Immune Netw.
2014 Oct;14(5):241-248. 10.4110/in.2014.14.5.241.
5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide Riboside Induces Apoptosis Through AMP-activated Protein Kinase-independent and NADPH Oxidase-dependent Pathways
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Molecular Cell Biology and Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon 440-746, Korea. thylee@skku.edu
- KMID: 2391720
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2014.14.5.241
Abstract
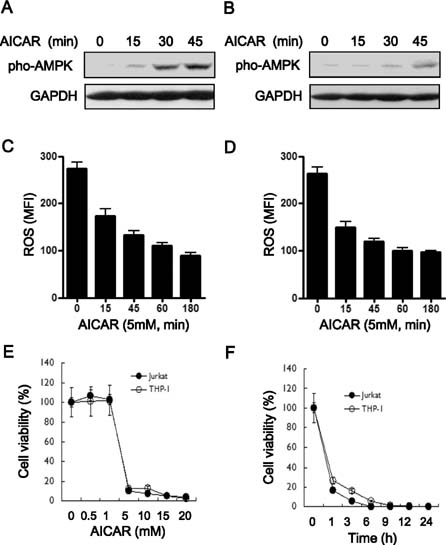
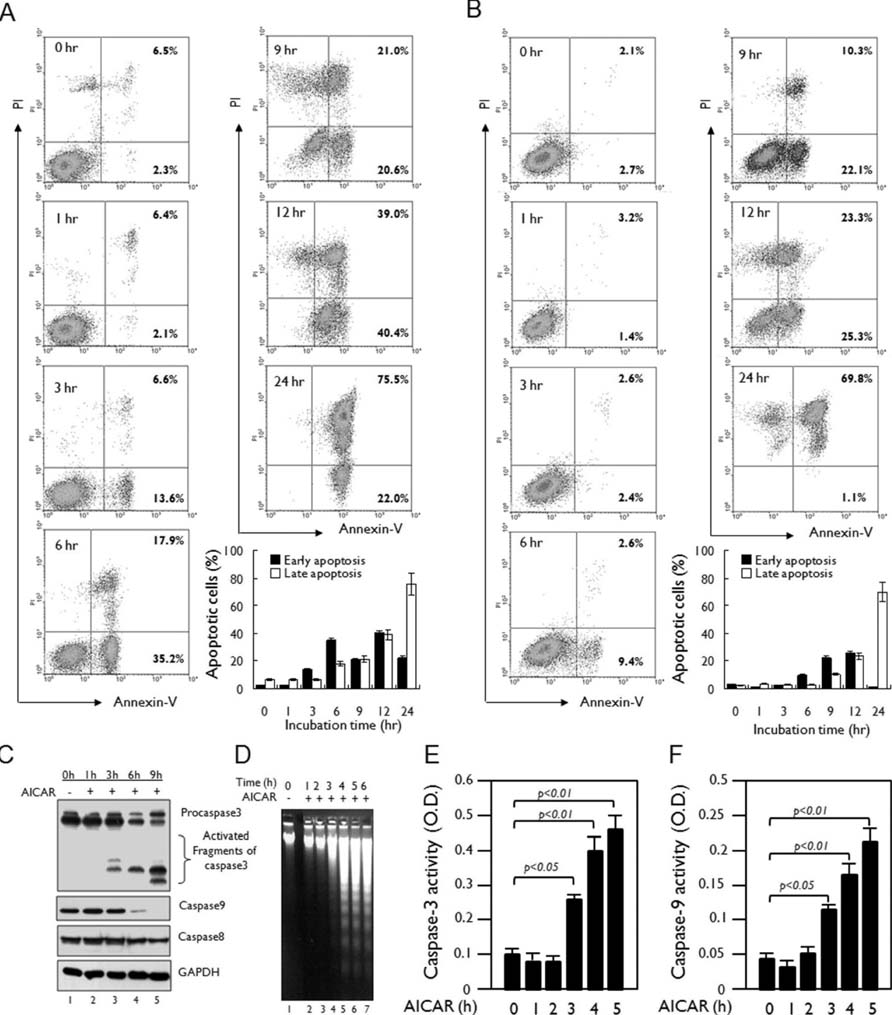
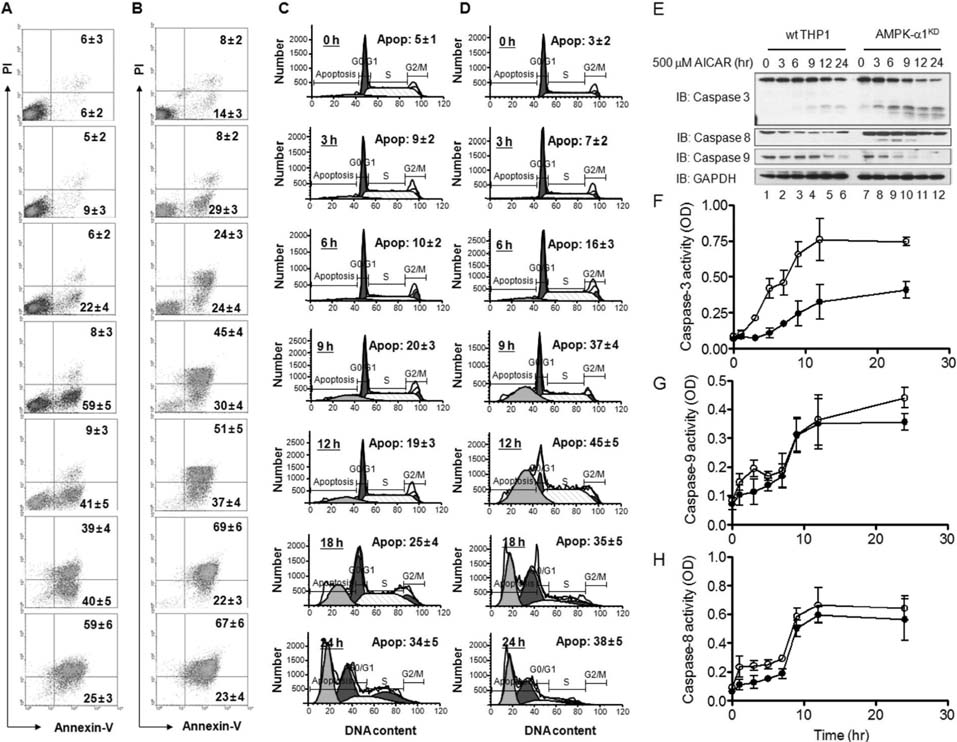
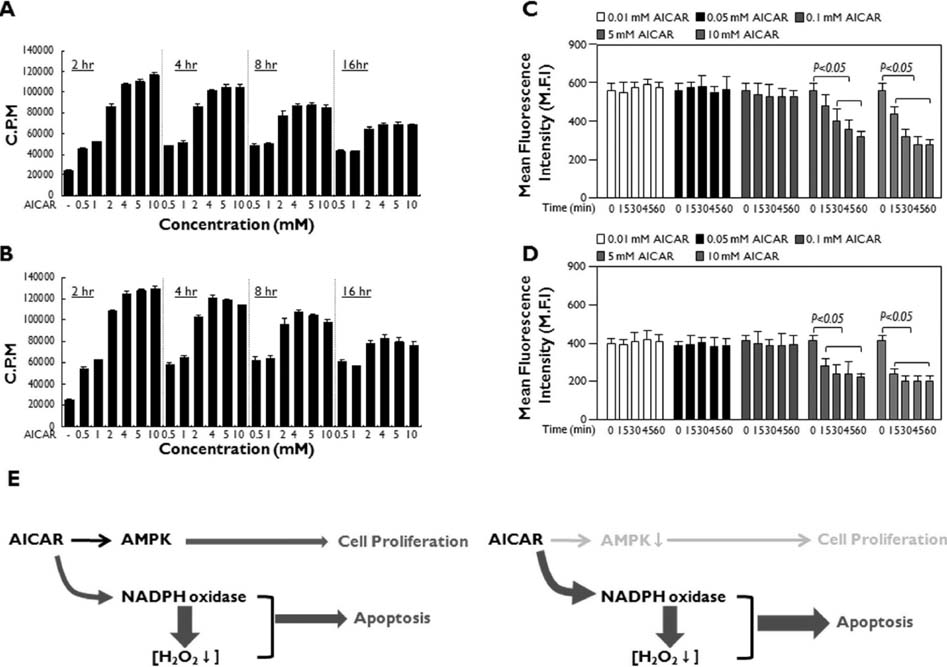
- It is debatable whether AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation is involved in anti-apoptotic or pro-apoptotic signaling. AICAR treatment increases AMPK-alpha1 phosphorylation, decreases intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, and significantly increases Annexin V-positive cells, DNA laddering, and caspase activity in human myeloid cell. AMPK activation is therefore implicated in apoptosis. However, AMPK-alpha1-knockdown THP-1 cells are more sensitive to apoptosis than control THP-1 cells are, suggesting that the apoptosis is AMPK-independent. Low doses of AICAR induce cell proliferation, whereas high doses of AICAR suppress cell proliferation. Moreover, these