Yonsei Med J.
2017 Jan;58(1):9-18. 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.1.9.
EGF Induced RET Inhibitor Resistance in CCDC6-RET Lung Cancer Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. hchang@ish.or.kr
- 2Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Catholic Kwandong University College of Medicine, International St. Mary’s Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Institute for Bio-Medical Convergence, Catholic Kwandong University College of Medicine, International St. Mary’s Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2374183
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2017.58.1.9
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Rearrangement of the proto-oncogene rearranged during transfection (RET) has been newly identified potential driver mutation in lung adenocarcinoma. Clinically available tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) target RET kinase activity, which suggests that patients with RET fusion genes may be treatable with a kinase inhibitor. Nevertheless, the mechanisms of resistance to these agents remain largely unknown. Thus, the present study aimed to determine whether epidermal growth factor (EGF) and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) trigger RET inhibitor resistance in LC-2/ad cells with CCDC6-RET fusion genes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
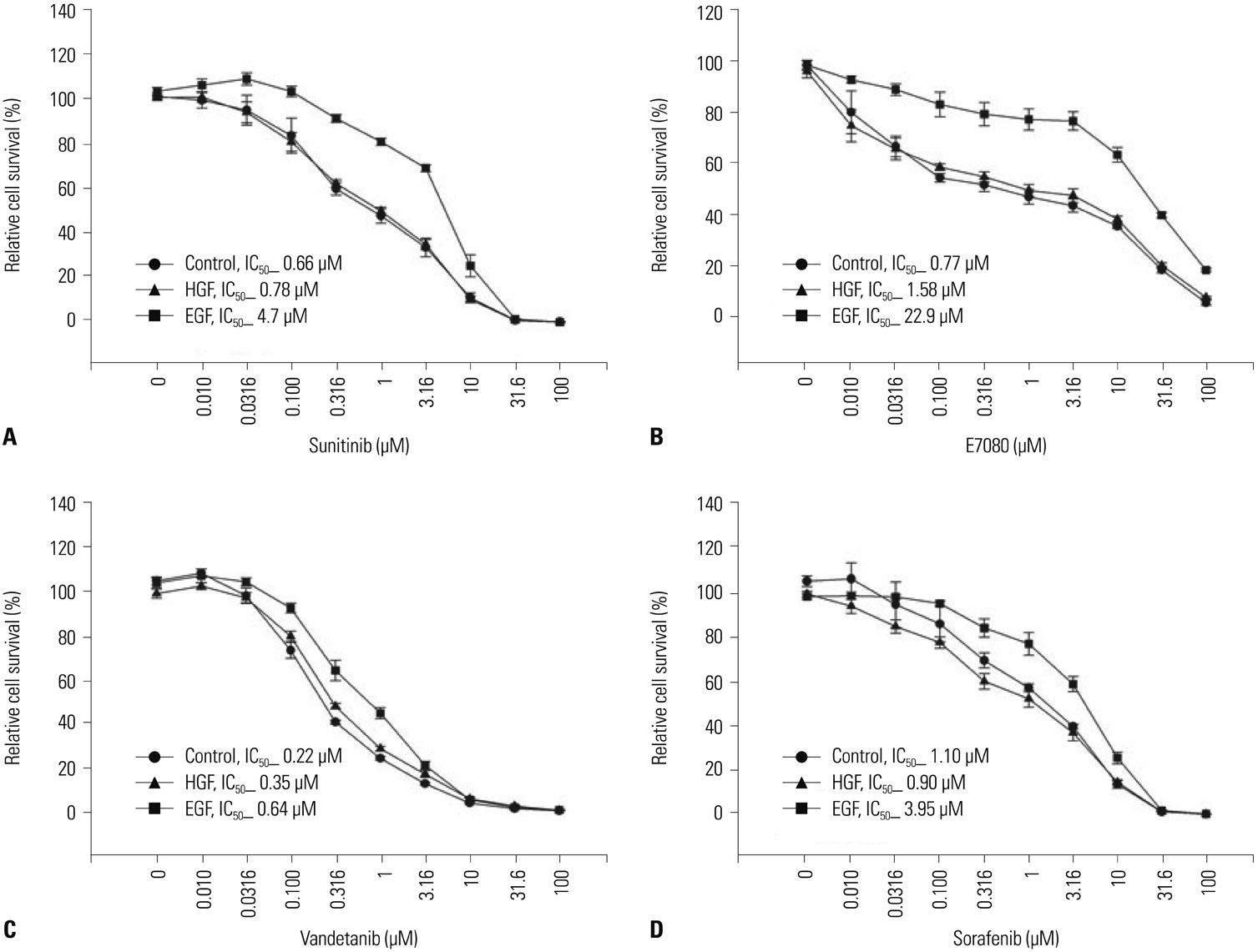
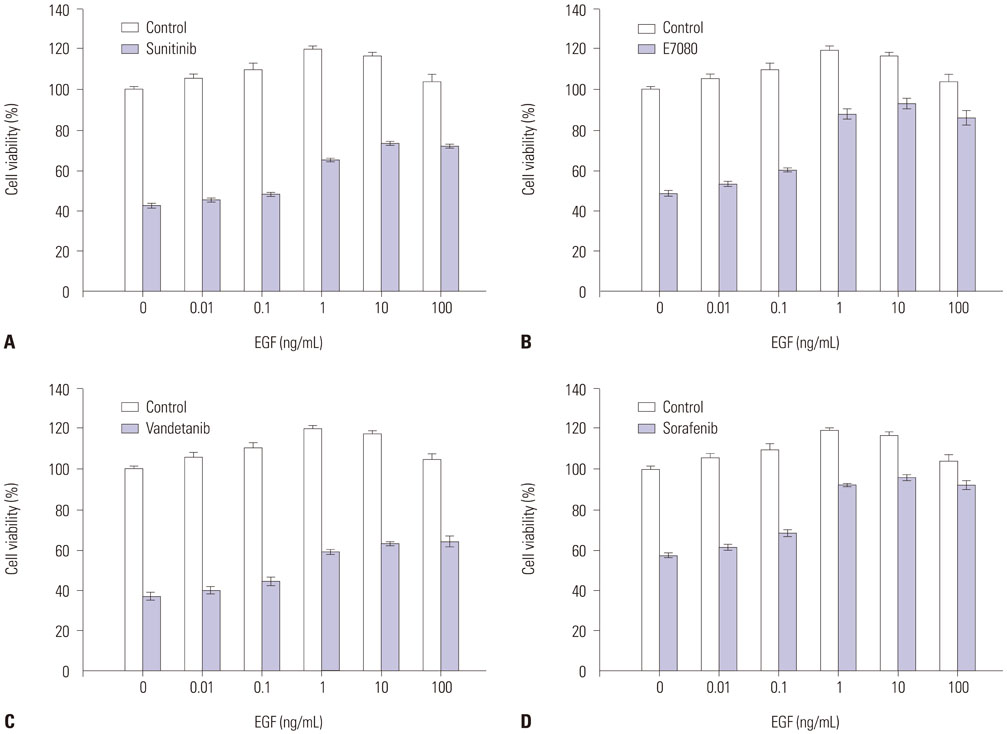
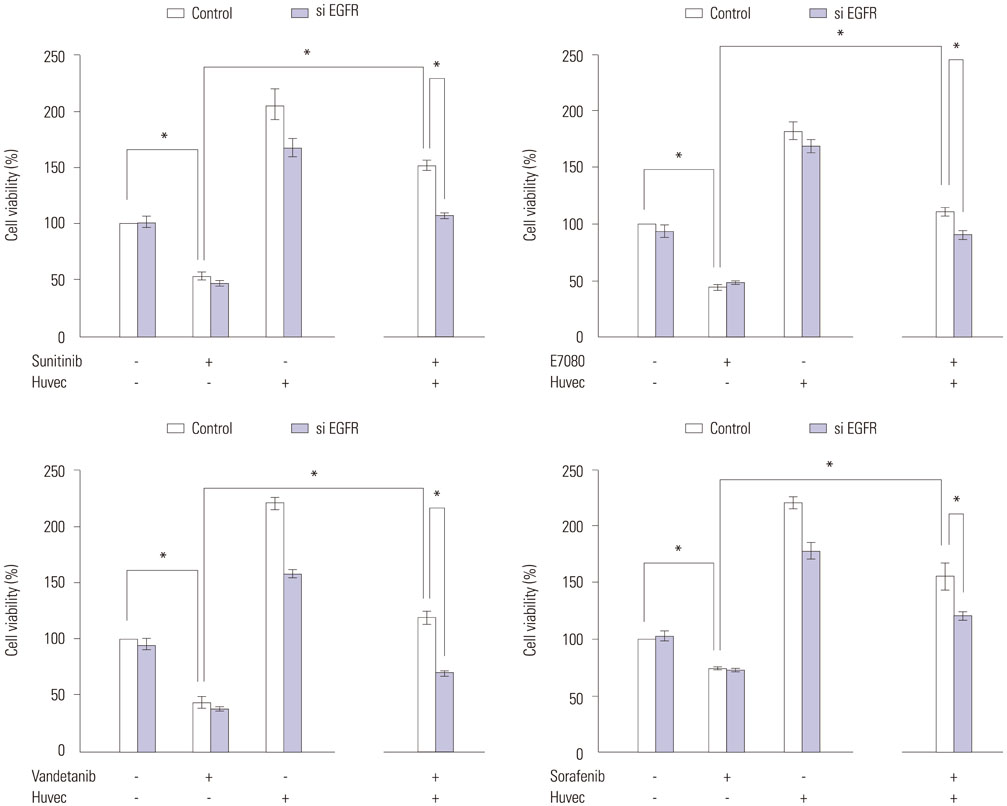
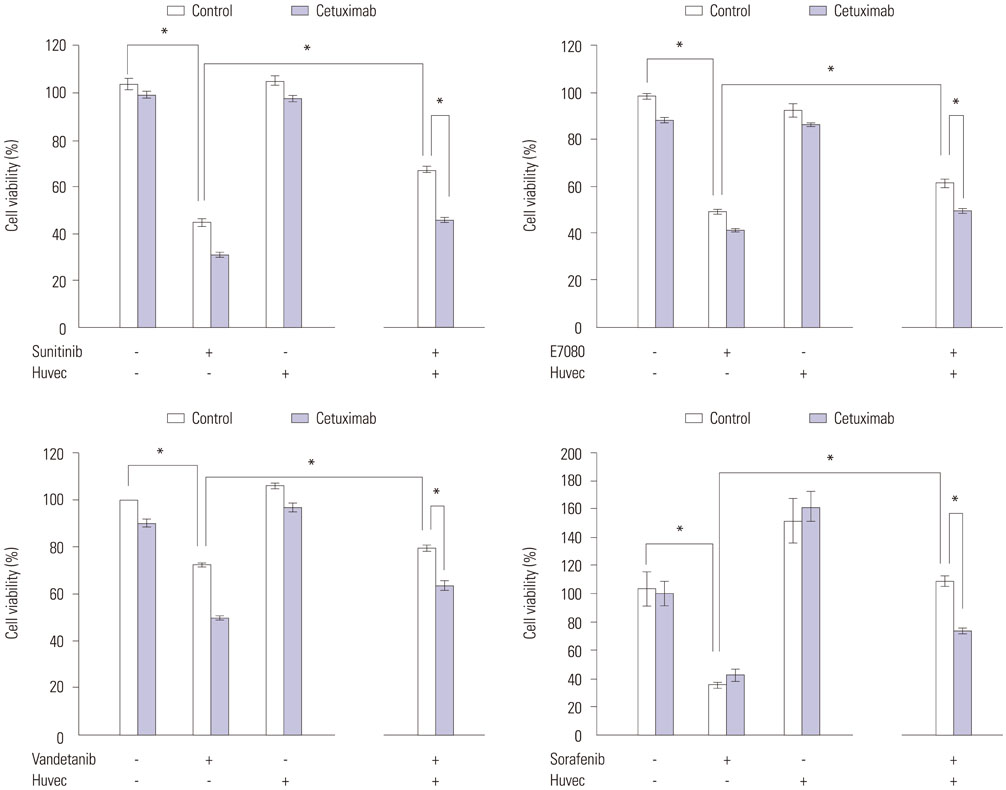
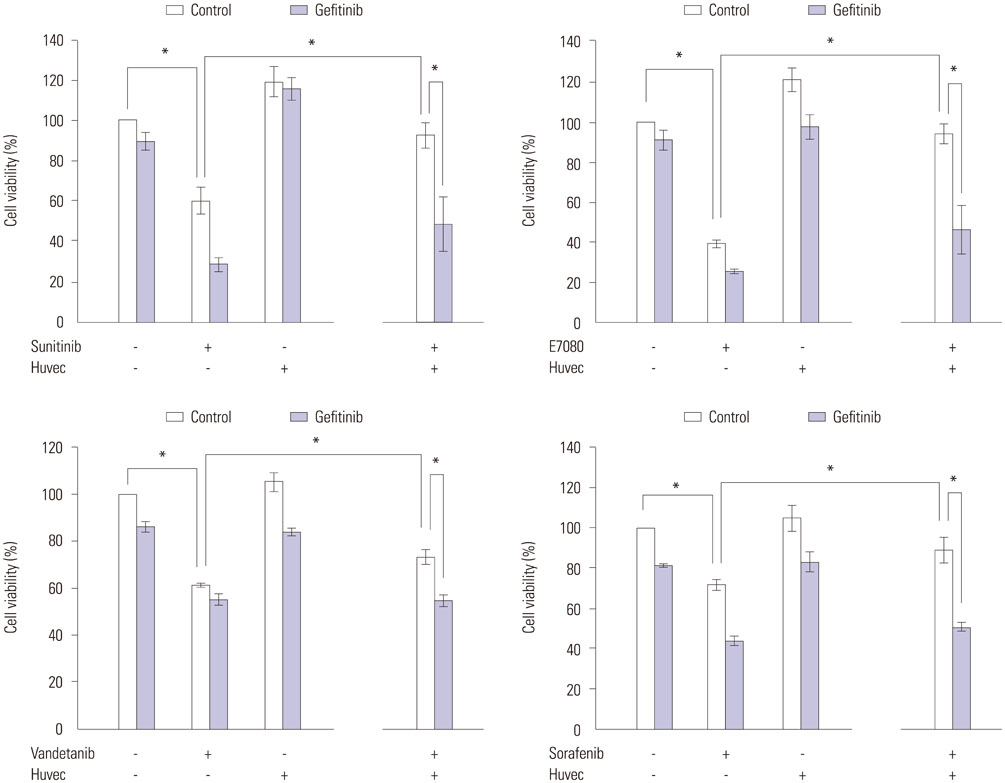
The effects of EGF and HGF on the susceptibility of a CCDC6-RET lung cancer cell line to RET inhibitors (sunitinib, E7080, vandetanib, and sorafenib) were examined.
