Asia Pac Allergy.
2017 Oct;7(4):206-212. 10.5415/apallergy.2017.7.4.206.
Comparison of nasal cytokine profiles of human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Asthma and Allergy Center, Department of Pediatrics, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul 01757, Korea. kimck@paik.ac.kr
- 2School of Biological Sciences, University of Ulsan, Ulsan 44610, Korea.
- 3Institute for Clinical Research, Mie National Hospital, Tsu 514-0125, Japan.
- KMID: 2410214
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2017.7.4.206
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) share some epidemiological and clinical characteristics; however, few studies have examined the mechanisms by which these viruses induce airway inflammation.
OBJECTIVE
This study was undertaken to compare cytokine profiles in hMPV and RSV patients to investigate possible differences in inflammatory pathways.
METHODS
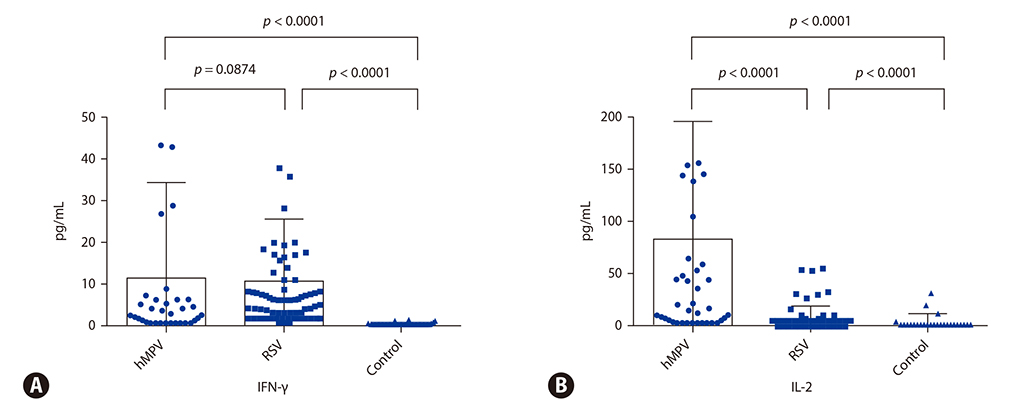
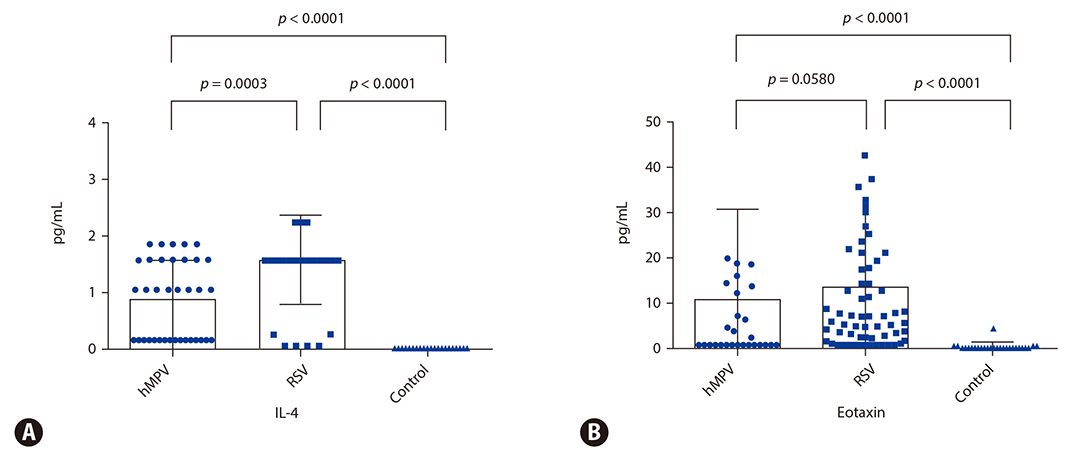
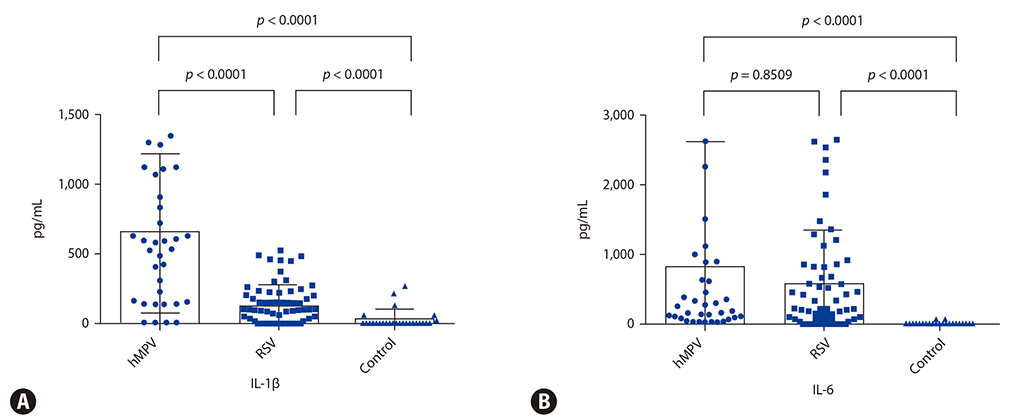
Nasopharyngeal aspirate specimens were collected from 1,008 pediatric patients hospitalized for acute lower respiratory tract infection with wheezing and 20 normal healthy controls. Patients were tested for 7 common respiratory viruses then divided into hMPV (n = 35) and RSV groups (n = 67). T helper (Th) 1 (interferon [IFN]-γ), Th2 (interleukin [IL]-4, eotaxin) and Th17 (IL-1β, IL-6) cytokine profiles were analyzed in the 3 groups.
