J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Apr;31(4):535-541. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.4.535.
Angiotensin II Modulates p130Cas of Podocytes by the Suppression of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. tsha@chungbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2363691
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.4.535
Abstract
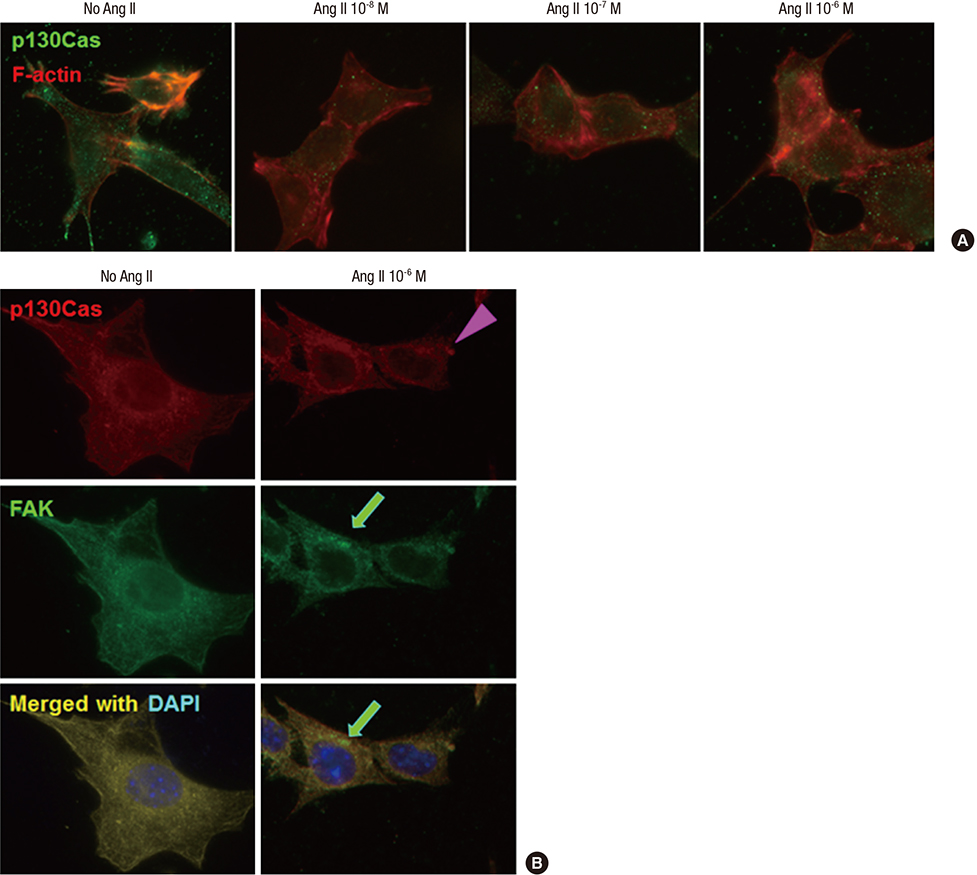
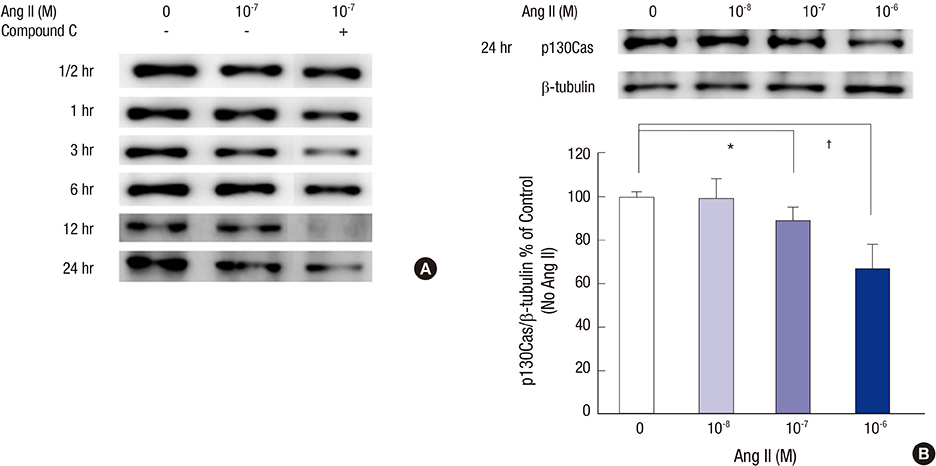
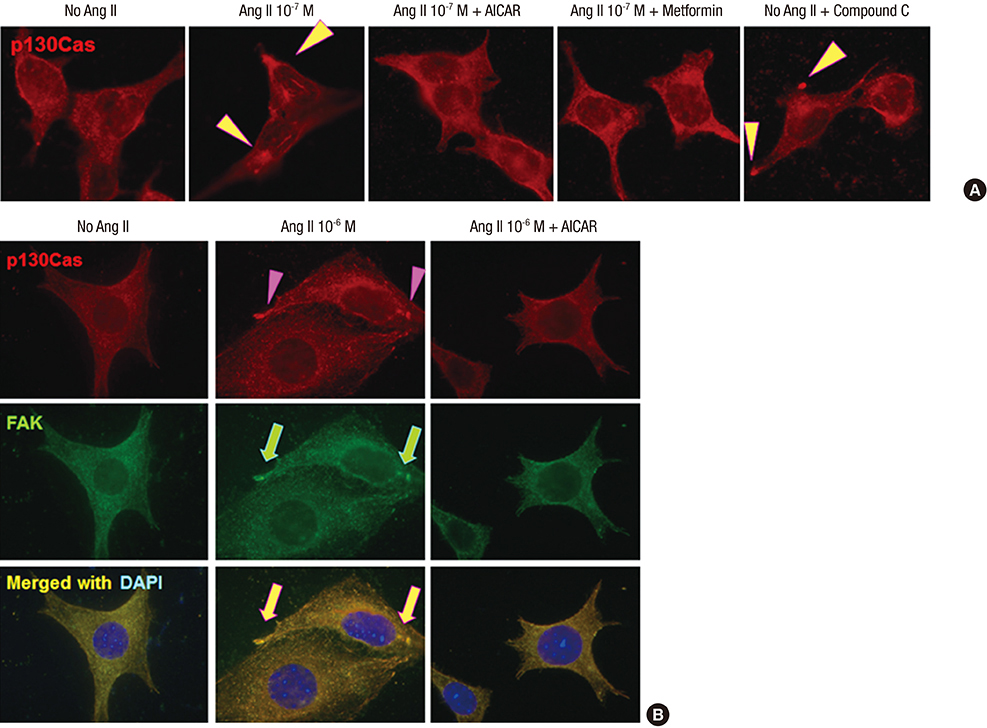
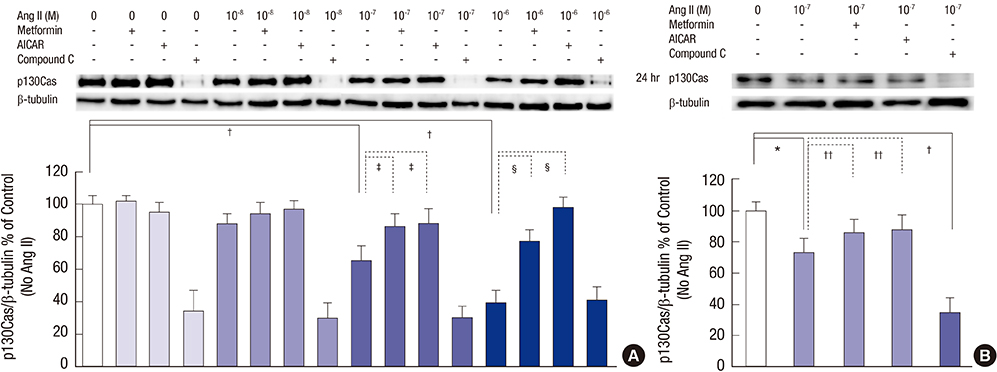
- Angiotensin II (Ang II) induces the pathological process of vascular structures, including renal glomeruli by hemodynamic and nonhemodynamic direct effects. In kidneys, Ang II plays an important role in the development of proteinuria by the modification of podocyte molecules. We have previously found that Ang II suppressed podocyte AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) via Ang II type 1 receptor and MAPK signaling pathway. In the present study, we investigated the roles of AMPK on the changes of p130Cas of podocyte by Ang II. We cultured mouse podocytes and treated them with various concentrations of Ang II and AMPK-modulating agents and analyzed the changes of p130Cas by confocal imaging and western blotting. In immunofluorescence study, Ang II decreased the intensity of p130Cas and changed its localization from peripheral cytoplasm into peri-nuclear areas in a concentrated pattern in podocytes. Ang II also reduced the amount of p130Cas in time and dose-sensitive manners. AMPK activators, metformin and AICAR, restored the suppressed and mal-localized p130Cas significantly, whereas, compound C, an AMPK inhibitor, further aggravated the changes of p130Cas. Losartan, an Ang II type 1 receptor antagonist, recovered the abnormal changes of p130Cas suppressed by Ang II. These results suggest that Ang II induces the relocalization and suppression of podocyte p130Cas by the suppression of AMPK via Ang II type 1 receptor, which would contribute to Ang II-induced podocyte injury.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
AMP-Activated Protein Kinases/antagonists & inhibitors/chemistry/*metabolism
Aminoimidazole Carboxamide/analogs & derivatives/pharmacology
