Transl Clin Pharmacol.
2017 Jun;25(2):67-73. 10.12793/tcp.2017.25.2.67.
Metabolomic analysis of healthy human urine following administration of glimepiride using a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Science, BK21 Plus KNU Bio-Medical Convergence Program for Creative Talent, Cell and Matrix Research Institute, and Clinical Trial Center, Kyungpook National University Graduate School and Hospital, Daegu 41944, Korea. yry@knu.ac.kr, biohjk@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2386763
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2017.25.2.67
Abstract
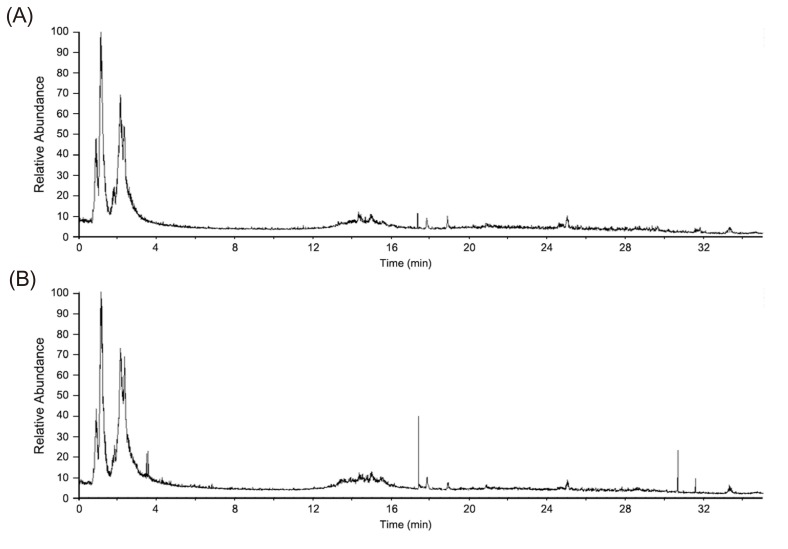
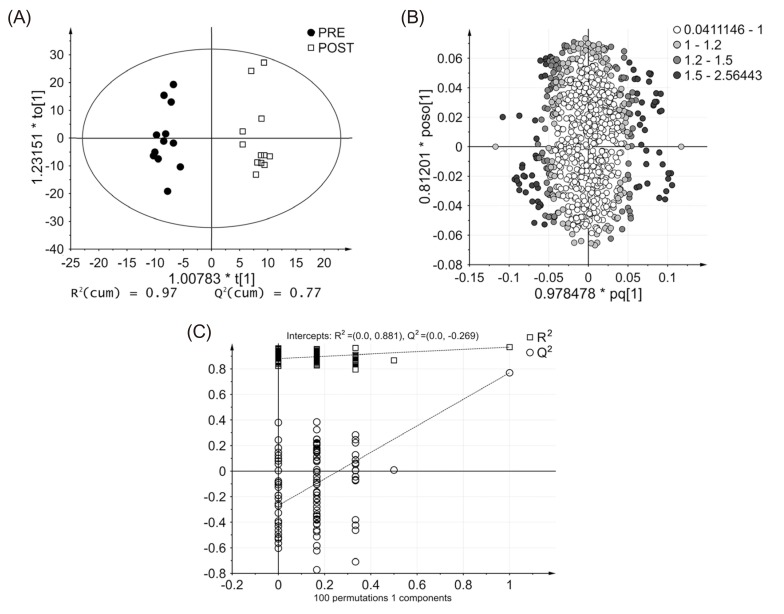
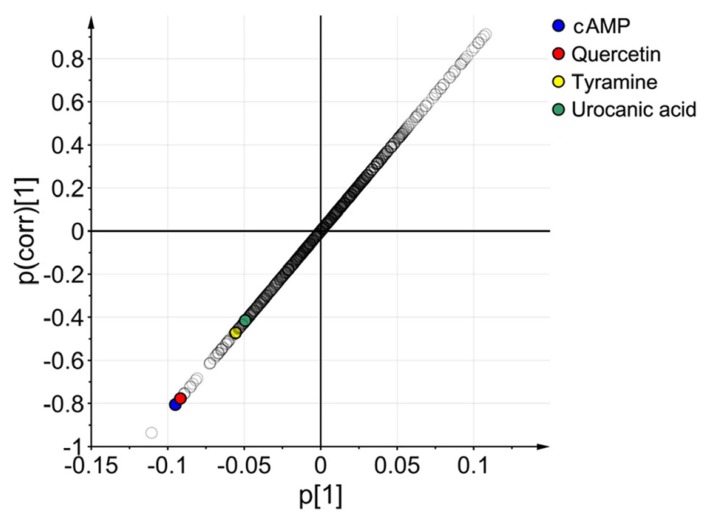
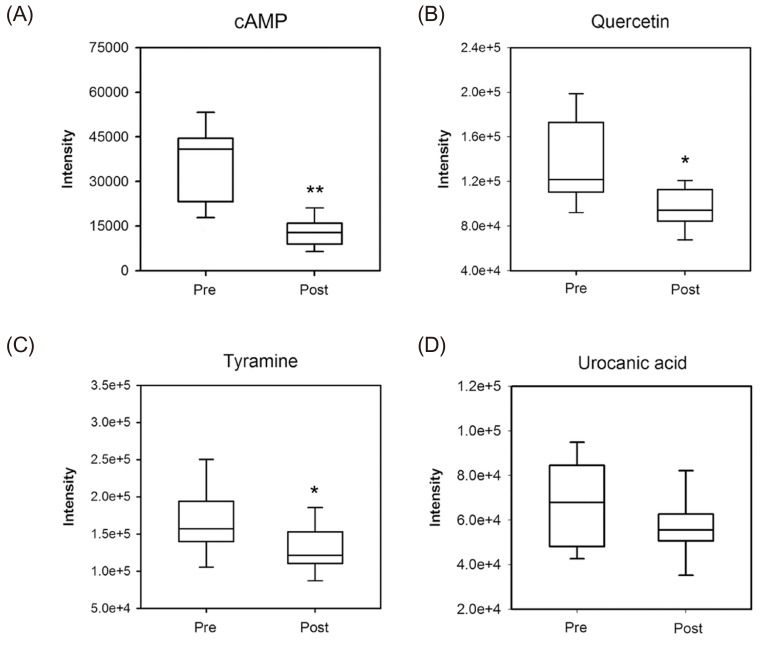
- Glimepiride, a third generation sulfonylurea, is an antihyperglycemic agent widely used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus. In this study, an untargeted urinary metabolomic analysis was performed to identify endogenous metabolites affected by glimepiride administration. Urine samples of twelve healthy male volunteers were collected before and after administration of 2 mg glimepiride. These samples were analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), and then subjected to multivariate data analysis including principal component analysis and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis. Through this metabolomic profiling, we identified several endogenous metabolites such as adenosine 3"², 5"²-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP), quercetin, tyramine, and urocanic acid, which exhibit significant metabolomic changes between pre- and posturine samples. Among these, cAMP, which is known to be related to insulin secretion, was the most significantly altered metabolite following glimepiride administration. In addition, the pathway analysis showed that purine, tyrosine, and histidine metabolism was affected by pharmacological responses to glimepiride. Together, the results suggest that the pharmacometabolomic approach, based on LC-MS/MS, is useful in understanding the alterations in biochemical pathways associated with glimepiride action.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fiehn O. Metabolomics–the link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Mol Biol. 2002; 48:155–171. PMID: 11860207.2. Wishart DS. Applications of metabolomics in drug discovery and development. Drugs R D. 2008; 9:307–322. PMID: 18721000.3. Phapale PB, Kim SD, Lee HW, Lim M, Kale DD, Kim YL, et al. An integrative approach for identifying a metabolic phenotype predictive of individualized pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2010; 87:426–436. DOI: 10.1038/clpt.2009.296. PMID: 20182421.
