J Bone Metab.
2016 Nov;23(4):207-214. 10.11005/jbm.2016.23.4.207.
Attenuation of RANKL-induced Osteoclast Formation via p38-mediated NFATc1 Signaling Pathways by Extract of Euphorbia Lathyris L
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Pharmacy, Sookmyung Women's University, Seoul, Korea. myim@sm.ac.kr
- KMID: 2361582
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2016.23.4.207
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
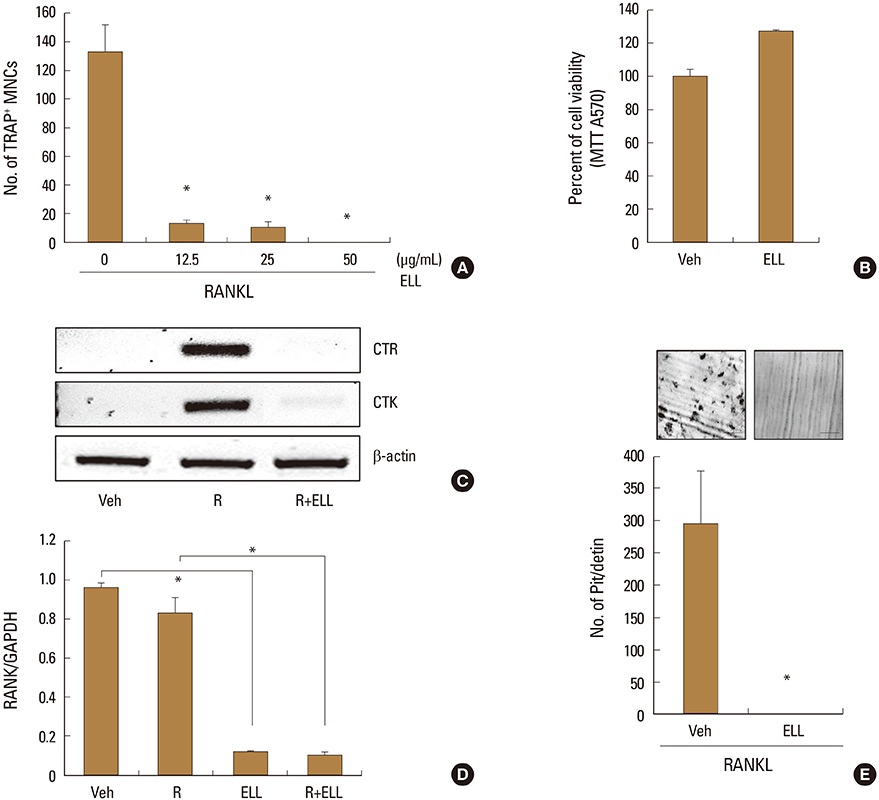
Osteoclasts are the only cell type capable of breaking down bone matrix, and its excessive activation is responsible for the development of bone-destructive diseases. Euphorbia lathyris L. (ELL) is an herbal plant that belongs to the Euphorbiaceae family. This study investigated the effects of the methanol extract of the aerial part of ELL on receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclast formation and signaling pathways.
METHODS
Osteoclasts were formed by co-culturing mouse bone marrow with osteoblasts or by culturing mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMMs) with macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) and RANKL. Bone resorption assays were performed using dentine slices. The expression level of mRNA was analyzed by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or reverse transcription (RT)-PCR. Western blotting assays were performed to detect the expression or activation level of proteins.
