J Korean Diabetes Assoc.
2006 Nov;30(6):466-475.
Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Glimepiride/Metformin Fixed Combination Versus Free Combination in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Kangnam St. Mary's hospital,, The Catholic University of Korea, Korea.
- 2Keimyung University Medical Center, Korea.
- 3Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea.
- 4Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea.
- 5Seoul National University Hospital, Korea.
- 6St. Vincent Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Korea.
- 7Ajou University Hospital, Korea.
- 8Severance Hospital, Yonsei University, Korea.
- 9Yongdong Severance Hospital, Yonsei University, Korea.
- 10Yeongnam University Medical Center, Korea.
- 11Wonju Christian Hospital, Korea.
- 12Inha Universtiy Hospital, Korea.
- 13Chonbuk National University Hospital, Korea.
- 14Pusan National Universtiy Hospital, Korea.
- 15Handok Pharmaceuticals Co., LTD., Korea.
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Failure to manage diabetes mellitus receiving monotherapy increases as the duration of the disease is protracted, and in many cases it becomes inevitable to introduce combined therapies. However, compliance of the patients tends to decrease. We conducted a clinical study to compare the efficacy and safety of preconstituted and fixed combination therapy of glimepiride plus metformin to those of free combination therapy.
METHODS
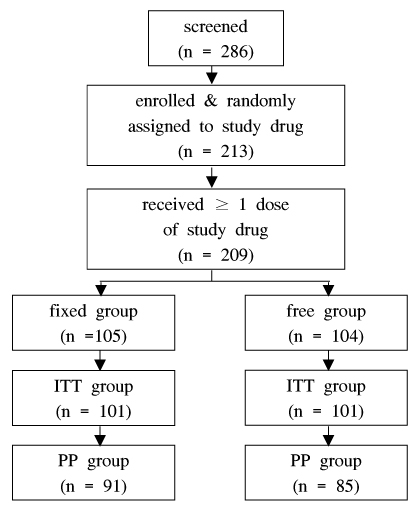
Two hundred and thirteen patients with type 2 diabetes who had been diagnosed at least six months ago were randomly assigned either to a fixed group or a free group. The initial dosage was chosen according to the previous treatment history and then adjusted every two weeks following a predefined titration algorithm to meet the target mean fasting glucose levels (140 mg/dL). The medications were given for 16 weeks. The primary endpoint was the change in HbA1c level from baseline to week 16. Various parameters were checked as secondary outcome measures and safety criteria.
RESULTS
HbA1c level of the fixed group and the free group decreased by 1.09% and 1.08%, respectively. The 95% CI of the changes' difference between the two groups (-0.21%, +0.19%) was within the predefined equivalence interval (-0.5%, +0.5%). Secondary outcome measures (the changes of fasting and postprandial plasma glucose level, response rate and compliance) and safety criteria (frequency of hypoglycemia and adverse reactions) were similar between the two groups.
CONCLUSION
Fixed combination of glimepiride/metformin is as effective and safe therapy as free combination in type 2 diabetes patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diabetes, 1995-2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care. 1998. 21:1414–1431.2. The Diabetes Control and Complication Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993. 329:977–986.3. United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study Group UKPDS 24. A 6-year, randomized, controlled trial comparing sulfonylurea, insulin and metformin therapy in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes that could not be controlled with diet therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1998. 28:165–175.4. United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study Group UKPDS 49. Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: progressive requirement for multiple therapies. JAMA. 1999. 281:2005–2012.5. DeFronzo RA, Goodman AM. Efficacy of metformin in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Eng J Med. 1995. 333(9):541–549.6. Hermann LS, Schersten B, Bitzen PO, Kjellstrom T, Lindgarde F, Melander A. Therapeutic comparison of metformin and sulfonylurea, alone and in various combinations. A double-blind controlled study. Diabetes Care. 1994. 17(10):1100–1109.7. Charpentier G, Fleury F, Kabir M, Vaur L, Halimi S. Improved glycemic control by addition of glimepiride to metformin monotherapy in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet Med. 2001. 18(10):828–834.8. Melikian C, White TJ, Vanderplas A, Dezii CM, Chang E. Adherence to oral antidiabetic therapy in a managed care organization: a comparison of monotherapy, combination therapy, and fixed-dose combination therapy. Clin Ther. 2002. 24(3):460–467.9. Del Prato S. Rationale for the association of sulfonylurea and insulin. Am J Med. 1991. 90:Suppl. 6A. 77S–82S.10. DeFronzo RA. Pharmacologic therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 1999. 131:281–303.11. Riddle M. Combining sulfonylureas and other oral agents. Am J Med. 2000. 108:Suppl. 6a. 15S–22S.12. Tosi F, Muggeo M, Brun E, Spiazzi G, Perobelli L, Zanolin E, Gori M, Coppini A, Moghetti P. Combination treatment with metformin and glibenclamide versus single-drug therapies in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blind, comparative study. Metabolism. 