Anesth Pain Med.
2017 Jul;12(3):224-229. 10.17085/apm.2017.12.3.224.
Morphologic changes in the spinal cord following intrathecal palonosetron-HCl injection in rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Uijeongbu, Korea. jbkim@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2388836
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2017.12.3.224
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Intravenous palonosetron-HCl, a second-generation antagonist of selective serotonin type 3 (5-HT3) receptors, can prevent chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) and postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV). 5-HT3 receptors are abundant in the lower brainstem and the substantia gelatinosa of the spinal cord, which provides a theoretical rationale for neuraxial administration of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists for CINV, PONV, and opioid-induced nausea and vomiting. However, there are no reports of neuraxial administration of palonosetron-HCl. Before neuraxial administration of a drug is accepted for clinical use, its safety must be proven. This study was conducted to determine whether neuraxial administration of palonosetron-HCl produces neurologic injury.
METHODS
Male Sprague-Dawley rats under general anesthesia were catheterized intrathecally and the catheter tip was advanced caudally to the L1 vertebra. After 7 days, 20 µl of normal saline (N group, n = 6) or 20 µl (1 µg) of palonosetron-HCl (P group, n = 6) were injected intrathecally once per day for 2 weeks. Neurotoxic changes were evaluated by light microscopy (LM) and electron microscopy (EM) of the spinal cord. Behavioral changes were also evaluated in both groups.
RESULTS
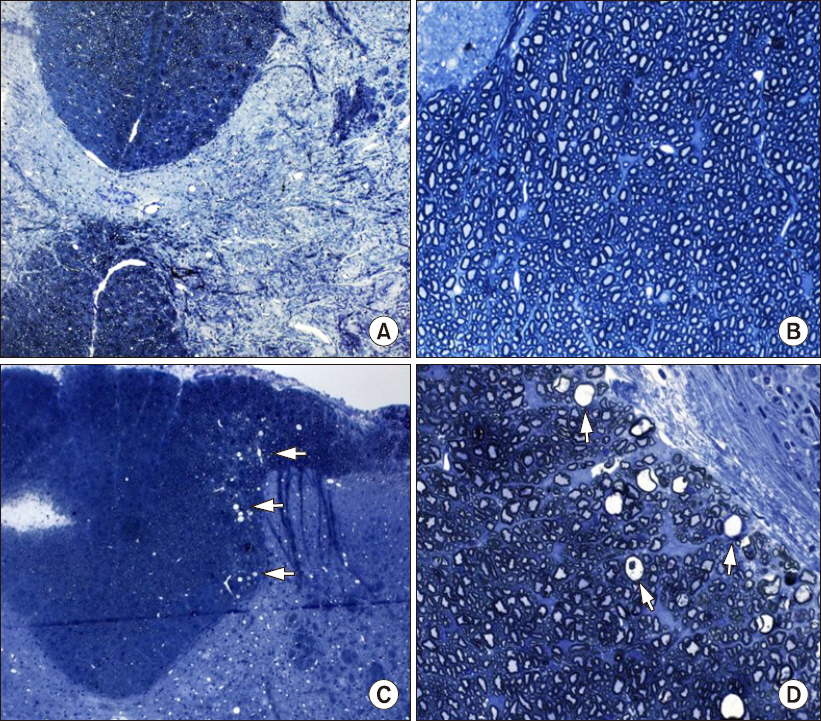
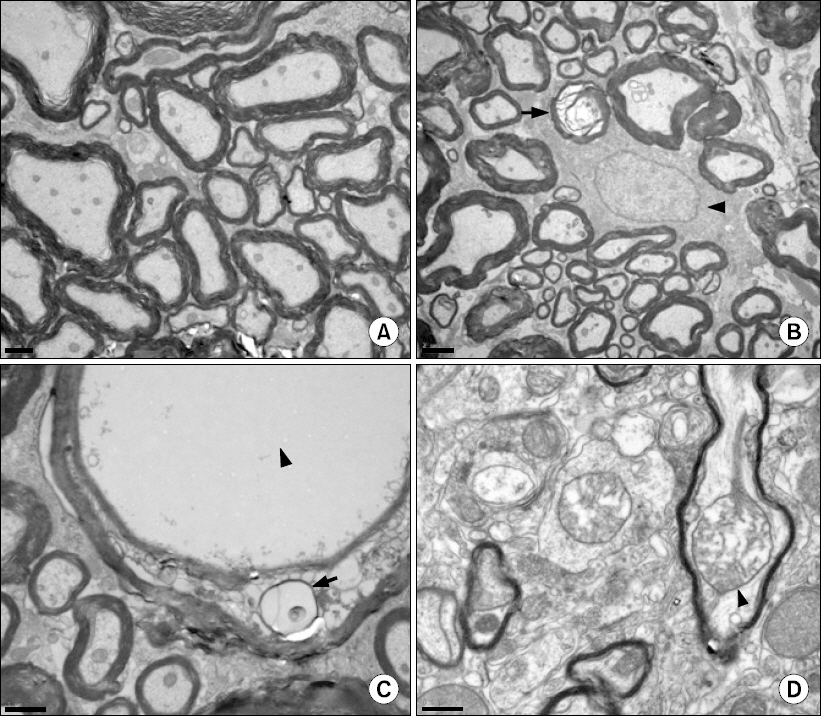
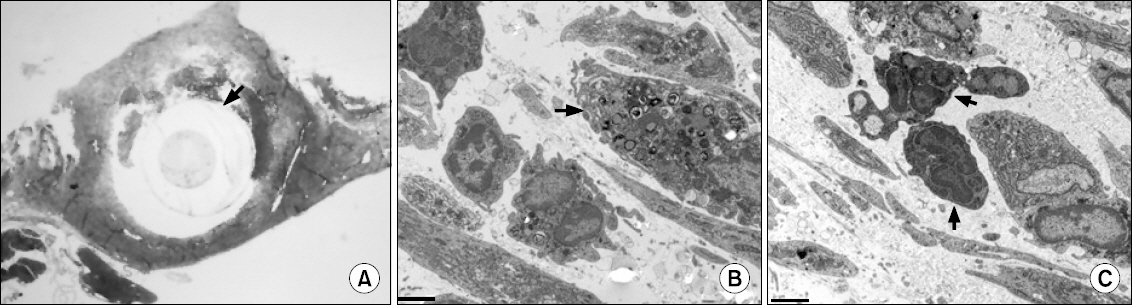
One of the N group rats and three of the P group rats demonstrated abnormal behavior during intrathecal drug injection, but otherwise their behavior was normal. The spinal cords of the N group did not have any abnormal findings by LM or EM. The spinal cords of the P group had multiple vacuoles in the white matter by LM, especially in the dorsal funiculus, and EM revealed myelin, axonal, and mitochondrial swelling.
CONCLUSIONS
Results suggest that chronic intrathecal administration of palonosetron-HCl produced microscopic morphologic changes in the spinal cords of rats.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Anesthesia, General
Animals
Axons
Brain Stem
Catheters
Humans
Injections, Spinal
Male
Microscopy
Microscopy, Electron
Mitochondrial Swelling
Myelin Sheath
Nausea
Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting
Rats*
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Receptors, Serotonin, 5-HT3
Serotonin
Spinal Cord*
Spine
Substantia Gelatinosa
Vacuoles
Vomiting
White Matter
Receptors, Serotonin, 5-HT3