Angiotensin II/*pharmacology
Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blockers/pharmacology
Animals
Blotting, Western
Cell Line
Cell Nucleus/metabolism
Crk-Associated Substrate Protein/*metabolism
Cytoplasm/metabolism
Focal Adhesion Kinase 1/metabolism
Losartan/pharmacology
Metformin/pharmacology
Mice
Microscopy, Confocal
Podocytes/cytology/drug effects/metabolism
Protein Kinase Inhibitors/*pharmacology
Ribonucleotides/pharmacology
Signal Transduction/*drug effects
AMP-Activated Protein Kinases
Aminoimidazole Carboxamide
Angiotensin II
Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blockers
Crk-Associated Substrate Protein
Focal Adhesion Kinase 1
Losartan
Metformin
Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Ribonucleotides
Figure
Reference
-
1. Remuzzi G, Benigni A, Remuzzi A. Mechanisms of progression and regression of renal lesions of chronic nephropathies and diabetes. J Clin Invest. 2006; 116:288–296.2. Kobori H, Nangaku M, Navar LG, Nishiyama A. The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: from physiology to the pathobiology of hypertension and kidney disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2007; 59:251–287.3. Wolf G. Angiotensin II as a mediator of tubulointerstitial injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000; 15:Suppl 6. 61–63.4. Luft FC. Proinflammatory effects of angiotensin II and endothelin: targets for progression of cardiovascular and renal diseases. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2002; 11:59–66.5. Benigni A, Tomasoni S, Gagliardini E, Zoja C, Grunkemeyer JA, Kalluri R, Remuzzi G. Blocking angiotensin II synthesis/activity preserves glomerular nephrin in rats with severe nephrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001; 12:941–948.6. Bonnet F, Cooper ME, Kawachi H, Allen TJ, Boner G, Cao Z. Irbesartan normalises the deficiency in glomerular nephrin expression in a model of diabetes and hypertension. Diabetologia. 2001; 44:874–877.7. Jia J, Ding G, Zhu J, Chen C, Liang W, Franki N, Singhal PC. Angiotensin II infusion induces nephrin expression changes and podocyte apoptosis. Am J Nephrol. 