2003. 52(7):862–867.13. Mudaliar S, Henry RR. Combination therapy for type 2 diabetes. Endocr Pract. 1999. 5(4):208–219.14. Bell DS, Ovalle F. How long can insulin therapy be avoided in the patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus by use of a combination of metformin and a sulfonylurea? Endocr Pract. 2000. 6(4):293–295.15. Charpentier G. Oral combination therapy for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2002. 18:S70–S76.16. Van Gaal LF, De Leeuw IH. Rationale and options for combination therapy in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2003. 46:Suppl1. M44–M50.17. Hermann LS, Lindberg G, Lindblad U, Melander A. Efficacy, effectiveness and safety of sulphonylurea-metformin combination therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes and Metab. 2002. 4(5):296–304.18. Vanderpoel DR, Hussein MA, Watson-Heidari T, Perry A. Adherence to a fixed-dose combination of rosiglitazone maleate/metformin hydrochloride in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a retrospective database analysis. Clin Ther. 2004. 26(12):2066–2075.19. Howlett H, Porte F, Allavoine T, Kuhn T, Nicholson G. The development of an oral antidiabetic combination tablet: design, evaluation and clinical benefits for patients with type 2 diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin. 2003. 19(3):218–225.20. Davidson JA, Scheen AJ, Howlett HC. Tolerability profile of metformin/glibenclamide combination tablets (Glucovance): a new treatment for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drug Saf. 2004. 27(15):1205–1216.21. D'Argenzio R, Cavallo P, Merante D, Morelli A. Comparison of two treatment models in type-II diabetic patients with poor metabolic control Preformed combination of glibenclamide 2.5 mg + metformin 400 mg or mono-therapy with sulfonylurea at maximal doses? An evaluation at six months. Minerva Endocrinol. 1996. 21(3):101–110.22. Scheen AJ. Medication of the month. Glucovance in type 2 diabetes, a fixed combination of metformin-glibenclamide for the treatment of a bipolar metabolic disease. Rev Med Liege. 2003. 58(6):448–452.23. Marre M, Howlett H, Lehertt P, Allavoine T. Improved glycaemic control with metformin-glibenclamide combined tablet therapy (Glucovance) in type 2 diabetic patients inadequately controlled on metformin. Diabet Med. 2002. 19:673–680.24. Bokhari SU, Gopal UM, Duckworth WC. Beneficial effects of a glyburide/metformin combination preparation in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Med Sci. 2003. 325(2):66–69.25. Blonde L, Rosenstock J, Mooradian AD, Piper BA, Henry D. Glyburide/metformin combination product is safe and efficacious in patients with type 2 diabetes failing sulphonylurea therapy. Diabetes Obes and Metab. 2002. 4:368–375.26. Erle G, Lovise S, Stocchiero C, Lora L, Coppini A, Marchetti P, Merante D. A comparison of preconstituted, fixed combinations of low-dose glyburide plus metformin versus high-dose glyburide alone in the treatment of type 2 diabetic patients. Acta Diabetol. 1999. 36:61–65.27. Goldstein BJ, Pans M, Rubin CJ. Multicenter, randomized, double-masked, parallel-group assessment of simultaneous glipizide/metformin as second-line pharmacologic treatment for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus that is inadequately controlled by a sulfonylurea. Clin Ther. 2003. 25(3):890–903.28. Charpentier G, Jolchine IE, Kabir M. Addition of glimepiride significantly improves glycaemic control in type 2 diabetic patients insufficiently controlled on metformin. Diabetes. 1998. 47:Suppl.1. A351.29. Horton ES, Foley JE, Shen SG, Baron MA. Efficacy and tolerability of initial combination therapy with nateglinide and metformin in treatment-nave patients with type 2 diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin. 2004. 20(6):883–889.30. Bell DS, Ovalle F. Outcomes of initiation of therapy with once-daily combination of a thiazolidinedione and a biguanide at an early stage of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2004. 6(5):363–366.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy and Safety of Pioglitazone versus Glimepiride after Metformin and Alogliptin Combination Therapy: A Randomized, Open-Label, Multicenter, Parallel-Controlled Study
- Letter: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43;276-86)
- Comparison of Vildagliptin-Metformin and Glimepiride-Metformin Treatments in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Efficacy of Sitagliptin When Added to Ongoing Therapy in Korean Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Efficacy and Safety of Alogliptin-Pioglitazone Combination for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Poorly Controlled with Metformin: A Multicenter, Double-Blind Randomized Trial