Anat Cell Biol.
2016 Sep;49(3):189-198. 10.5115/acb.2016.49.3.189.
Rhus verniciflua Stokes attenuates cholestatic liver cirrhosis-induced interstitial fibrosis via Smad3 down-regulation and Smad7 up-regulation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. jjzzy@konyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Dermatology, Chung-Ang University R&D Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Lifetree Co., Ltd., Suwon, Korea.
- 4Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Konyang University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. medidrug@kyuh.ac.kr
- 5Myunggok Research Institute, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2353344
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2016.49.3.189
Abstract
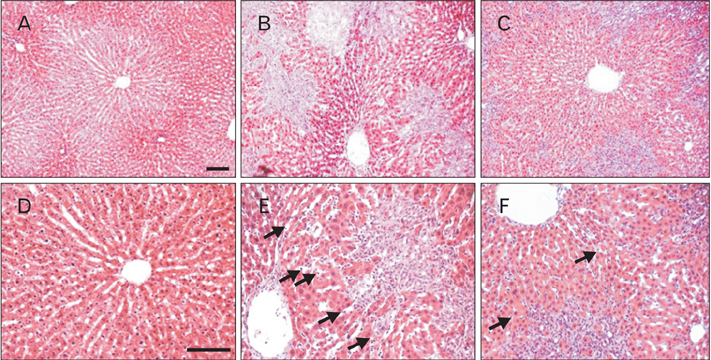
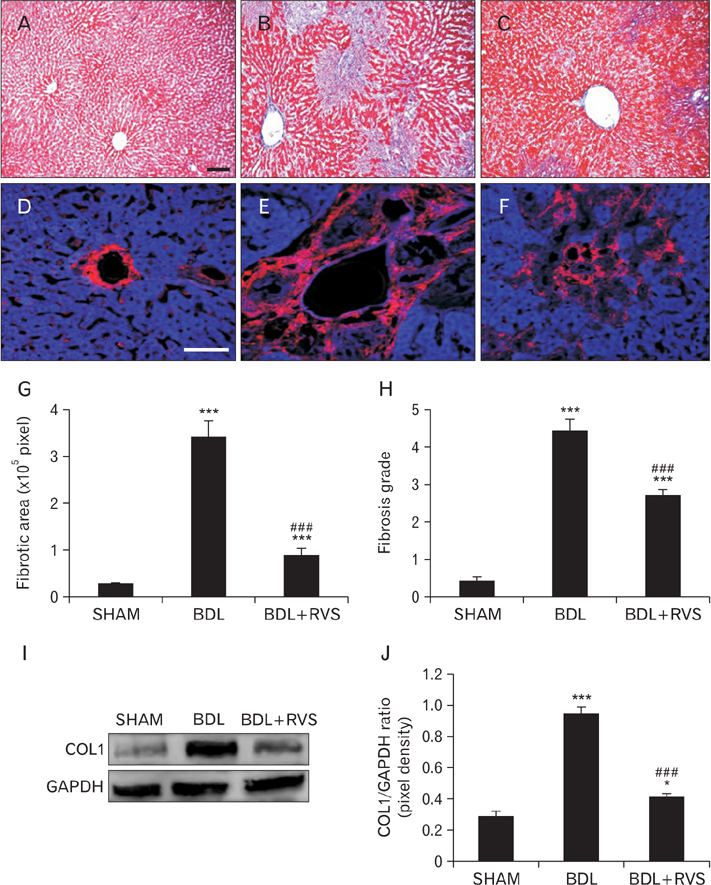
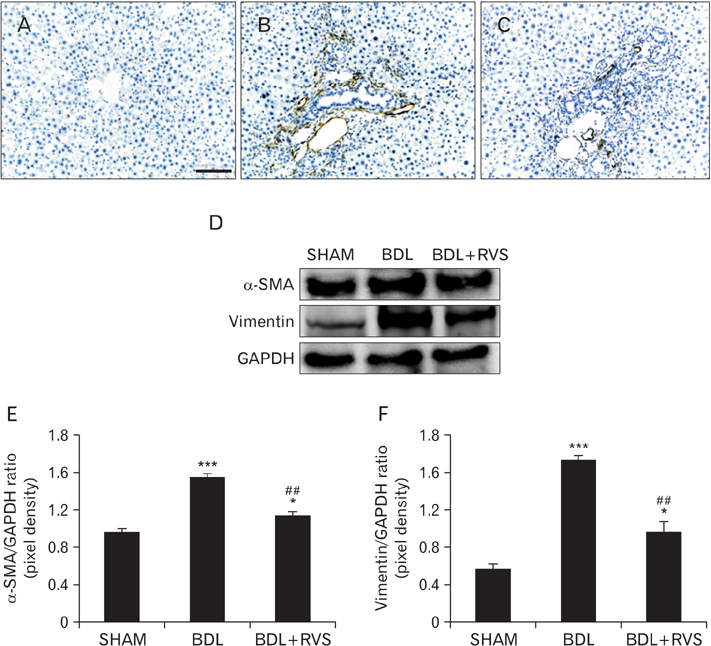
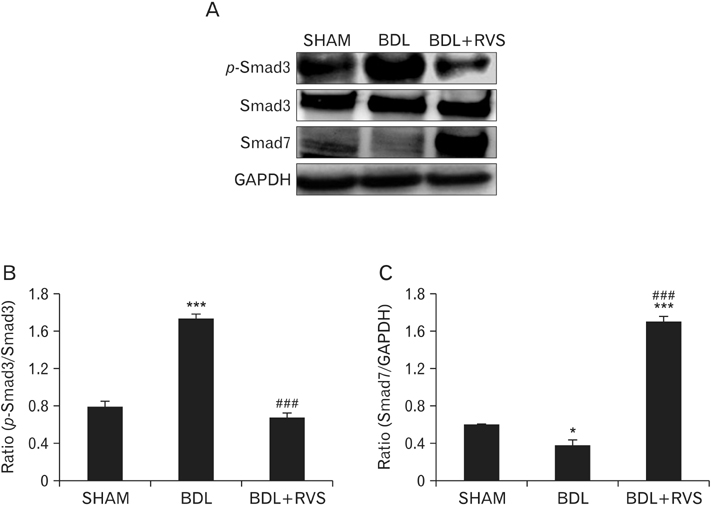
- Cholestatic liver cirrhosis (CLC) eventually proceeds to end-stage liver failure by mediating overwhelming deposition of collagen, which is produced by activated interstitial myofibroblasts. Although the beneficial effects of Rhus verniciflua Stokes (RVS) on various diseases are well-known, its therapeutic effect and possible underlying mechanism on interstitial fibrosis associated with CLC are not elucidated. This study was designed to assess the protective effects of RVS and its possible underlying mechanisms in rat models of CLC established by bile duct ligation (BDL). We demonstrated that BDL markedly elevated the serological parameters such as aspartate aminotransferase, alanine transaminase, total bilirubin, and direct bilirubin, all of which were significantly attenuated by the daily uptake of RVS (2 mg/kg/day) for 28 days (14 days before and after operation) via intragastric route. We observed that BDL drastically induced the deterioration of liver histoarchitecture and excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM), both of which were significantly attenuated by RVS. In addition, we revealed that RVS inhibited BDL-induced proliferation and activation of interstitial myofibroblasts, a highly suggestive cell type for ECM production, as shown by immunohistochemical and semi-quantitative detection of α-smooth muscle actin and vimentin. Finally, we demonstrated that the anti-fibrotic effect of RVS was associated with the inactivation of Smad3, the key downstream target of a major fibrogenic cytokine, i.e., transforming growth factor β (TGF-β). Simultaneously, we also found that RVS reciprocally increased the expression of Smad7, a negative regulatory protein of the TGF-β/Smad3 pathway. Taken together, these results suggested that RVS has a therapeutic effect on CLC, and these effects are, at least partly, due to the inhibition of liver fibrosis by the downregulation of Smad3 and upregulation of Smad7.