RESULTS
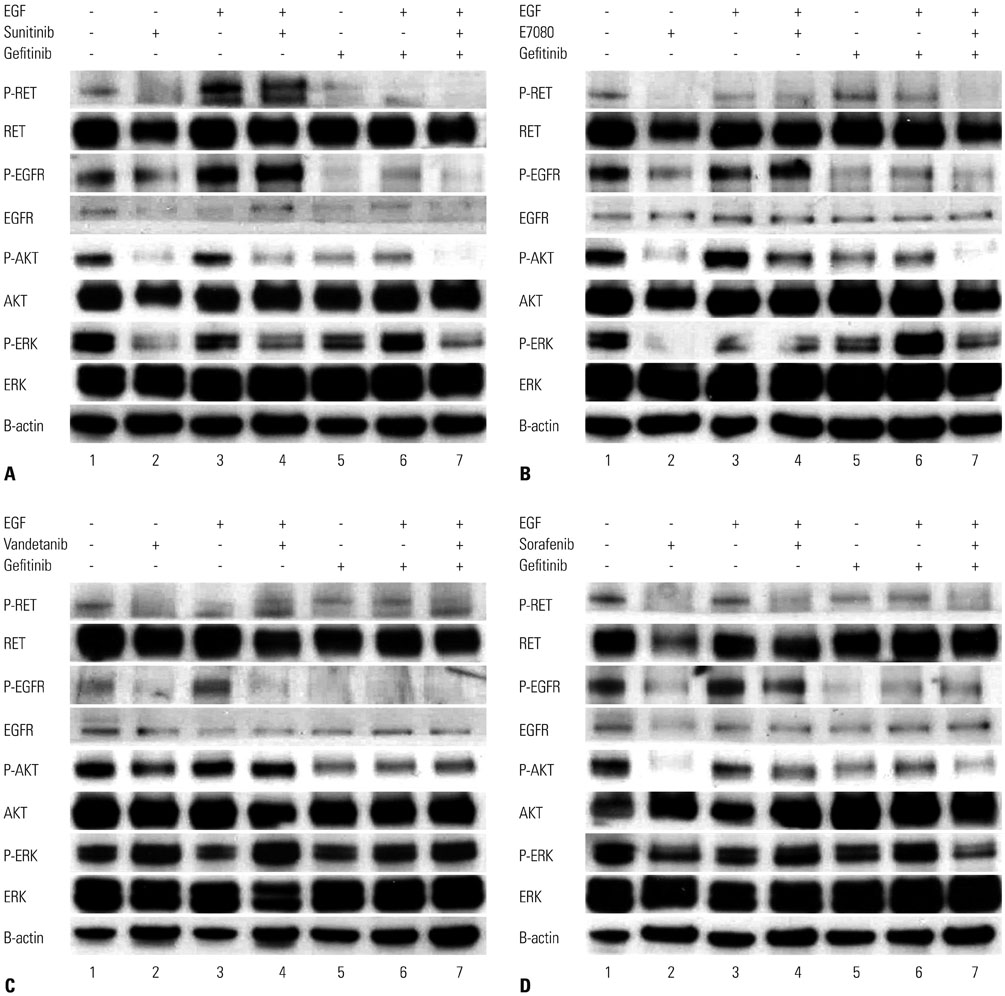
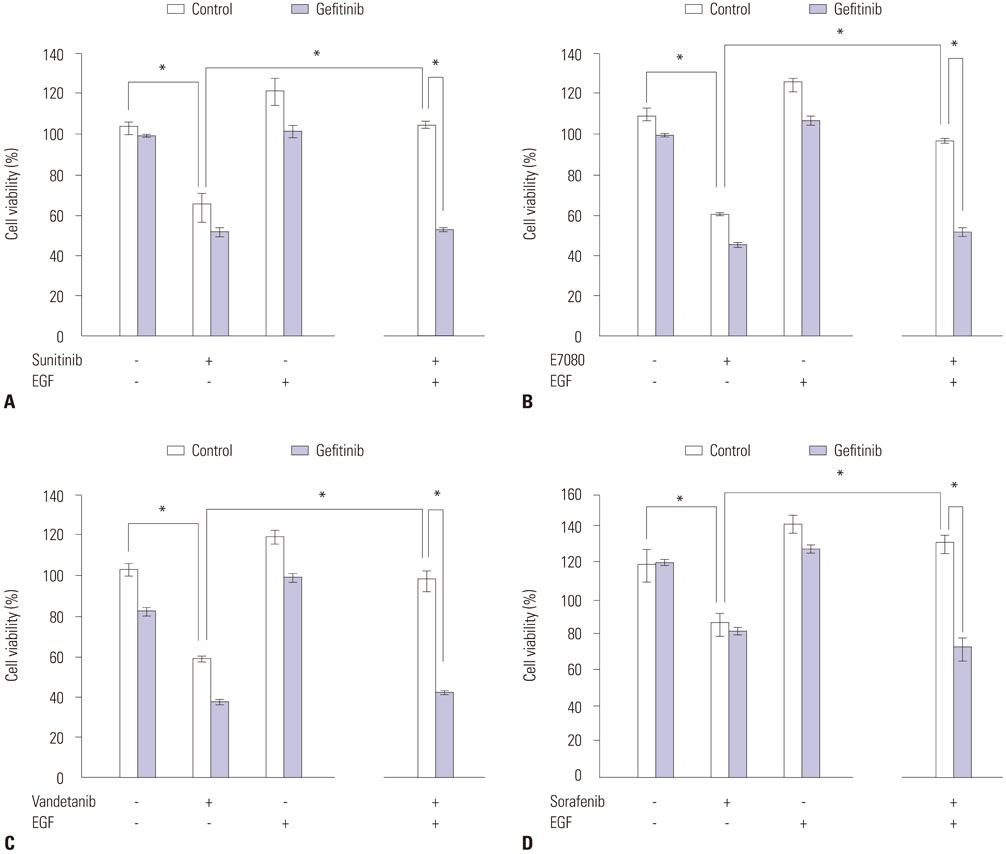
CCDC6-RET lung cancer cells were highly sensitive to RET inhibitors. EGF activated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and triggered resistance to sunitinib, E7080, vandetanib, and sorafenib by transducing bypass survival signaling through ERK and AKT. Reversible EGFR-TKI (gefitinib) resensitized cancer cells to RET inhibitors, even in the presence of EGF. Endothelial cells, which are known to produce EGF, decreased the sensitivity of CCDC6-RET lung cancer cells to RET inhibitors, an effect that was inhibited by EGFR small interfering RNA (siRNA), anti-EGFR antibody (cetuximab), and EGFR-TKI (Iressa). HGF had relatively little effect on the sensitivity to RET inhibitors.
CONCLUSION
EGF could trigger resistance to RET inhibition in CCDC6-RET lung cancer cells, and endothelial cells may confer resistance to RET inhibitors by EGF. E7080 and other RET inhibitors may provide therapeutic benefits in the treatment of RET-positive lung cancer patients.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma/drug therapy/*genetics
Cell Line, Tumor
Cetuximab/pharmacology
Drug Resistance, Neoplasm/drug effects/*genetics
Epidermal Growth Factor/metabolism/*pharmacology
*Gene Rearrangement
Hepatocyte Growth Factor/*pharmacology
Humans
Indoles/pharmacology
Lung Neoplasms/drug therapy/*genetics
MAP Kinase Signaling System
*Mutation
Niacinamide/analogs & derivatives/pharmacology
Phenylurea Compounds/pharmacology
Piperidines/pharmacology
Protein Kinase Inhibitors/therapeutic use