2008; 28:500–507.8. Suzuki K, Han GD, Miyauchi N, Hashimoto T, Nakatsue T, Fujioka Y, Koike H, Shimizu F, Kawachi H. Angiotensin II type 1 and type 2 receptors play opposite roles in regulating the barrier function of kidney glomerular capillary wall. Am J Pathol. 2007; 170:1841–1853.9. Hardie DG. The AMP-activated protein kinase pathway--new players upstream and downstream. J Cell Sci. 2004; 117:5479–5487.10. Steinberg GR, Kemp BE. AMPK in health and disease. Physiol Rev. 2009; 89:1025–1078.11. Hardie DG, Ross FA, Hawley SA. AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012; 13:251–262.12. Sharma K, Ramachandrarao S, Qiu G, Usui HK, Zhu Y, Dunn SR, Ouedraogo R, Hough K, McCue P, Chan L, et al. Adiponectin regulates albuminuria and podocyte function in mice. J Clin Invest. 2008; 118:1645–1656.13. Piwkowska A, Rogacka D, Jankowski M, Dominiczak MH, Stepiński JK, Angielski S. Metformin induces suppression of NAD(P)H oxidase activity in podocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010; 393:268–273.14. Gao K, Chi Y, Sun W, Takeda M, Yao J. 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase attenuates adriamycin-induced oxidative podocyte injury through thioredoxin-mediated suppression of the apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1-P38 signaling pathway. Mol Pharmacol. 2014; 85:460–471.15. Choi JY, Ha TS, Park HY, Ahn HY. Angiotensin II suppresses adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase of podocytes via angiotensin II type 1 receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2013; 17:16–23.16. Barrett A, Pellet-Many C, Zachary IC, Evans IM, Frankel P. p130Cas: a key signalling node in health and disease. Cell Signal. 2013; 25:766–777.17. O’Neill GM, Fashena SJ, Golemis EA. Integrin signalling: a new Cas(t) of characters enters the stage. Trends Cell Biol. 2000; 10:111–119.18. Defilippi P, Di Stefano P, Cabodi S. p130Cas: a versatile scaffold in signaling networks. Trends Cell Biol. 2006; 16:257–263.19. Welsch T, Endlich N, Kriz W, Endlich K. CD2AP and p130Cas localize to different F-actin structures in podocytes. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001; 281:F769–77.20. Ha TS, Choi JY, Park HY, Han GD. Changes of podocyte p130Cas in diabetic conditions. J Nephrol. 