MeSH Terms
-
Actins
Alanine Transaminase
Aspartate Aminotransferases
Bile Ducts
Bilirubin
Collagen
Down-Regulation*
Extracellular Matrix
Fibrosis*
Ligation
Liver Cirrhosis
Liver Failure
Liver*
Models, Animal
Myofibroblasts
Negotiating
Rhus*
Transforming Growth Factors
Up-Regulation*
Vimentin
Actins
Alanine Transaminase
Aspartate Aminotransferases
Bilirubin
Collagen
Transforming Growth Factors
Vimentin
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Cytological, histochemical, and ultrastructural study of human foetal liver of various gestation with future implications in segmental resection: an anatomical perspective
Arpan Haldar, Manisha Rajanand Gaikwad, Apurba Patra, Soumya C. Bhattacharya
Anat Cell Biol. 2022;55(1):92-99. doi: 10.5115/acb.21.152.
Reference
-
1. Feld JJ, Heathcote EJ. Epidemiology of autoimmune liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003; 18:1118–1128.2. Iredale JP. Cirrhosis: new research provides a basis for rational and targeted treatments. BMJ. 2003; 327:143–147.3. Schuppan D, Ruehl M, Somasundaram R, Hahn EG. Matrix as a modulator of hepatic fibrogenesis. Semin Liver Dis. 2001; 21:351–372.4. Bataller R, Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115:209–218.5. Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:1655–1669.6. Sasaki T, Ohta S, Kamogawa A, Shinoda M. Protective effects of various Chinese traditional medicines against experimental cholestasis. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1990; 38:513–516.7. Dooley S, Hamzavi J, Breitkopf K, Wiercinska E, Said HM, Lorenzen J, Ten Dijke P, Gressner AM. Smad7 prevents activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis in rats. Gastroenterology. 2003; 125:178–191.8. Dooley S, Hamzavi J, Ciuclan L, Godoy P, Ilkavets I, Ehnert S, Ueberham E, Gebhardt R, Kanzler S, Geier A, Breitkopf K, Weng H, Mertens PR. Hepatocyte-specific Smad7 expression attenuates TGF-beta-mediated fibrogenesis and protects against liver damage. Gastroenterology. 2008; 135:642–659.9. Meindl-Beinker NM, Dooley S. Transforming growth factor-beta and hepatocyte transdifferentiation in liver fibrogenesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:Suppl 1. S122–S127.10. Kershenobich Stalnikowitz D, Weissbrod AB. Liver fibrosis and inflammation: a review. Ann Hepatol. 2003; 2:159–163.11. Szabo G, Mandrekar P, Dolganiuc A. Innate immune response and hepatic inflammation. Semin Liver Dis. 2007; 27:339–350.12. Luper S. A review of plants used in the treatment of liver disease: part 1. Altern Med Rev. 1998; 3:410–421.13. Kitts DD, Lim KT. Antitumorigenic and cytotoxic properties of an ethanol extract derived from Rhus verniciflua Stokes (RVS). J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2001; 64:357–371.14. Lim KT, Hu C, Kitts DD. Antioxidant activity of a Rhus verniciflua Stokes ethanol extract. Food Chem Toxicol. 2001; 39:229–237.15. Jeon WK, Kim JH, Lee HW, Ko BS, Kim HK. Effects of Rhus verniciflua Stokes (RVS) extract on diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mouse. Korean J Pharmacogn. 2003; 34:339–343.16. Kim MJ, Choi WC, Barshinikov AM, Kobayashi A. Anticancer and antioxidant activity of allergen-removed extract in Rhus verniciflua Stokes. Korean J Med Crop Sci. 2002; 10:288–293.17. Kim IT, Park YM, Shin KM, Ha J, Choi J, Jung HJ, Park HJ, Lee KT. Anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects of the extract from Kalopanax pictus, Pueraria thunbergiana and Rhus verniciflua. J Ethnopharmacol. 