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-ret/*antagonists & inhibitors/genetics
Pyrroles/pharmacology
Quinazolines/pharmacology
RNA, Small Interfering/pharmacology
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor/genetics/metabolism
Signal Transduction/drug effects
fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase 3/metabolism
Cetuximab
Epidermal Growth Factor
Hepatocyte Growth Factor
Indoles
Phenylurea Compounds
Piperidines
Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-ret
Pyrroles
Niacinamide
Quinazolines
RNA, Small Interfering
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase 3
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2129–2139.
Article2. Bergethon K, Shaw AT, Ou SH, Katayama R, Lovly CM, McDonald NT, et al. ROS1 rearrangements define a unique molecular class of lung cancers. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30:863–870.3. Tanizaki J, Okamoto I, Okabe T, Sakai K, Tanaka K, Hayashi H, et al. Activation of HER family signaling as a mechanism of acquired resistance to ALK inhibitors in EML4-ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012; 18:6219–6226.
Article4. Eng C. RET proto-oncogene in the development of human cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999; 17:380–393.5. Wang R, Hu H, Pan Y, Li Y, Ye T, Li C, et al. RET fusions define a unique molecular and clinicopathologic subtype of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30:4352–4359.
Article6. Kohno T, Ichikawa H, Totoki Y, Yasuda K, Hiramoto M, Nammo T, et al. KIF5B-RET fusions in lung adenocarcinoma. Nat Med. 2012; 18:375–377.
