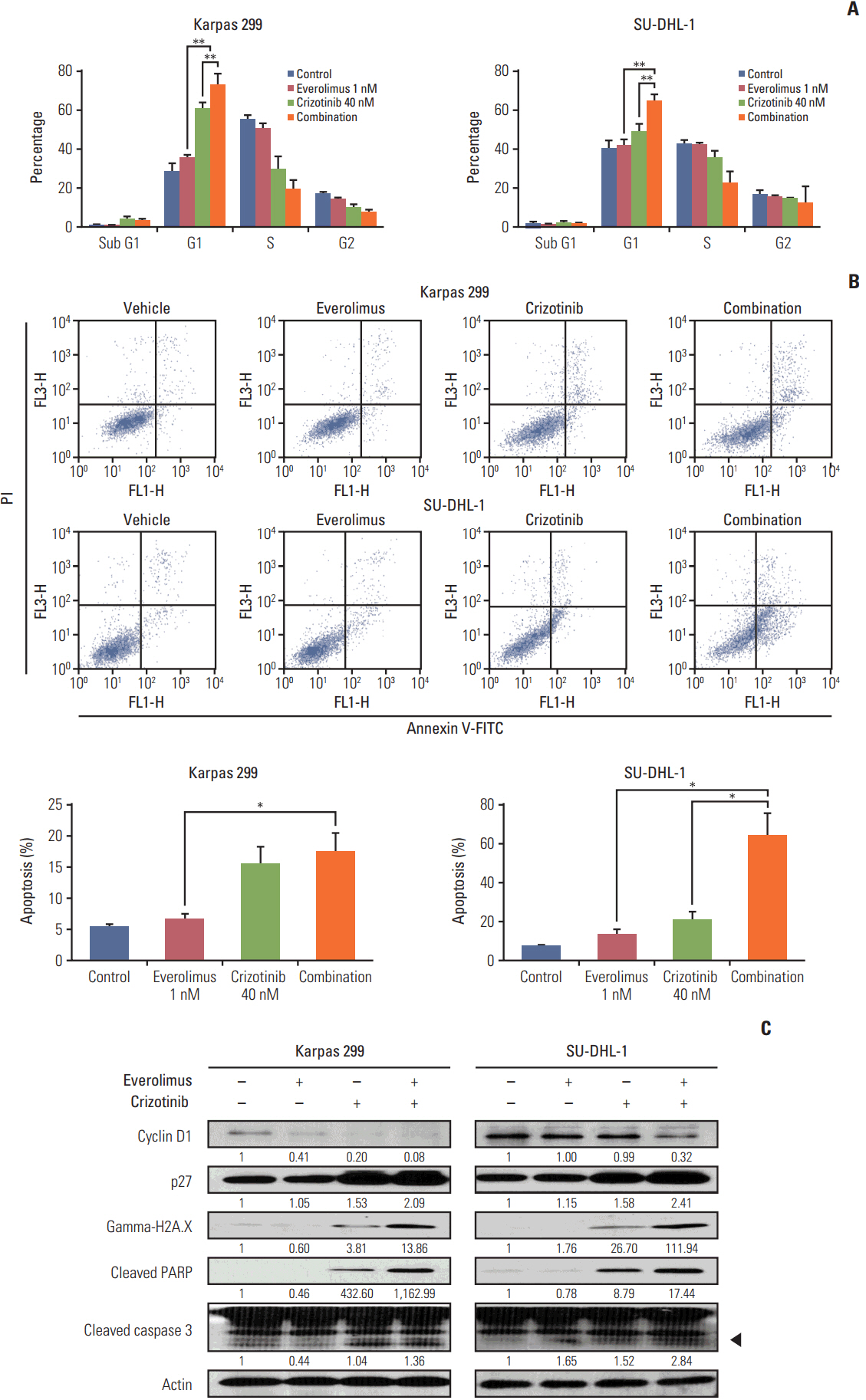
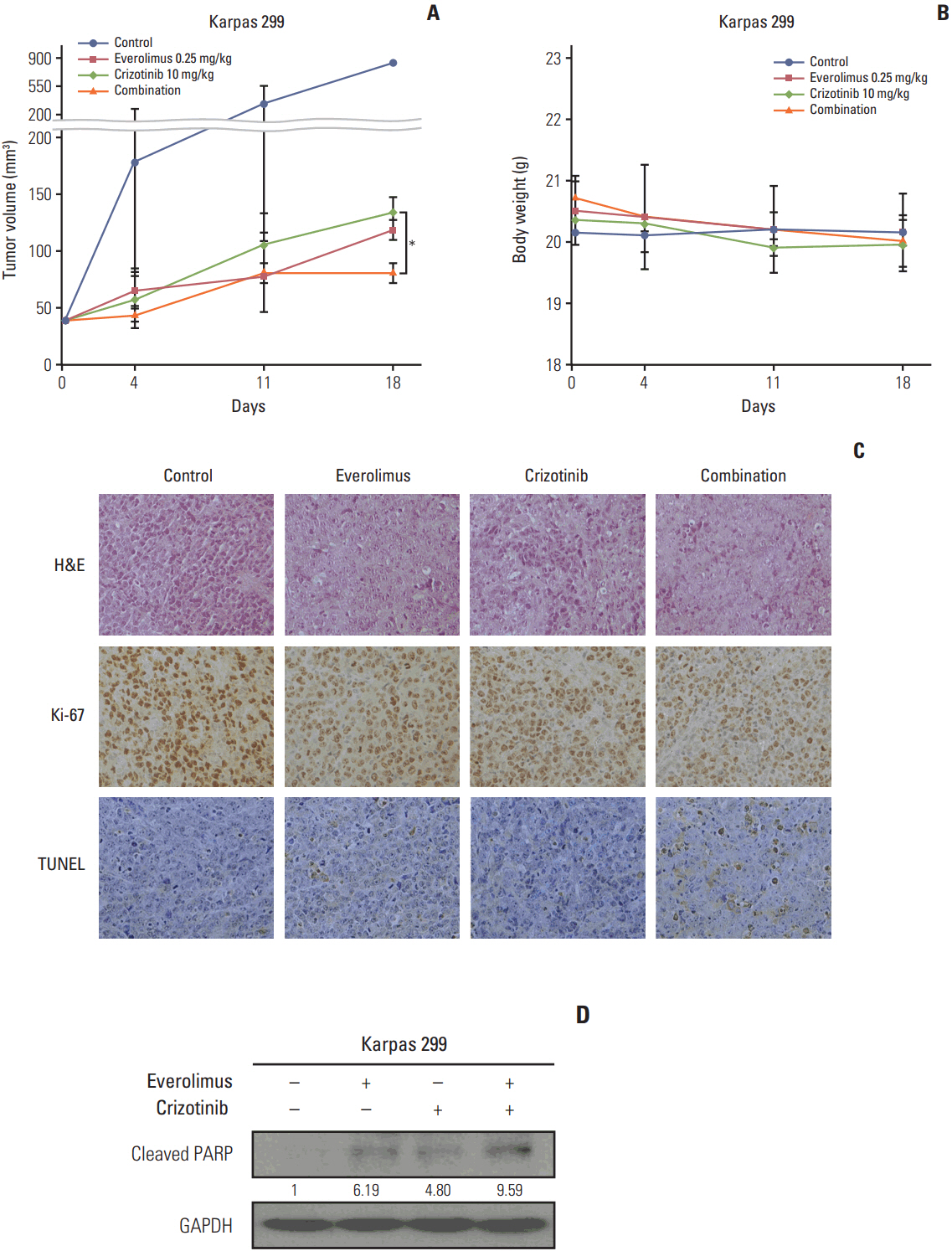
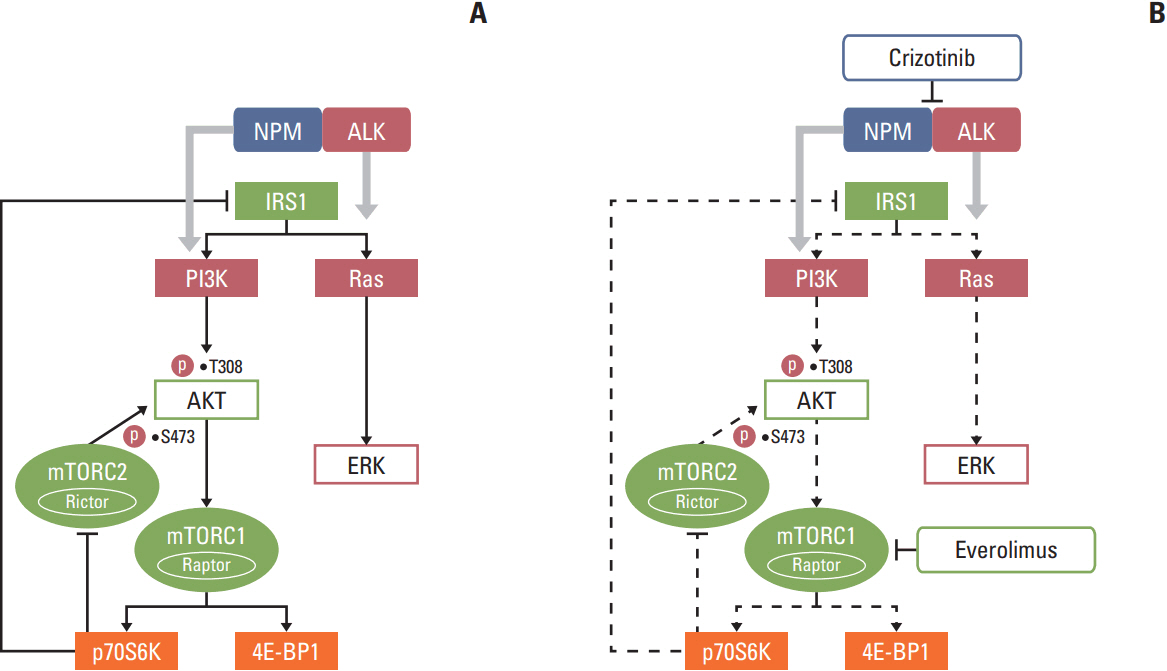
We found that individually, both everolimus and crizotinib potently inhibited cell growth in a dose-dependent manner in both Karpas 299 and SU-DHL-1 cells. A combination of these agents synergistically inhibited proliferation in the two cell lines. Crizotinib down-regulated aberrant AKT and ERK phosphorylation induced by everolimus. Combination treatment also significantly increased G0/G1 cell-cycle arrest, DNA damage, and apoptosis compared with everolimus or crizotinib alone in ALK-positive ALCL cells. In the Karpas 299 xenograft model, the combination treatment exerted a stronger antitumor effect than monotherapies, without significant change in body weight. The synergistic effect of everolimus and crizotinib was also reproduced in the ALK-positive lung adenocarcinoma cell line NCI-H2228. The combination treatment abrogated phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT and mTOR signaling pathways with little effect on the Ras/ERK pathway in NCI-H2228 cells.
CONCLUSION