2013; 26:870–876.21. Mundel P, Reiser J, Zúñiga Mejía Borja A, Borja A. Pavenst?t H, Davidson GR, Kriz W, Zeller R. Rearrangements of the cytoskeleton and cell contacts induce process formation during differentiation of conditionally immortalized mouse podocyte cell lines. Exp Cell Res. 1997; 236:248–258.22. Janoštiak R, Pataki AC, Brábek J, Rösel D. Mechanosensors in integrin signaling: the emerging role of p130Cas. Eur J Cell Biol. 2014; 93:445–454.23. Ha TS. Roles of adaptor proteins in podocyte biology. World J Nephrol. 2013; 2:1–10.24. Mundel P, Shankland SJ. Podocyte biology and response to injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002; 13:3005–3015.25. Bains R, Furness PN, Critchley DR. A quantitative immunofluorescence study of glomerular cell adhesion proteins in proteinuric states. J Pathol. 1997; 183:272–280.26. Eddy AA, Symons JM. Nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Lancet. 2003; 362:629–639.27. Ha TS, Choi JY, Park HY. Puromycin aminonucleoside modulates p130Cas of podocytes. Korean J Pediatr. 2012; 55:371–376.28. Ha TS, Lee JS, Choi JY, Park HY. Ginseng total saponin modulates podocyte p130Cas in diabetic condition. J Ginseng Res. 2013; 37:94–99.29. Eid AA, Ford BM, Block K, Kasinath BS, Gorin Y, Ghosh-Choudhury G, Barnes JL, Abboud HE. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) negatively regulates Nox4-dependent activation of p53 and epithelial cell apoptosis in diabetes. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285:37503–37512.30. Ha TS, Park HY, Nam JA, Han GD. Diabetic conditions modulate the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase of podocytes. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2014; 33:26–32.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Puromycin aminonucleoside modulates p130Cas of podocytes
- Losartan Inhibits Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation through Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase
- Diabetic conditions modulate the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase of podocytes
- Letter to the Editor: 17Beta-estradiol Stimulates Glucose Uptake Through Estrogen Receptor and AMP-activated Protein Kinase Activation in C2C12 Myotubes (Korean J Obes 2016;25:190-6)
- Autophagy: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Diabetic Nephropathy