Article4. Hossain P, Kawar B, El Nahas M. Obesity and diabetes in the developing world–a growing challenge. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356:213–215. PMID: 17229948.5. Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001; 414:782–787. PMID: 11742409.
Article6. Rendell M. The role of sulphonylureas in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs. 2004; 64:1339–1358. PMID: 15200348.
Article7. Bijlstra PJ, Lutterman JA, Russel FG, Thien T, Smits P. Interaction of sulphonylurea derivatives with vascular ATP-sensitive potassium channels in humans. Diabetologia. 1996; 39:1083–1090. PMID: 8877293.
Article8. Raptis SA, Dimitriadis GD. Oral hypoglycemic agents: insulin secretagogues, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors and insulin sensitizers. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2001; 109(Suppl 2):S265–S287. PMID: 11460577.9. Mocanu MM, Maddock HL, Baxter GF, Lawrence CL, Standen NB, Yellon DM. Glimepiride, a novel sulfonylurea, does not abolish myocardial protection afforded by either ischemic preconditioning or diazoxide. Circulation. 2001; 103:3111–3116. PMID: 11425777.
Article10. Dills DG, Schneider J. Clinical evaluation of glimepiride versus glyburide in NIDDM in a double-blind comparative study. Glimepiride/Glyburide Research Group. Horm Metab Res. 1996; 28:426–429. PMID: 8911977.11. Massi-Benedetti M. Glimepiride in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review of the worldwide therapeutic experience. Clin Ther. 2003; 25:799–816. PMID: 12852703.12. Lehr KH, Damm P. Simultaneous determination of the sulphonylurea glimepiride and its metabolites in human serum and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography after pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1990; 526:497–505. PMID: 2361988.
Article13. Pistos C, Koutsopoulou M, Panderi I. Improved liquid chromatographic tandem mass spectrometric determination and pharmacokinetic study of glimepiride in human plasma. Biomed Chromatogr. 2005; 19:394–401. PMID: 15651098.