effects are significantly correlated with the downregulation of intracellular ROS, strongly suggesting that AICAR-induced apoptosis is critically associated with the inhibition of NADPH oxidase by AICAR. Collectively, our results demonstrate that in AICAR-induced apoptosis, intracellular ROS levels are far more relevant than AMPK activation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Peroxiredoxin-3 Is Involved in Bactericidal Activity through the Regulation of Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species
Sena Lee, Sae Mi Wi, Yoon Min, Ki-Young Lee
Immune Netw. 2016;16(6):373-380. doi: 10.4110/in.2016.16.6.373.4-(Tert-butyl)-2,6-bis(1-phenylethyl)phenol induces pro-apoptotic activity
Jun Ho Kim, Yunmi Lee, Mi-Yeon Kim, Jae Youl Cho
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016;20(3):253-259. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.3.253.
Reference
-
1. Hardie DG, Carling D, Carlson M. The AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinase subfamily: metabolic sensors of the eukaryotic cell? Annu Rev Biochem. 1998; 67:821–855.
Article2. Kemp BE, Mitchelhill KI, Stapleton D, Michell BJ, Chen ZP, Witters LA. Dealing with energy demand: the AMP-activated protein kinase. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999; 24:22–25.
Article3. Hardie DG, Carling D. The AMP-activated protein kinase-fuel gauge of the mammalian cell? Eur J Biochem. 1997; 246:259–273.
Article4. Corton JM, Gillespie JG, Hawley SA, Hardie DG. 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleoside. A specific method for activating AMP-activated protein kinase in intact cells? Eur J Biochem. 1995; 229:558–565.
Article5. Garcia-Gil M, Pesi R, Perna S, Allegrini S, Giannecchini M, Camici M, Tozzi MG. 5'-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside induces apoptosis in human neuroblastoma cells. Neuroscience. 2003; 117:811–820.
Article6. Thomas CB, Meade JC, Holmes EW. Aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleoside toxicity: a model for study of pyrimidine starvation. J Cell Physiol. 1981; 107:335–344.
Article7. Sabina RL, Patterson D, Holmes EW. 5-Amino-4-imidazolecarboxamide riboside (Zriboside) metabolism in eukaryotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1985; 260:6107–6114.
Article8. Swain JL, Hines JJ, Sabina RL, Holmes EW. Accelerated repletion of ATP and GTP pools in postischemic canine myocardium using a precursor of purine de novo synthesis. Circ Res. 1982; 51:102–105.
Article9. Swain JL, Hines JJ, Sabina RL, Harbury OL, Holmes EW. Disruption of the purine nucleotide cycle by inhibition of adenylosuccinate lyase produces skeletal muscle dysfunction. J Clin Invest. 1984; 74:1422–1427.