Article7. Lipson D, Capelletti M, Yelensky R, Otto G, Parker A, Jarosz M, et al. Identification of new ALK and RET gene fusions from colorectal and lung cancer biopsies. Nat Med. 2012; 18:382–384.
Article8. Takeuchi K, Soda M, Togashi Y, Suzuki R, Sakata S, Hatano S, et al. RET, ROS1 and ALK fusions in lung cancer. Nat Med. 2012; 18:378–381.
Article9. Drilon A, Wang L, Hasanovic A, Suehara Y, Lipson D, Stephens P, et al. Response to Cabozantinib in patients with RET fusion-positive lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Discov. 2013; 3:630–635.
Article10. Oxnard GR, Arcila ME, Chmielecki J, Ladanyi M, Miller VA, Pao W, et al. New strategies in overcoming acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17:5530–5537.
Article11. Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, Ueno T, Takashima J, Nakajima T, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in lung cancer that confer resistance to ALK inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:1734–1739.
Article12. Katayama R, Shaw AT, Khan TM, Mino-Kenudson M, Solomon BJ, Halmos B, et al. Mechanisms of acquired crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung Cancers. Sci Transl Med. 2012; 4:120ra17.
Article13. Alderton GK. The haves and the have nots. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012; 12:505.
Article14. Wilson TR, Fridlyand J, Yan Y, Penuel E, Burton L, Chan E, et al. Widespread potential for growth-factor-driven resistance to anticancer kinase inhibitors. Nature. 2012; 487:505–509.
Article15. Janku F, Stewart DJ, Kurzrock R. Targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer--is it becoming a reality? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010; 7:401–414.
Article16. Meert AP, Martin B, Delmotte P, Berghmans T, Lafitte JJ, Mascaux C, et al. The role of EGF-R expression on patient survival in lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Eur Respir J. 2002; 20:975–981.
Article17. Matsubara D, Kanai Y, Ishikawa S, Ohara S, Yoshimoto T, Sakatani T, et al. Identification of CCDC6-RET fusion in the human lung adenocarcinoma cell line, LC-2/ad. J Thorac Oncol. 2012; 7:1872–1876.
Article18. Yamada T, Takeuchi S, Nakade J, Kita K, Nakagawa T, Nanjo S, et al. Paracrine receptor activation by microenvironment triggers bypass survival signals and ALK inhibitor resistance in EML4-ALK lung cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2012; 18:3592–3602.
Article19. Sasaki T, Koivunen J, Ogino A, Yanagita M, Nikiforow S, Zheng W, et al. A novel ALK secondary mutation and EGFR signaling cause resistance to ALK kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2011; 71:6051–6060.
Article20. Shaw AT, Engelman JA. ALK in lung cancer: past, present, and future. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:1105–1111.21. Ohashi K, Sequist LV, Arcila ME, Moran T, Chmielecki J, Lin YL, et al. Lung cancers with acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors occasionally harbor BRAF gene mutations but lack mutations in KRAS, NRAS, or MEK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109:E2127–E2133.22. Matsui J, Funahashi Y, Uenaka T, Watanabe T, Tsuruoka A, Asada M, et al. Multi-kinase inhibitor E7080 suppresses lymph node and lung metastases of human mammary breast tumor MDA-MB-231 via inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-receptor (VEGF-R) 2 and VEGF-R3 kinase. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14:5459–5465.
Article23. Yamada K, Yamamoto N, Yamada Y, Nokihara H, Fujiwara Y, Hirata T, et al. Phase I dose-escalation study and biomarker analysis of E7080 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17:2528–2537.
Article24. Chang H, Zhang X, Cho BC, Park HJ, Kim JH. Tumor MET expression profile predicts the outcome of non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Thorac Cancer. 2014; 5:517–524.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- RET Fusion Genes in Korean Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- RET: A Multi-Faceted Gene in Human Cancer
- A Case of Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Cancer with RET G691S Polymorphism
- Expression of RET in Thyroid Diseases of a Korean Population
- Expanded Access Program Pralsetinib in Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer with Rearranged during Transfection (RET) Gene Rearrangement