Article14. Noh K, Kim E, Jeong T, Na M, Baek MC, Liu KH, et al. Simultaneous determination of glimepiride and its metabolites in human plasma by liquid chromatography coupled to a tandem mass spectrometry. Arch Pharm Res. 2011; 34:2073–2078. DOI: 10.1007/s12272-011-1210-0. PMID: 22210033.
Article15. Huo T, Xiong Z, Lu X, Cai S. Metabonomic study of biochemical changes in urinary of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients after the treatment of sulfonylurea antidiabetic drugs based on ultra-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Biomed Chromatogr. 2015; 29:115–122. DOI: 10.1002/bmc.3247. PMID: 24890121.
Article16. Smith CA, Want EJ, O'Maille G, Abagyan R, Siuzdak G. XCMS: processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Anal Chem. 2006; 78:779–787. PMID: 16448051.
Article17. Lee J, Park J, Lim MS, Seong SJ, Seo JJ, Park SM, et al. Quantile normalization approach for liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based metabolomic data from healthy human volunteers. Anal Sci. 2012; 28:801–805. PMID: 22878636.
Article18. Bylesjo M, Rantalainen M, Cloarec O, Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Trygg J. OPLS discriminant analysis: combining the strengths of PLS-DA and SIMCA classification. J Chemometr. 2006; 20:341–351.19. Trygg J, Holmes E, Lundstedt T. Chemometrics in metabonomics. J Proteome Res. 2007; 6:469–479. PMID: 17269704.
Article20. Mahadevan S, Shah SL, Marrie TJ, Slupsky CM. Analysis of metabolomic data using support vector machines. Anal Chem. 2008; 80:7562–7570. DOI: 10.1021/ac800954c. PMID: 18767870.
Article21. Wiklund S, Johansson E, Sjöström L, Mellerowicz EJ, Edlund U, Shockcor JP, et al. Visualization of GC/TOF-MS-based metabolomics data for identification of biochemically interesting compounds using OPLS class models. Anal Chem. 2008; 80:115–122. PMID: 18027910.
Article22. Zhang CL, Katoh M, Shibasaki T, Minami K, Sunaga Y, Takahashi H, et al. The cAMP sensor Epac2 is a direct target of antidiabetic sulfonylurea drugs. Science. 2009; 325:607–610. DOI: 10.1126/science.1172256. PMID: 19644119.
Article23. Osegawa M, Makino H, Kanatsuka A, Kumagai A. Effects of sulfonylureas on membrane-bound low Km cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982; 721:289–296. PMID: 6293588.
Article24. Solomon SS, Deaton J, Shankar TP, Palazzolo M. Cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in diabetes: effect of glyburide. Diabetes. 1986; 35:1233–1236. PMID: 3019808.
Article25. Müller G, Wied S, Wetekam EM, Crecelius A, Unkelbach A, Pünter J. Stimulation of glucose utilization in 3T3 adipocytes and rat diaphragm in vitro by the sulphonylureas, glimepiride and glibenclamide, is correlated with modulations of the cAMP regulatory cascade. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994; 48:985–996. PMID: 8093111.
Article26. Müller G, Satoh Y, Geisen K. Extrapancreatic effects of sulfonylureas–a comparison between glimepiride and conventional sulfonylureas. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1995; 28(Suppl):S115–S137. PMID: 8529504.27. Loten EG, Sneyd JG. An effect of insulin on adipose-tissue adenosine 3′: 5′-cyclic monophosphate phosphodiesterase. Biochem J. 1970; 120:187–193. PMID: 4321931.28. Manganiello V, Vaughan M. An effect of insulin on cyclic adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate phosphodiesterase activity in fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1973; 248:7164–7170. PMID: 4355201.
Article29. Solomon SS. Effect of insulin and lipolytic hormones on cyclic AMP phosphodieterase activity in normal and diabetic rat adipose tissue. Endocrinology. 1975; 96:1366–1373. PMID: 165058.30. Hepp KD. Inhibition of glucagon-stimulated adenyl cyclase by insulin. FEBS Lett. 1971; 12:263–266. PMID: 11945594.
Article31. Kwok RP, Juorio AV. Concentration of striatal tyramine and dopamine metabolism in diabetic rats and effect of insulin administration. Neuroendocrinology. 1986; 43:590–596. PMID: 3528901.
Article32. Jeong SM, Kang MJ, Choi HN, Kim JH, Kim JI. Quercetin ameliorates hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia and improves antioxidant status in type 2 diabetic db/db mice. Nutr Res Pract. 2012; 6:201–207. DOI: 10.4162/nrp.2012.6.3.201. PMID: 22808343.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Simultaneous Screening of 177 Drugs of Abuse in Urine Using Ultra-performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Drug-intoxicated Patients
- Determination of donepezil in human plasma using ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- Metabolism and excretion of novel pulmonary-targeting docetaxel liposome in rabbits
- Sporozoite proteome analysis of Cryptosporidium parvum by one-dimensional SDS-PAGE and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
- Identification of Novel Metabolic Proteins Released by Insulin Signaling of the Rat Hypothalmus Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)