Diabetes Metab J.
2011 Oct;35(5):529-535. 10.4093/dmj.2011.35.5.529.
Comparison of Vildagliptin-Metformin and Glimepiride-Metformin Treatments in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. tgohkjs@chungbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 1857509
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.5.529
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The present study investigated the efficacy and safety of vildagliptin-metformin treatment compared to those of glimepiride-metformin treatment for type 2 diabetes.
METHODS
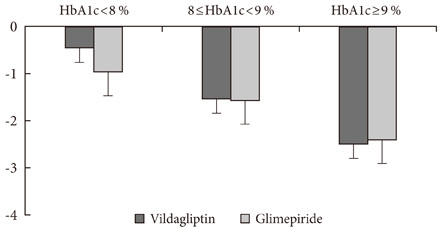
In a randomized, open-label, comparative study, 106 patients with type 2 diabetes were enrolled. The primary endpoint was a reduction in HbA1c from baseline and secondary endpoints included fasting plasma glucose (FPG) or 2-hour postprandial glucose (2h-PPG) reduction from baseline, as well as HbA1c responder rate and HbA1c reduction according to baseline HbA1c category.
RESULTS
Comparable HbA1c reduction was observed with a mean+/-standard deviation change from baseline to the 32-week endpoint of -0.94+/-1.15% in the vildagliptin group and -1.00+/-1.32% in the glimepiride group. A similar reduction in 2h-PPG (vildagliptin group 3.53+/-4.11 mmol/L vs. the glimepiride group 3.72+/-4.17 mmol/L) was demonstrated, and the decrements in FPG (vildagliptin group 1.54+/-2.41 mmol/L vs. glimepiride group 2.16+/-2.51 mmol/L) were not different between groups. The proportion of patients who achieved an HbA1c less than 7% at week 32 was 50.1% in the vildagliptin group and 56.0% in the glimepiride group. An average body weight gain of 2.53+/-1.21 kg in the glimepiride group was observed in contrast with the 0.23+/-0.69 kg weight gain noted in the vildagliptin group. A 10-fold lower incidence of hypoglycemia was demonstrated in the vildagliptin group, in addition to an absence of severe hypoglycemia.
CONCLUSION
Vildagliptin-metformin treatment provided blood glucose control efficacy comparable to that of glimepiride-metformin treatment and resulted in better adverse event profiles with lower risks of hypoglycemia and weight gain.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998. 352:837–853.2. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008. 359:1577–1589.3. Nathan DM. Long-term complications of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993. 328:1676–1685.4. Nathan DM, Cleary PA, Backlund JY, Genuth SM, Lachin JM, Orchard TJ, Raskin P, Zinman B. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Study Research Group. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2005. 353:2643–2653.5. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group. Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, Goff DC Jr, Bigger JT, Buse JB, Cushman WC, Genuth S, Ismail-Beigi F, Grimm RH Jr, Probstfield JL, Simons-Morton DG, Friedewald WT. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008. 358:2545–2559.6. ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, Woodward M, Marre M, Cooper M, Glasziou P, Grobbee D, Hamet P, Harrap S, Heller S, Liu L, Mancia G, Mogensen CE, Pan C, Poulter N, Rodgers A, Williams B, Bompoint S, de Galan BE, Joshi R, Travert F. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008. 358:2560–2572.7. Duckworth W, Abraira C, Moritz T, Reda D, Emanuele N, Reaven PD, Zieve FJ, Marks J, Davis SN, Hayward R, Warren SR, Goldman S, McCarren M, Vitek ME, Henderson WG, Huang GD. VADT Investigators. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009. 360:129–139.8. Gavin JR 3rd, Bohannon NJ. A review of the response to oral antidiabetes agents in patients with type 2 diabetes. Postgrad Med. 2010. 122:43–51.9. Palalau AI, Tahrani AA, Piya MK, Barnett AH. DPP-4 inhibitors in clinical practice. Postgrad Med. 2009. 121:70–100.10. Kulasa KM, Henry RR. Pharmacotherapy of hyperglycemia. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009. 10:2415–2432.11. Rosenstock J, Fitchet M. Vildagliptin: clinical trials programme in monotherapy and combination therapy for type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2008. (159):15–23.12. Bolli G, Dotta F, Rochotte E, Cohen SE. Efficacy and tolerability of vildagliptin vs. pioglitazone when added to metformin: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008. 10:82–90.13. Fonseca V, Baron M, Shao Q, Dejager S. Sustained efficacy and reduced hypoglycemia during one year of treatment with vildagliptin added to insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Horm Metab Res. 2008. 40:427–430.14. Garber AJ, Foley JE, Banerji MA, Ebeling P, Gudbjornsdottir S, Camisasca RP, Couturier A, Baron MA. Effects of vildagliptin on glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with a sulphonylurea. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008. 10:1047–1056.15. Rodriguez A, Cipres L, Tofe S, Polavieja P, Reviriego J. Clinical evaluation of combined therapy for type 2 diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010. 26:1171–1183.16. Pareek A, Chandurkar N, Zawar S, Agrawal N. Evaluation of efficacy and tolerability of gliclazide and metformin combination: a multicentric study in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus uncontrolled on monotherapy with sulfonylurea or metformin. Am J Ther. 2010. 17:559–565.17. Zoungas S, Patel A, Chalmers J, de Galan BE, Li Q, Billot L, Woodward M, Ninomiya T, Neal B, MacMahon S, Grobbee DE, Kengne AP, Marre M, Heller S. ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Severe hypoglycemia and risks of vascular events and death. N Engl J Med. 2010. 363:1410–1418.18. Wiedeman PE, Trevillyan JM. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors for the treatment of impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2003. 4:412–420.19. Nauck MA, Meininger G, Sheng D, Terranella L, Stein PP. Sitagliptin Study 024 Group. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, compared with the sulfonylurea, glipizide, in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin alone: a randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007. 9:194–205.20. DeFronzo RA. Current issues in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Overview of newer agents: where treatment is going. Am J Med. 2010. 123:3 Suppl. S38–S48.21. Ferrannini E, Fonseca V, Zinman B, Matthews D, Ahren B, Byiers S, Shao Q, Dejager S. Fifty-two-week efficacy and safety of vildagliptin vs. glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009. 11:157–166.22. Matthews DR, Dejager S, Ahren B, Fonseca V, Ferrannini E, Couturier A, Foley JE, Zinman B. Vildagliptin add-on to metformin produces similar efficacy and reduced hypoglycaemic risk compared with glimepiride, with no weight gain: results from a 2-year study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010. 12:780–789.23. Dejager S, Razac S, Foley JE, Schweizer A. Vildagliptin in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multiple-dose study. Horm Metab Res. 2007. 39:218–223.24. Mohan V, Yang W, Son HY, Xu L, Noble L, Langdon RB, Amatruda JM, Stein PP, Kaufman KD. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes in China, India, and Korea. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009. 83:106–116.25. Matsumoto K, Miyake S, Yano M, Ueki Y, Yamaguchi Y, Akazawa S, Tominaga Y. Glucose tolerance, insulin secretion, and insulin sensitivity in nonobese and obese Japanese subjects. Diabetes Care. 1997. 20:1562–1568.