Article10. Nath N, Giri S, Prasad R, Salem ML, Singh AK, Singh I. 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleoside: a novel immunomodulator with therapeutic efficacy in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2005; 175:566–574.
Article11. Alba G, El Bekay R, Alvarez-Maqueda M, Chacon P, Vega A, Monteseirin J, Santa Maria C, Pintado E, Bedoya FJ, Bartrons R, Sobrino F. Stimulators of AMP-activated protein kinase inhibit the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 2004; 573:219–225.
Article12. Stone JR, Yang S. Hydrogen peroxide: a signaling messenger. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006; 8:243–270.
Article13. Immenschuh S, Baumgart-Vogt E. Peroxiredoxins, oxidative stress, and cell proliferation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005; 7:768–777.
Article14. Gechev TS, Hille J. Hydrogen peroxide as a signal controlling plant programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 2005; 168:17–20.
Article15. Saito Y, Nishio K, Ogawa Y, Kimata J, Kinumi T, Yoshida Y, Noguchi N, Niki E. Turning point in apoptosis/necrosis induced by hydrogen peroxide. Free Radic Res. 2006; 40:619–630.
Article16. Rhee SG, Bae YS, Lee SR, Kwon J. Hydrogen peroxide: a key messenger that modulates protein phosphorylation through cysteine oxidation. Sci STKE. 2000; (53):PE1.
Article17. Lambeth JD. NOX enzymes and the biology of reactive oxygen. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004; 4:181–189.
Article18. Davies KJ. The broad spectrum of responses to oxidants in proliferating cells: a new paradigm for oxidative stress. IUBMB Life. 1999; 48:41–47.
Article19. Hampton MB, Orrenius S. Dual regulation of caspase activity by hydrogen peroxide: implications for apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 1997; 414:552–556.
Article20. Kefas BA, Cai Y, Ling Z, Heimberg H, Hue L, Pipeleers D, Van de Casteele M. AMP-activated protein kinase can induce apoptosis of insulin-producing MIN6 cells through stimulation of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase. J Mol Endocrinol. 2003; 30:151–161.
Article21. Meisse D, Van de Casteele M, Beauloye C, Hainault I, Kefas BA, Rider MH, Foufelle F, Hue L. Sustained activation of AMP-activated protein kinase induces c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation and apoptosis in liver cells. FEBS Lett. 2002; 526:38–42.
Article22. Busch C, Jacob C, Anwar A, Burkholz T, Aicha Ba L, Cerella C, Diederich M, Brandt W, Wessjohann L, Montenarh M. Diallylpolysulfides induce growth arrest and apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 2010; 36:743–749.
Article23. Li N, Ragheb K, Lawler G, Sturgis J, Rajwa B, Melendez JA, Robinson JP. DPI induces mitochondrial superoxide-mediated apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003; 34:465–477.
Article24. Yasmeen A, Beauchamp MC, Piura E, Segal E, Pollak M, Gotlieb WH. Induction of apoptosis by metformin in epithelial ovarian cancer: involvement of the Bcl-2 family proteins. Gynecol Oncol. 2011; 121:492–498.
Article25. Liu C, Liang B, Wang Q, Wu J, Zou MH. Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha1 alleviates endothelial cell apoptosis by increasing the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and survivin. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285:15346–15355.
Article26. Du JH, Xu N, Song Y, Xu M, Lu ZZ, Han C, Zhang YY. AICAR stimulates IL-6 production via p38 MAPK in cardiac fibroblasts in adult mice: a possible role for AMPK. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005; 337:1139–1144.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside in the Growth Regulation of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells Lines
- The effect of 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-ribonucleoside was mediated by p38 mitogen activated protein kinase signaling pathway in FRO thyroid cancer cells
- Angiotensin II Modulates p130Cas of Podocytes by the Suppression of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase
- Metformin Promotes Apoptosis but Suppresses Autophagy in Glucose-Deprived H4IIE Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
- Inhibitory Action of 1,3,5-Trihydroxybenzene on UVB-Induced NADPH Oxidase 4 through AMPK and JNK Signaling Pathways