Crizotinib combinedwith everolimus synergistically inhibits proliferation of ALK-positive ALCL cells. Our results suggest that this novel combination is worthy of further clinical development in patients with ALK-positive ALCL.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ferreri AJ, Govi S, Pileri SA, Savage KJ. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK-positive. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2012; 83:293–302.
Article2. Savage KJ, Harris NL, Vose JM, Ullrich F, Jaffe ES, Connors JM, et al. ALK- anaplastic large-cell lymphoma is clinically and immunophenotypically different from both ALK+ ALCL and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: report from the International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project. Blood. 2008; 111:5496–504.
Article3. Marzec M, Kasprzycka M, Liu X, Raghunath PN, Wlodarski P, Wasik MA. Oncogenic tyrosine kinase NPM/ALK induces activation of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway independently of c-Raf. Oncogene. 2007; 26:813–21.
Article4. Bai RY, Ouyang T, Miething C, Morris SW, Peschel C, Duyster J. Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase associated with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt antiapoptotic signaling pathway. Blood. 2000; 96:4319–27.
Article5. Hamedani FS, Cinar M, Mo Z, Cervania MA, Amin HM, Alkan S. Crizotinib (PF-2341066) induces apoptosis due to downregulation of pSTAT3 and BCL-2 family proteins in NPM-ALK(+) anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Leuk Res. 2014; 38:503–8.
Article6. Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, Seto T, Crino L, Ahn MJ, et al. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:2385–94.
Article7. Huang J, Manning BD. The TSC1-TSC2 complex: a molecular switchboard controlling cell growth. Biochem J. 2008; 412:179–90.
Article8. Vega F, Medeiros LJ, Leventaki V, Atwell C, Cho-Vega JH, Tian L, et al. Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway contributes to tumor cell survival in anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:6589–97.
Article9. Jundt F, Raetzel N, Muller C, Calkhoven CF, Kley K, Mathas S, et al. A rapamycin derivative (everolimus) controls proliferation through down-regulation of truncated CCAAT enhancer binding protein β and NF-κB activity in Hodgkin and anaplastic large cell lymphomas. Blood. 2005; 106:1801–7.
Article10. Witzig TE, Reeder CB, LaPlant BR, Gupta M, Johnston PB, Micallef IN, et al. A phase II trial of the oral mTOR inhibitor everolimus in relapsed aggressive lymphoma. Leukemia. 2011; 25:341–7.
