Yonsei Med J.
2014 Mar;55(2):487-492.
Injection of Bupivacaine into Disc Space to Detect Painful Nonunion after Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF) Surgery in Patients with Discogenic Low Back Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan. sohtori@faculty.chiba-u.jp
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Bupivacaine is commonly used for the treatment of back pain and the diagnosis of its origin. Nonunion is sometimes observed after spinal fusion surgery; however, whether the nonunion causes pain is controversial. In the current study, we aimed to detect painful nonunion by injecting bupivacaine into the disc space of patients with nonunion after anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) surgery for discogenic low back pain.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
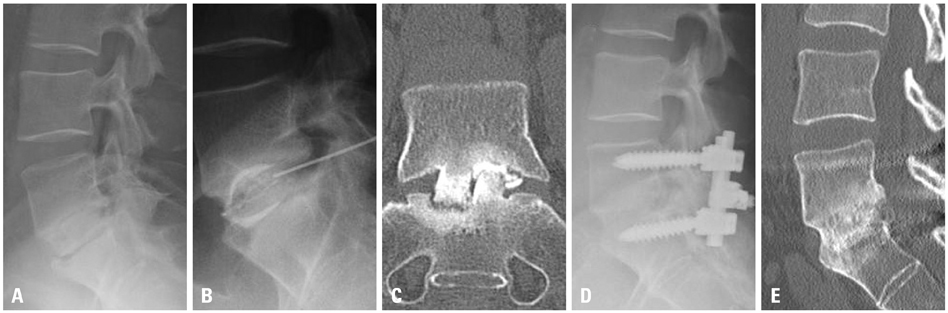
From 52 patients with low back pain, we selected 42 who showed disc degeneration at only one level (L4-L5 or L5-S1) on magnetic resonance imaging and were diagnosed by pain provocation on discography and pain relief by discoblock (the injection of bupivacaine). They underwent ALIF surgery. If the patients showed low back pain and nonunion 2 years after surgery, we injected bupivacaine into the nonunion disc space. Patients showing pain relief after injection of bupivacaine underwent additional posterior fixation using pedicle screws. These patients were followed up 2 years after the revision surgery.
RESULTS
Of the 42 patient subjects, 7 showed nonunion. Four of them did not show low back pain; whereas 3 showed moderate or severe low back pain. These 3 patients showed pain reduction after injection of bupivacaine into their nonunion disc space and underwent additional posterior fixation. They showed bony union and pain relief 2 years after the revision surgery.
CONCLUSION
Injection of bupivacaine into the nonunion disc space after ALIF surgery for discogenic low back pain is useful for diagnosis of the origin of pain.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nachemson AL. The lumbar spine, an orthopaedic challenge. Spine. 1976; 1:59–71.
Article2. Mooney V. Presidential address. International Society for the Study of the Lumbar Spine. Dallas, 1986. Where is the pain coming from? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1987; 12:754–759.
Article3. Deyo RA, Weinstein JN. Low back pain. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:363–370.
Article4. Pauza KJ, Howell S, Dreyfuss P, Peloza JH, Dawson K, Bogduk N. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of intradiscal electrothermal therapy for the treatment of discogenic low back pain. Spine J. 2004; 4:27–35.
Article5. Shuff C, An HS. Artificial disc replacement: the new solution for discogenic low back pain? Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2005; 34:8–12.6. Buenaventura RM, Shah RV, Patel V, Benyamin R, Singh V. Systematic review of discography as a diagnostic test for spinal pain: an update. Pain Physician. 2007; 10:147–164.7. Carragee EJ, Lincoln T, Parmar VS, Alamin T. A gold standard evaluation of the "discogenic pain" diagnosis as determined by provocative discography. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:2115–2123.
Article8. Ohtori S, Kinoshita T, Yamashita M, Inoue G, Yamauchi K, Koshi T, et al. Results of surgery for discogenic low back pain: a randomized study using discography versus discoblock for diagnosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:1345–1348.9. Ohtori S, Koshi T, Yamashita M, Yamauchi K, Inoue G, Suzuki M, et al. Surgical versus nonsurgical treatment of selected patients with discogenic low back pain: a small-sized randomized trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36:347–354.
Article10. Mirza SK, Deyo RA. Systematic review of randomized trials comparing lumbar fusion surgery to nonoperative care for treatment of chronic back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:816–823.
Article11. Fischgrund JS, Mackay M, Herkowitz HN, Brower R, Montgomery DM, Kurz LT. 1997 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective, randomized study comparing decompressive laminectomy and arthrodesis with and without spinal instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22:2807–2812.12. Herkowitz HN, Kurz LT. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis A prospective study comparing decompression with decompression and intertransverse process arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991; 73:802–808.
Article13. Ploumis A, Pinto MR, Schellhas KP. Disc space injection with marcaine as a method to evaluate painful nonunion of an interbody fusion device: a case report. Spine J. 2007; 7:74–78.
Article14. Vamvanij V, Fredrickson BE, Thorpe JM, Stadnick ME, Yuan HA. Surgical treatment of internal disc disruption: an outcome study of four fusion tec hniques. J Spinal Disord. 1998; 11:375–382.15. Chu CR, Izzo NJ, Papas NE, Fu FH. In vitro exposure to 0.5% bupivacaine is cytotoxic to bovine articular chondrocytes. Arthroscopy. 2006; 22:693–699.
Article16. Dogan N, Erdem AF, Erman Z, Kizilkaya M. The effects of bupivacaine and neostigmine on articular cartilage and synovium in the rabbit knee joint. J Int Med Res. 2004; 32:513–519.
Article17. Gomoll AH, Kang RW, Williams JM, Bach BR, Cole BJ. Chondrolysis after continuous intra-articular bupivacaine infusion: an experimental model investigating chondrotoxicity in the rabbit shoulder. Arthroscopy. 2006; 22:813–819.
Article18. Lee H, Sowa G, Vo N, Vadala G, O'Connell S, Studer R, et al. Effect of bupivacaine on intervertebral disc cell viability. Spine J. 2010; 10:159–166.
Article19. Wang D, Vo NV, Sowa GA, Hartman RA, Ngo K, Choe SR, et al. Bupivacaine decreases cell viability and matrix protein synthesis in an intervertebral disc organ model system. Spine J. 2011; 11:139–146.
Article20. Chu CR, Coyle CH, Chu CT, Szczodry M, Seshadri V, Karpie JC, et al. In vivo effects of single intra-articular injection of 0.5% bupivacaine on articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92:599–608.
Article21. Ohtori S, Inoue G, Orita S, Eguchi Y, Ochiai N, Kishida S, et al. No acceleration of intervertebral disc degeneration after a single injection of bupivacaine in young age group with follow-up of 5 years. Asian Spine J. 2013; 7:212–217.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Minimally invasive anterior approach to the lumbar spine
- Isthmic Spondylolisthesis Associated with Foraminal Disc Herniation Treated by Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Two-Year Results with a Modular Interbody Device
- The Result of Minimal Invasive Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion on Degenerative Lumbar Flat Back Disease
- Clinical Comparison between Decompression and Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Chronic Lower Back Pain Involving Degenerative Disc Disease and Spinal Stenosis