RESULTS
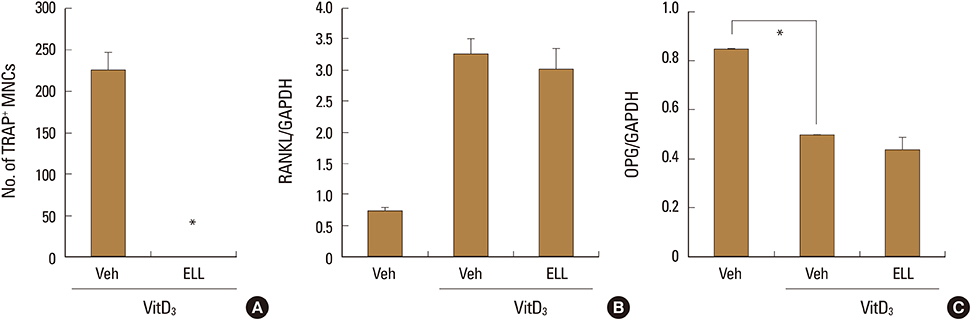
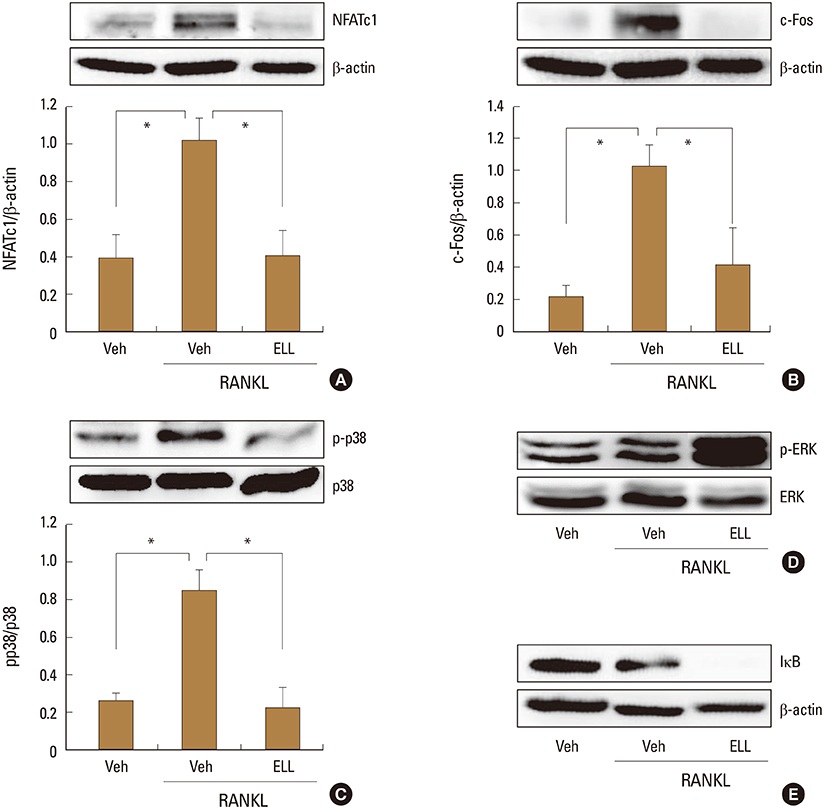
ELL inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclast formation without cytotoxicity. Furthermore, the RANKL-stimulated bone resorption was diminished by ELL. Mechanistically, ELL blocked the RANKL-triggered p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation, which resulted in the suppression of the expression of c-Fos and nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFATc1). In osteoblasts, ELL had little effect on the mRNA expression of RANKL and osteoprotegerin (OPG).
CONCLUSIONS
The present data suggest that ELL has an inhibitory effect on osteoclast differentiation and function via downregulation of the p38/c-Fos/NFATc1 signaling pathways. Thus, ELL could be useful for the treatment of bone diseases associated with excessive bone resorption.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Blotting, Western
Bone Diseases
Bone Marrow
Bone Matrix
Bone Resorption
Dentin
Down-Regulation
Euphorbia*
Euphorbiaceae
Humans
Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
Macrophages
Methanol
Mice
Osteoblasts
Osteoclasts*
Osteoprotegerin
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Phosphorylation
Plants
Protein Kinases
RANK Ligand
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Reverse Transcription
RNA, Messenger
T-Lymphocytes
Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
Methanol
Osteoprotegerin
Protein Kinases
RANK Ligand
RNA, Messenger
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tanaka Y, Nakayamada S, Okada Y. Osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone remodeling and inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2005; 4:325–328.
Article2. Teitelbaum SL. Bone resorption by osteoclasts. Science. 2000; 289:1504–1508.
Article3. Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, et al. Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev. 1999; 20:345–357.
Article4. Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003; 423:337–342.