Article11. Schatz JH. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in nonHodgkin's lymphoma: results, biology, and development strategies. Curr Oncol Rep. 2011; 13:398–406.
Article12. Berry T, Luther W, Bhatnagar N, Jamin Y, Poon E, Sanda T, et al. The ALK(F1174L) mutation potentiates the oncogenic activity of MYCN in neuroblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2012; 22:117–30.
Article13. Copp J, Manning G, Hunter T. TORC-specific phosphorylation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): phospho-Ser2481 is a marker for intact mTOR signaling complex 2. Cancer Res. 2009; 69:1821–7.
Article14. Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, et al. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science. 2004; 304:554.15. O'Reilly KE, Rojo F, She QB, Solit D, Mills GB, Smith D, et al. mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and activates Akt. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:1500–8.16. Julien LA, Carriere A, Moreau J, Roux PP. mTORC1-activated S6K1 phosphorylates Rictor on threonine 1135 and regulates mTORC2 signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 2010; 30:908–21.
Article17. Zhang H, Bajraszewski N, Wu E, Wang H, Moseman AP, Dabora SL, et al. PDGFRs are critical for PI3K/Akt activation and negatively regulated by mTOR. J Clin Invest. 2007; 117:730–8.
Article18. Carracedo A, Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Rojo F, Salmena L, Alimonti A, et al. Inhibition of mTORC1 leads to MAPK pathway activation through a PI3K-dependent feedback loop in human cancer. J Clin Invest. 2008; 118:3065–74.
Article19. Christensen JG, Zou HY, Arango ME, Li Q, Lee JH, McDonnell SR, et al. Cytoreductive antitumor activity of PF-2341066, a novel inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase and c-Met, in experimental models of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007; 6(12 Pt 1):3314–22.
Article20. Gambacorti-Passerini C, Messa C, Pogliani EM. Crizotinib in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:775–6.
Article21. Gambacorti Passerini C, Farina F, Stasia A, Redaelli S, Ceccon M, Mologni L, et al. Crizotinib in advanced, chemoresistant anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive lymphoma patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014; 106:djt378.
Article22. Megiorni F, McDowell HP, Camero S, Mannarino O, Ceccarelli S, Paiano M, et al. Crizotinib-induced antitumour activity in human alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma cells is not solely dependent on ALK and MET inhibition. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015; 34:112.
Article23. Xu ZZ, Wang WF, Fu WB, Wang AH, Liu ZY, Chen LY, et al. Combination of rituximab and mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor everolimus (RAD001) in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014; 55:1151–7.
Article24. Redaelli S, Ceccon M, Pirola A, Peronaci M, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Mologni L. Synergistic activity of ALK and mTOR inhibitors for the treatment of NPM-ALK positive lymphoma. Blood. 2015; 126:3710.
Article25. Choo AY, Yoon SO, Kim SG, Roux PP, Blenis J. Rapamycin differentially inhibits S6Ks and 4E-BP1 to mediate cell-type-specific repression of mRNA translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105:17414–9.
Article26. Sang J, Acquaviva J, Friedland JC, Smith DL, Sequeira M, Zhang C, et al. Targeted inhibition of the molecular chaperone Hsp90 overcomes ALK inhibitor resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2013; 3:430–43.
Article27. Ren H, Chen M, Yue P, Tao H, Owonikoko TK, Ramalingam SS, et al. The combination of RAD001 and NVP-BKM120 synergistically inhibits the growth of lung cancer in vitro and In vivo . Cancer Lett. 2012; 325:139–46.
Article28. Xu CX, Li Y, Yue P, Owonikoko TK, Ramalingam SS, Khuri FR, et al. The combination of RAD001 and NVP-BEZ235 exerts synergistic anticancer activity against non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and In vivo . PLoS One. 2011; 6:e20899.
Article29. Marzec M, Kasprzycka M, Liu X, El-Salem M, Halasa K, Raghunath PN, et al. Oncogenic tyrosine kinase NPM/ALK induces activation of the rapamycin-sensitive mTOR signaling pathway. Oncogene. 2007; 26:5606–14.
Article30. Roskoski R Jr. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK): structure, oncogenic activation, and pharmacological inhibition. Pharmacol Res. 2013; 68:68–94.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dermatofibroma in Patient with Relapsing Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
- Immunohistochemical Study for Ki-1 and EMA Antigens in Large Cell Lymphoma including Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
- CD30-Positive Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Negative Systemic Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma in a 9-Year-Old Boy
- Ki-I Lymphoma In a Young Adult
- A Case of ALK-Negative Systemic Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma