Cancer Res Treat.
2017 Oct;49(4):947-959. 10.4143/crt.2016.280.
Upregulation of MicroRNA-1246 Is Associated with BRAF Inhibitor Resistance in Melanoma Cells with Mutant BRAF
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Life Sciences, College of Life Sciences and Bioengineering, Incheon National University, Incheon, Korea. mikelee@inu.ac.kr
- 2Genome Structure Research Center, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2394814
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2016.280
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Intrinsic and acquired resistance limit the therapeutic benefits of inhibitors of oncogenic BRAF in melanoma. To identify microRNAs (miRNAs) associated with resistance to a BRAF inhibitor, we compared miRNA expression levels in three cell lines with different BRAF inhibitor sensitivity.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
miRNA microarray analysis was conducted to compare miRNA expression levels. Real-time quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed to confirm the expression of differentially expressed miRNAs. The cellular effects of miR-1246 were further examined by MTT assay, immunoblotting analysis, cell cycle analysis, flow cytometric assay of apoptosis, and autophagy assay.
RESULTS
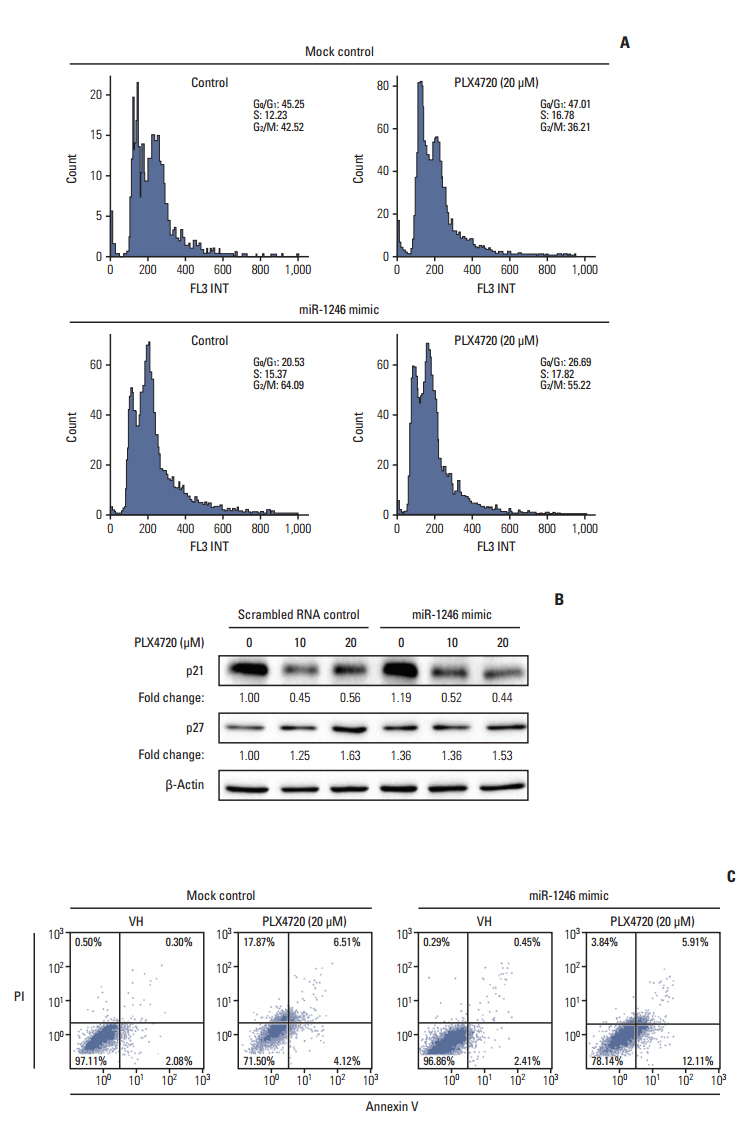
The miRNA microarray analysis and qRT-PCR identified five miRNAs (miR-3617, miR-92a-1, miR-1246, miR-193b-3p, and miR-17-3p) with expression that was consistently altered in two BRAF inhibitor-resistant cell lines. Among the five miRNAs, a miR-1246 mimic significantly reduced the antiproliferative effects of the BRAF inhibitor PLX4720 in BRAF inhibitor-resistant A375P (A375P/Mdr) cells, suggesting that miR-1246 upregulation confers acquired resistance to BRAF inhibition. In particular, apoptosis was identified as a major type of cell death in miR-1246-transfected cells; however, necrosis predominated in mimic-control-transfected cells, indicating that the resistance to PLX4720 in miR-1246 mimic-transfected cells is predominantly due to a reduction in necrosis. Furthermore, we found that miR-1246 promoted G2/M arrest through autophagy as a way to escape cell death by necrosis and apoptosis in response to PLX4720. The promotion of BRAF inhibitor resistance by miR-1246 was associated with lowered levels of p-ERK.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that miR-1246 may be a potential therapeutic target in melanoma with acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002; 417:949–54.
Article2. Holderfield M, Deuker MM, McCormick F, McMahon M. Targeting RAF kinases for cancer therapy: BRAF-mutated melanoma and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014; 14:455–67.
Article3. Kim YK, Ahn SK, Lee M. Differential sensitivity of melanoma cell lines with differing B-Raf mutational status to the new oncogenic B-Raf kinase inhibitor UI-152. Cancer Lett. 2012; 320:215–24.
Article4. Rizos H, Menzies AM, Pupo GM, Carlino MS, Fung C, Hyman J, et al. BRAF inhibitor resistance mechanisms in metastatic melanoma: spectrum and clinical impact. Clin Cancer Res. 2014; 20:1965–77.