2004; 94:165–173.18. Park KY, Jung GO, Lee KT, Choi J, Choi MY, Kim GT, Jung HJ, Park HJ. Antimutagenic activity of flavonoids from the heartwood of Rhus verniciflua. J Ethnopharmacol. 2004; 90:73–79.19. Ko JH, Lee SJ, Lim KT. Rhus verniciflua Stokes glycoprotein (36kDa) has protective activity on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2006; 22:8–14.20. Szuster-Ciesielska A, Mizerska-Dudka M, Daniluk J, Kandefer-Szerszeń M. Butein inhibits ethanol-induced activation of liver stellate cells through TGF-beta, NFkappaB, p38, and JNK signaling pathways and inhibition of oxidative stress. J Gastroenterol. 2013; 48:222–237.21. Han QB, Song JZ, Qiao CF, Wong L, Xu HX. Preparative separation of gambogic acid and its C-2 epimer using recycling high-speed counter-current chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2006; 1127:298–301.22. Kim SA, Kim SH, Kim IS, Lee D, Dong MS, Na CS, Nhiem NX, Yoo HH. Simultaneous determination of bioactive phenolic compounds in the stem extract of Rhus verniciflua stokes by high performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2013; 141:3813–3819.23. Tag CG, Sauer-Lehnen S, Weiskirchen S, Borkham-Kamphorst E, Tolba RH, Tacke F, Weiskirchen R. Bile duct ligation in mice: induction of inflammatory liver injury and fibrosis by obstructive cholestasis. J Vis Exp. 2015; (96):52438.24. Fischer AH, Jacobson KA, Rose J, Zeller R. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. CSH Protoc. 2008; 2008:pdb.prot4986.25. Goldner J. A modification of the masson trichrome technique for routine laboratory purposes. Am J Pathol. 1938; 14:237–243.26. Knodell RG, Ishak KG, Black WC, Chen TS, Craig R, Kaplowitz N, Kiernan TW, Wollman J. Formulation and application of a numerical scoring system for assessing histological activity in asymptomatic chronic active hepatitis. Hepatology. 1981; 1:431–435.27. Kim JH, Yu KS, Jeong JH, Lee NS, Lee JH, Jeong YG, Yoo YC, Han SY. All-trans-retinoic acid rescues neurons after global ischemia by attenuating neuroinflammatory reactions. Neurochem Res. 2013; 38:2604–2615.28. Rigato I, Cravatari M, Avellini C, Ponte E, Crocè SL, Tiribelli C. Drug-induced acute cholestatic liver damage in a patient with mutation of UGT1A1. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 4:403–408.29. Shah B, Shah G. Antifibrotic effect of heparin on liver fibrosis model in rats. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 3:86–92.30. Scott S, Thompson J. Adverse drug reactions. Anaesth Intensive Care Med. 2014; 15:245–249.31. Kashaw V, Nema AK, Agarwal A. Hepatoprotective prospective of herbal drugs and their vesicular carriers: a review. Int J Res Pharm Biomed Sci. 2011; 2:360–374.32. Zhang A, Sun H, Wang X. Recent advances in natural products from plants for treatment of liver diseases. Eur J Med Chem. 2013; 63:570–577.33. Balandrin MF, Klocke JA, Wurtele ES, Bollinger WH. Natural plant chemicals: sources of industrial and medicinal materials. Science. 1985; 228:1154–1160.34. Srivastava J, Lambert J, Vietmeyer N. Medicinal plants: an expanding role in development. World Bank Technical Paper 320. Washington, DC: World Bank Publications;1996.35. Kim TJ. Korean resource plants. Vol. II. Seoul: Seoul National University Press;1996. p. 292–297.36. Hong DH, Han SB, Lee CW, Park SH, Jeon YJ, Kim MJ, Kwak SS, Kim HM. Cytotoxicity of urushiols isolated from sap of Korean lacquer tree (Rhus vernicifera Stokes). Arch Pharm Res. 1999; 22:638–641.37. Namba T. Coloured illustrations of Wakan-Yaku. Osaka: Hoikusha Publishing Co.;1980.38. Lee JC, Kim J, Lim KT, Yang MS, Jang YS. Ethanol eluted extract of Rhus verniciflua Stokes showed both antioxidant and cytotoxic effects on mouse thymocytes depending on the dose and time of the treatment. BMB Rep. 2001; 34:250–258.39. Lee JC, Lim KT. Screening of antioxidant and antimicrobial effects from Rhus verniciflua Stokes (RVS) ethanolic extract. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2000; 9:139–145.40. Lee JD, Huh JE, Jeon G, Yang HR, Woo HS, Choi DY, Park DS. Flavonol-rich RVHxR from Rhus verniciflua Stokes and its major compound fisetin inhibits inflammation-related cytokines and angiogenic factor in rheumatoid arthritic fibroblast-like synovial cells and in vivo models. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009; 9:268–276.41. Lee JC, Jung HY, Lim KT. Effects of Rhus verniciflua Stokes (RVS) on the plasma level of cholesterol and tumor growth in mouse. J Toxicol Public Health. 1999; 15:169–175.42. Cho N, Choi JH, Yang H, Jeong EJ, Lee KY, Kim YC, Sung SH. Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids isolated from Rhus verniciflua in neuronal HT22 and microglial BV2 cell lines. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012; 50:1940–1945.43. Choi KC, Chung WT, Kwon JK, Jang YS, Yu JY, Park SM, Lee JC. Chemoprevention of a flavonoid fraction from Rhus verniciflua Stokes on aflatoxin B1-induced hepatic damage in mice. J Appl Toxicol. 2011; 31:150–156.44. Lee JC, Lim KT, Jang YS. Identification of Rhus verniciflua Stokes compounds that exhibit free radical scavenging and anti-apoptotic properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002; 1570:181–191.45. Park HJ, Lee KT, Park KY, Han GY, Jung MH, Choi J. Protective mechanism of flavonoids isolated from Rhus verniciflua on the biliary liver fibrosis in rat. Korean J Life Sci. 2002; 12:332–339.46. Faubion WA, Guicciardi ME, Miyoshi H, Bronk SF, Roberts PJ, Svingen PA, Kaufmann SH, Gores GJ. Toxic bile salts induce rodent hepatocyte apoptosis via direct activation of Fas. J Clin Invest. 1999; 103:137–145.47. Patel T, Bronk SF, Gores GJ. Increases of intracellular magnesium promote glycodeoxycholate-induced apoptosis in rat hepatocytes. J Clin Invest. 1994; 94:2183–2192.48. Fernández M, Semela D, Bruix J, Colle I, Pinzani M, Bosch J. Angiogenesis in liver disease. J Hepatol. 2009; 50:604–620.49. Zavadil J, Bottinger EP. TGF-beta and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions. Oncogene. 2005; 24:5764–5774.50. Hernandez-Gea V, Friedman SL. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2011; 6:425–456.51. Maher JJ. Interactions between hepatic stellate cells and the immune system. Semin Liver Dis. 2001; 21:417–426.52. Mehal WZ, Friedman SL. The role of inflammation and immunity in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. In : Gershwin ME, Vierling JM, Manns MP, editors. Liver Immunology. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press;2007. p. 111–121.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Smads as therapeutic targets for chronic kidney disease
- Experimental Study on Latent Sensitivity to Rhus Trees
- Urushiol V Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Enhances Antitumor Activity of 5-FU in Human Colon Cancer Cells by Downregulating FoxM1
- The Effect of Rhus verniciflua Stokes Extracts on Photo-Aged Mouse Skin
- Protective effect of Rhus verniciflua Stokes extract in an experimental model of post-menopausal osteoporosis