RESULTS
IFN-γ and IL-2 levels were significantly increased in the hMPV and RSV groups compared to the control group (p < 0.0001 and p < 0.0001, respectively). IL-4 levels were significantly higher in the RSV group compared to the hMPV and control groups (p = 0.0003 and p < 0.0001, respectively). Eotaxin levels showed a tendency to be higher in the RSV group compared to the hMPV group (p = 0.0580), and significantly higher compared to the control group (p < 0.0001). IL-1β levels were significantly higher in the hMPV compared to the RSV group (p < 0.0001), and IL-6 levels were significantly higher in the hMPV group compared to the control group (p < 0.0001).
CONCLUSION
Our results suggest that hMPV and RSV have different inflammatory mechanisms. hMPV induces airway inflammation by the Th17 pathway through release of IL-1β and IL-6, whereas RSV acts through the Th2 pathway.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Autumn leaves: about aging and allergy
Yoon-Seok Chang
Asia Pac Allergy. 2017;7(4):183-184. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2017.7.4.183.
Reference
-
1. Peret TC, Boivin G, Li Y, Couillard M, Humphrey C, Osterhaus AD, Erdman DD, Anderson LJ. Characterization of human metapneumoviruses isolated from patients in North America. J Infect Dis. 2002; 185:1660–1663.
Article2. Jartti T, van den Hoogen B, Garofalo RP, Osterhaus AD, Ruuskanen O. Metapneumovirus and acute wheezing in children. Lancet. 2002; 360:1393–1394.
Article3. Glezen P, Denny FW. Epidemiology of acute lower respiratory disease in children. N Engl J Med. 1973; 288:498–505.
Article4. Sigurs N, Bjarnason R, Sigurbergsson F, Kjellman B. Respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis in infancy is an important risk factor for asthma and allergy at age 7. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 161:1501–1507.
Article5. Kim CK, Choi J, Callaway Z, Kim HB, Chung JY, Koh YY, Shin BM. Clinical and epidemiological comparison of human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus in seoul, Korea, 2003-2008. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:342–347.
Article6. van den Hoogen BG, de Jong JC, Groen J, Kuiken T, de Groot R, Fouchier RA, Osterhaus AD. A newly discovered human pneumovirus isolated from young children with respiratory tract disease. Nat Med. 2001; 7:719–724.
Article7. Asthma: a follow up statement from an international paediatric asthma consensus group. Arch Dis Child. 1992; 67:240–248.8. Barczyk A, Pierzchala W, Sozañska E. Interleukin-17 in sputum correlates with airway hyperresponsiveness to methacholine. Respir Med. 2003; 97:726–733.
Article9. Laan M, Cui ZH, Hoshino H, Lötvall J, Sjöstrand M, Gruenert DC, Skoogh BE, Lindén A. Neutrophil recruitment by human IL-17 via C-X-C chemokine release in the airways. J Immunol. 1999; 162:2347–2352.10. Doe C, Bafadhel M, Siddiqui S, Desai D, Mistry V, Rugman P, McCormick M, Woods J, May R, Sleeman MA, Anderson IK, Brightling CE. Expression of the T helper 17-associated cytokines IL-17A and IL-17F in asthma and COPD. Chest. 2010; 138:1140–1147.
Article11. McKinley L, Alcorn JF, Peterson A, Dupont RB, Kapadia S, Logar A, Henry A, Irvin CG, Piganelli JD, Ray A, Kolls JK. TH17 cells mediate steroid-resistant airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in mice. J Immunol. 2008; 181:4089–4097.
Article12. Esnault S, Kelly EA, Nettenstrom LM, Cook EB, Seroogy CM, Jarjour NN. Human eosinophils release IL-1β and increase expression of IL-17A in activated CD4+ T lymphocytes. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012; 42:1756–1764.13. Rathinam VA, Vanaja SK, Fitzgerald KA. Regulation of inflammasome signaling. Nat Immunol. 2012; 13:333–342.