Article5. Arai F, Miyamoto T, Ohneda O, et al. Commitment and differentiation of osteoclast precursor cells by the sequential expression of c-Fms and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB (RANK) receptors. J Exp Med. 1999; 190:1741–1754.
Article6. Kong YY, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, et al. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature. 1999; 397:315–323.
Article7. Darnay BG, Ni J, Moore PA, et al. Activation of NF-kappaB by RANK requires tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6 and NF-kappaB-inducing kinase. Identification of a novel TRAF6 interaction motif. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:7724–7731.
Article8. Asagiri M, Takayanagi H. The molecular understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 2007; 40:251–264.
Article9. Feng X. RANKing intracellular signaling in osteoclasts. IUBMB Life. 2005; 57:389–395.
Article10. Grigoriadis AE, Wang ZQ, Cecchini MG, et al. c-Fos: a key regulator of osteoclast-macrophage lineage determination and bone remodeling. Science. 1994; 266:443–448.
Article11. Kim K, Kim JH, Lee J, et al. Nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 induces osteoclast-associated receptor gene expression during tumor necrosis factor-related activation-induced cytokine-mediated osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280:35209–35216.
Article12. Kim JH, Kim N. Regulation of NFATc1 in osteoclast differentiation. J Bone Metab. 2014; 21:233–241.
Article13. Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 2002; 3:889–901.
Article14. Shi QW, Su XH, Kiyota H. Chemical and pharmacological research of the plants in genus Euphorbia. Chem Rev. 2008; 108:4295–4327.
Article15. Takami M, Cho ES, Lee SY, et al. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors stimulate osteoclast formation via TRANCE/RANKL expression in osteoblasts: possible involvement of ERK and p38 MAPK pathways. FEBS Lett. 2005; 579:832–838.
Article16. O'Brien CA, Gubrij I, Lin SC, et al. STAT3 activation in stromal/osteoblastic cells is required for induction of the receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand and stimulation of osteoclastogenesis by gp130-utilizing cytokines or interleukin-1 but not 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 or parathyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:19301–19308.17. Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, et al. Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell. 1997; 89:309–319.
Article18. Ikeda F, Nishimura R, Matsubara T, et al. Critical roles of c-Jun signaling in regulation of NFAT family and RANKL-regulated osteoclast differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2004; 114:475–484.
Article19. Matsumoto M, Sudo T, Saito T, et al. Involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in osteoclastogenesis mediated by receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL). J Biol Chem. 2000; 275:31155–31161.
Article20. Mizukami J, Takaesu G, Akatsuka H, et al. Receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) activates TAK1 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase through a signaling complex containing RANK, TAB2, and TRAF6. Mol Cell Biol. 2002; 22:992–1000.
Article21. Takayanagi H. Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007; 7:292–304.
Article22. Walsh MC, Kim N, Kadono Y, et al. Osteoimmunology: interplay between the immune system and bone metabolism. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006; 24:33–63.
Article23. Franzoso G, Carlson L, Xing L, et al. Requirement for NF-kappaB in osteoclast and B-cell development. Genes Dev. 1997; 11:3482–3496.24. Iotsova V, Caamaño J, Loy J, et al. Osteopetrosis in mice lacking NF-kappaB1 and NF-kappaB2. Nat Med. 1997; 3:1285–1289.25. Chang EJ, Kim HJ, Ha J, et al. Hyaluronan inhibits osteoclast differentiation via Toll-like receptor 4. J Cell Sci. 2007; 120:166–176.
Article26. Humphrey MB, Nakamura MC. A Comprehensive review of immunoreceptor regulation of osteoclasts. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016; 51:48–58.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Iris Koreana NAKAI Inhibits Osteoclast Formation via p38-Mediated Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells 1 Signaling Pathway
- Effects of Liriopis Tuber Water Extract on RANKL-induced Osteoclast Differentiation
- Fexaramine Inhibits Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand-induced Osteoclast Formation via Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells Signaling Pathways
- Limonium tetragonum Reduces Osteoclast Formation and Resorption through Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase-c-Fos-NFATc1 Signaling Pathways
- The Molecular Mechanism of Baicalin on RANKL-induced Osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 Cells