Article5. Johannessen CM, Boehm JS, Kim SY, Thomas SR, Wardwell L, Johnson LA, et al. COT drives resistance to RAF inhibition through MAP kinase pathway reactivation. Nature. 2010; 468:968–72.6. Ahn JH, Han BI, Lee M. Induction of resistance to BRAF inhibitor is associated with the inability of Spry2 to inhibit BRAF-V600E activity in BRAF mutant cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2015; 23:320–6.
Article7. Chandarlapaty S. Negative feedback and adaptive resistance to the targeted therapy of cancer. Cancer Discov. 2012; 2:311–9.
Article8. Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004; 116:281–97.9. Ma J, Dong C, Ji C. MicroRNA and drug resistance. Cancer Gene Ther. 2010; 17:523–31.
Article10. Pinto R, Strippoli S, De Summa S, Albano A, Azzariti A, Guida G, et al. MicroRNA expression in BRAF-mutated and wildtype metastatic melanoma and its correlation with response duration to BRAF inhibitors. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015; 19:1027–35.
Article11. Stark MS, Bonazzi VF, Boyle GM, Palmer JM, Symmons J, Lanagan CM, et al. miR-514a regulates the tumour suppressor NF1 and modulates BRAFi sensitivity in melanoma. Oncotarget. 2015; 6:17753–63.
Article12. Ahn JH, Lee M. Autophagy-dependent survival of mutant B-Raf melanoma cells selected for resistance to apoptosis induced by inhibitors against oncogenic B-Raf. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2013; 21:114–20.
Article13. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001; 25:402–8.14. Oeste CL, Seco E, Patton WF, Boya P, Perez-Sala D. Interactions between autophagic and endo-lysosomal markers in endothelial cells. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013; 139:659–70.
Article15. Jang GH, Kim NY, Lee M. Low inducible expression of p21Cip1 confers resistance to paclitaxel in BRAF mutant melanoma cells with acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitor. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015; 406:53–62.
Article16. Ahn JH, Lee YW, Ahn SK, Lee M. Oncogenic BRAF inhibitor UAI-201 induces cell cycle arrest and autophagy in BRAF mutant glioma cells. Life Sci. 2014; 104:38–46.
Article17. Lee JS, Lee GM. Monitoring of autophagy in Chinese hamster ovary cells using flow cytometry. Methods. 2012; 56:375–82.
Article18. Segura MF, Greenwald HS, Hanniford D, Osman I, Hernando E. MicroRNA and cutaneous melanoma: from discovery to prognosis and therapy. Carcinogenesis. 2012; 33:1823–32.
Article19. Mishra RR, Kneitz S, Schartl M. Comparative analysis of melanoma deregulated miRNAs in the medaka and Xiphophorus pigment cell cancer models. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2014; 163:64–76.
Article20. Zhu J, Dong H, Zhang Q, Zhang S. Combined assays for serum carcinoembryonic antigen and microRNA-17-3p offer improved diagnostic potential for stage I/II colon cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 2015; 3:1315–8.
Article21. Bar M, Wyman SK, Fritz BR, Qi J, Garg KS, Parkin RK, et al. MicroRNA discovery and profiling in human embryonic stem cells by deep sequencing of small RNA libraries. Stem Cells. 2008; 26:2496–505.
Article22. Zhang Q, Cao LY, Cheng SJ, Zhang AM, Jin XS, Li Y. p53-induced microRNA-1246 inhibits the cell growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting NFIB. Oncol Rep. 2015; 33:1335–41.
Article23. Sun Z, Meng C, Wang S, Zhou N, Guan M, Bai C, et al. MicroRNA-1246 enhances migration and invasion through CADM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2014; 14:616.
Article24. Huang W, Li H, Luo R. The microRNA-1246 promotes metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding protein 4. Diagn Pathol. 2015; 10:127.
Article25. Chen J, Yao D, Zhao S, He C, Ding N, Li L, et al. MiR-1246 promotes SiHa cervical cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration through suppression of its target gene thrombospondin 2. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014; 290:725–32.
Article26. Hasegawa S, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Konno M, Tomimaru Y, Wada H, et al. MicroRNA-1246 expression associated with CCNG2-mediated chemoresistance and stemness in pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 2014; 111:1572–80.
Article27. Zhang Y, Liao JM, Zeng SX, Lu H. p53 downregulates Down syndrome-associated DYRK1A through miR-1246. EMBO Rep. 2011; 12:811–7.
Article28. Eisenberg-Lerner A, Bialik S, Simon HU, Kimchi A. Life and death partners: apoptosis, autophagy and the cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ. 2009; 16:966–75.
Article29. Kawabe T. G2 checkpoint abrogators as anticancer drugs. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004; 3:513–9.30. Roskoski R Jr. MEK1/2 dual-specificity protein kinases: structure and regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012; 417:5–10.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Induction of Resistance to BRAF Inhibitor Is Associated with the Inability of Spry2 to Inhibit BRAF-V600E Activity in BRAF Mutant Cells
- Differential Sensitivity of Wild-Type and BRAF-Mutated Cells to Combined BRAF and Autophagy Inhibition
- Targeting BRAF pathway in low-grade serous ovarian cancer
- Differential Gene Expression Common to Acquired and Intrinsic Resistance to BRAF Inhibitor Revealed by RNA-Seq Analysis
- Sensitivity and Usefulness of VE1 Immunohistochemical Staining in Acral Melanomas with BRAF Mutation