Article14. Malmo J, Moe N, Krokstad S, Ryan L, Loevenich S, Johnsen IB, Espevik T, Nordbø SA, Døllner H, Anthonsen MW. Cytokine profiles in human metapneumovirus infected children: identification of genes involved in the antiviral response and pathogenesis. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0155484.
Article15. Laham FR, Israele V, Casellas JM, Garcia AM, Lac Prugent CM, Hoffman SJ, Hauer D, Thumar B, Name MI, Pascual A, Taratutto N, Ishida MT, Balduzzi M, Maccarone M, Jackli S, Passarino R, Gaivironsky RA, Karron RA, Polack NR, Polack FP. Differential production of inflammatory cytokines in primary infection with human metapneumovirus and with other common respiratory viruses of infancy. J Infect Dis. 2004; 189:2047–2056.
Article16. Cheemarla NR, Guerrero-Plata A. Immune response to human metapneumovirus infection: what we have learned from the mouse model. Pathogens. 2015; 4:682–696.
Article17. Guerrero-Plata A, Casola A, Suarez G, Yu X, Spetch L, Peeples ME, Garofalo RP. Differential response of dendritic cells to human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006; 34:320–329.
Article18. Guerrero-Plata A, Casola A, Garofalo RP. Human metapneumovirus induces a profile of lung cytokines distinct from that of respiratory syncytial virus. J Virol. 2005; 79:14992–14997.
Article19. Mukherjee S, Lindell DM, Berlin AA, Morris SB, Shanley TP, Hershenson MB, Lukacs NW. IL-17-induced pulmonary pathogenesis during respiratory viral infection and exacerbation of allergic disease. Am J Pathol. 2011; 179:248–258.
Article20. Stoppelenburg AJ, Salimi V, Hennus M, Plantinga M, Huis in, Walk J, Meerding J, Coenjaerts F, Bont L, Boes M. Local IL-17A potentiates early neutrophil recruitment to the respiratory tract during severe RSV infection. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e78461.
Article21. Molet S, Hamid Q, Davoine F, Nutku E, Taha R, Pagé N, Olivenstein R, Elias J, Chakir J. IL-17 is increased in asthmatic airways and induces human bronchial fibroblasts to produce cytokines. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:430–438.
Article22. Cosmi L, Maggi L, Santarlasci V, Capone M, Cardilicchia E, Frosali F, Querci V, Angeli R, Matucci A, Fambrini M, Liotta F, Parronchi P, Maggi E, Romagnani S, Annunziato F. Identification of a novel subset of human circulating memory CD4(+) T cells that produce both IL-17A and IL-4. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:222–230. 230.e1–230.e4.
Article23. Sly PD, Boner AL, Björksten B, Bush A, Custovic A, Eigenmann PA, Gern JE, Gerritsen J, Hamelmann E, Helms PJ, Lemanske RF, Martinez F, Pedersen S, Renz H, Sampson H, von Mutius E, Wahn U, Holt PG. Early identification of atopy in the prediction of persistent asthma in children. Lancet. 2008; 372:1100–1106.
Article24. Kim CK, Chung CY, Choi SJ, Kim DK, Park Y, Koh YY. Bronchoalveolar lavage cellular composition in acute asthma and acute bronchiolitis. J Pediatr. 2000; 137:517–522.
Article25. Kim CK, Kim SW, Park CS, Kim BI, Kang H, Koh YY. Bronchoalveolar lavage cytokine profiles in acute asthma and acute bronchiolitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 112:64–71.
Article26. Pifferi M, Ragazzo V, Caramella D, Baldini G. Eosinophil cationic protein in infants with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis: predictive value for subsequent development of persistent wheezing. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2001; 31:419–424.
Article27. Pringle EJ, Richardson HB, Miller D, Cornish DS, Devereux GS, Walsh GM, Turner SW. Nasal and bronchial airway epithelial cell mediator release in children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2012; 47:1215–1225.
Article28. McDougall CM, Blaylock MG, Douglas JG, Brooker RJ, Helms PJ, Walsh GM. Nasal epithelial cells as surrogates for bronchial epithelial cells in airway inflammation studies. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008; 39:560–568.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Features of Human Metapneumovirus and Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Hospitalized Children
- Detection of Respiratory Viruses and Atypical Bacterial Pathogens in Infants with Acute Respiratory Infections Using Multiplex PCR
- A Case of Severe Human Metapneumovirus Pneumonia Requiring Mechanical Ventilation in an Immunocompetent Adult
- Acute Myopericarditis caused by Human Metapneumovirus
- Recovery of respiratory syncytial virus, adenovirus, influenza virus , and parainfluenza virus from nasopharyngeal aspirates from children with acute respiratory tract infections