Serotonin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schug SA, Saunders D, Kurowski I, Paech MJ. Neuraxial drug administration: a review of treatment options for anaesthesia and analgesia. CNS Drugs. 2006; 20:917–33. DOI: 10.2165/00023210-200620110-00005. PMID: 17044729.2. Yang LP, Scott LJ. Palonosetron: in the prevention of nausea and vomiting. Drugs. 2009; 69:2257–78. DOI: 10.2165/11200980-000000000-00000. PMID: 19852528.3. Bunce KT, Tyers MB. The role of 5-HT in postoperative nausea and vomiting. Br J Anaesth. 1992; 69(7 Suppl 1):S60–2. DOI: 10.1093/bja/69.supplement_1.60S.4. Raphael JH, Norton AC. Antiemetic efficacy of prophylactic ondansetron in laparoscopic surgery: randomized, double-blind comparison with metoclopramide. Br J Anaesth. 1993; 71:845–8. DOI: 10.1093/bja/71.6.845.5. Han DW, Hong SW, Kwon JY, Lee JW, Kim KJ. Epidural ondansetron is more effective to prevent postoperative pruritus and nausea than intravenous ondansetron in elective cesarean delivery. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2007; 86:683–7. DOI: 10.1080/00016340701302616. PMID: 17520399.6. Moon YE, Joo J, Kim JE, Lee Y. Anti-emetic effect of ondansetron and palonosetron in thyroidectomy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Br J Anaesth. 2012; 108:417–22. DOI: 10.1093/bja/aer423. PMID: 22277663.7. Yaksh TL, Rudy TA. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1976; 17:1031–6. DOI: 10.1016/0031-9384(76)90029-9.8. Navari RM. Palonosetron: a second-generation 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor antagonist. Future Oncol. 2006; 2:591–602. DOI: 10.2217/14796694.2.5.591. PMID: 17026451.9. Rojas C, Stathis M, Thomas AG, Massuda EB, Alt J, Zhang J, et al. Palonosetron exhibits unique molecular interactions with the 5-HT3 receptor. Anesth Analg. 2008; 107:469–78. DOI: 10.1213/ane.0b013e318172fa74. PMID: 18633025.10. Eisenberg P, Figueroa-Vadillo J, Zamora R, Charu V, Hajdenberg J, Cartmell A, et al. Improved prevention of moderately emetogenic chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting with palonosetron, a pharmacologically novel 5-HT3 receptor antagonist: results of a phase III, single-dose trial versus dolasetron. Cancer. 2003; 98:2473–82. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.11817. PMID: 14635083.11. Gralla R, Lichinitser M, Van Der Vegt S, Sleeboom H, Mezger J, Peschel C, et al. Palonosetron improves prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting following moderately emetogenic chemotherapy: results of a double-blind randomized phase III trial comparing single doses of palonosetron with ondansetron. Ann Oncol. 2003; 14:1570–7. DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdg417. PMID: 14504060.12. Lacassie HJ, Schultz JR, Cummings TJ, Morris R, Trasti SL, Reynolds JD. Behavioural testing and histological assessments of rabbit spinal cord following intrathecal administration of ondansetron. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2006; 33:798–801. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2006.04442.x. PMID: 16922809.13. Waeber C, Hoyer D, Palacios JM. 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptors in the human brain: autoradiographic visualization using [3H]ICS 205-930. Neuroscience. 1989; 31:393–400. DOI: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90382-5.14. Morales M, Battenberg E, de Lecea L, Sanna PP, Bloom FE. Cellular and subcellular immunolocalization of the type 3 serotonin receptor in the rat central nervous system. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1996; 36:251–60. DOI: 10.1016/0169-328X(96)88406-3.15. Vranken JH, Troost D, Wegener JT, Kruis MR, van der Vegt MH. Neuropathological findings after continuous intrathecal administration of S(+)-ketamine for the management of neuropathic cancer pain. Pain. 2005; 117:231–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2005.06.014. PMID: 16098665.16. Adornato B, Lampert P. Status spongiosus of nervous tissue. Electron microscopic studies. Acta Neuropathol. 1971; 19:271–89. DOI: 10.1007/BF00692148. PMID: 5004121.17. Yamashita A, Matsumoto M, Matsumoto S, Itoh M, Kawai K, Sakabe T. A comparison of the neurotoxic effects on the spinal cord of tetracaine, lidocaine, bupivacaine, and ropivacaine administered intrathecally in rabbits. Anesth Analg. 2003; 97:512–9. DOI: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000068885.78816.5B. PMID: 12873946.18. Oka S, Matsumoto M, Ohtake K, Kiyoshima T, Nakakimura K, Sakabe T. The addition of epinephrine to tetracaine injected intrathecally sustains an increase in glutamate concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid and worsens neuronal injury. Anesth Analg. 2001; 93:1050–7. DOI: 10.1097/00000539-200110000-00051. PMID: 11574382.19. Coombs DW, Fratkin JD. Neurotoxicology of spinal agents. Anesthesiology. 1987; 66:724–6. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-198706000-00002.20. Gordh T Jr, Post C, Olsson Y. Evaluation of the toxicity of subarachnoid clonidine, guanfacine, and a substance P-antagonist on rat spinal cord and nerve roots: light and electron microscopic observations after chronic intrathecal administration. Anesth Analg. 1986; 65:1303–11. DOI: 10.1213/00000539-198612000-00010. PMID: 2430489.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Palonosetron might not attenuate spinal anesthesia-induced hypotension during orthopedic surgery
- Effects of Intrathecal Calcium Channel Blockers on the MAC of Isoflurane in Rats
- A Case of Myelopathy after Intrathecal Injection of Fluorescein
- Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical Allodynia in a Rat Model of Postoperative Pain
- IV Morphine Produced Spinal Antinociception Partly by Nitric Oxide