Tuberc Respir Dis.
2011 Oct;71(4):259-265.
Enhanced Sensitivity to Gefitinib after Radiation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea. cheol@kcch.re.kr
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors, gefitinib and erlotinib, are effective therapies for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients whose tumors harbor somatic mutations in EGFR. The mutations are, however, only found in about 30% of Asian NSCLC patients and all patients ultimately develop resistance to these agents. Ionizing radiation has been shown to induce autophosphorylation of EGFR and activate its downstream signaling pathways. In the present study, we have tested whether the effect of gefitinib treatment can be enhanced after ionizing radiation.
METHODS
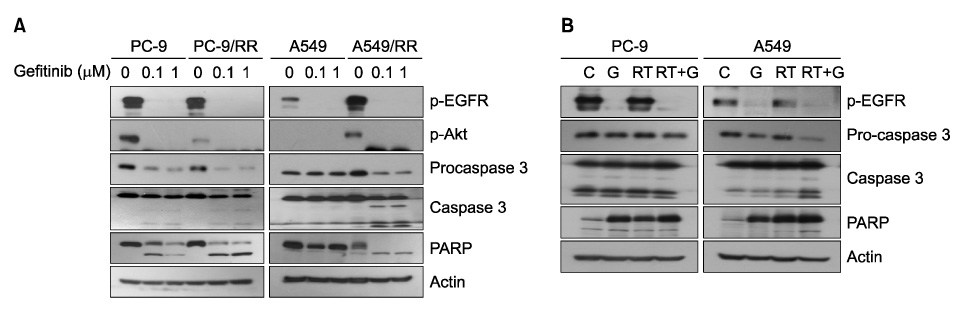
We compared the PC-9 and A549 cell line with its radiation-resistant derivatives after gefitinib treatment with cell proliferation and apoptosis assay. We also analyzed the effect of gefitinib after ionizing radiation in PC-9, A549, and NCI-H460 cells. Cell proliferation was determined by MTT assay and induction of apoptosis was evaluated by flow cytometry. Caspase 3 activation and PARP cleavage were evaluated by western blot analysis.
RESULTS
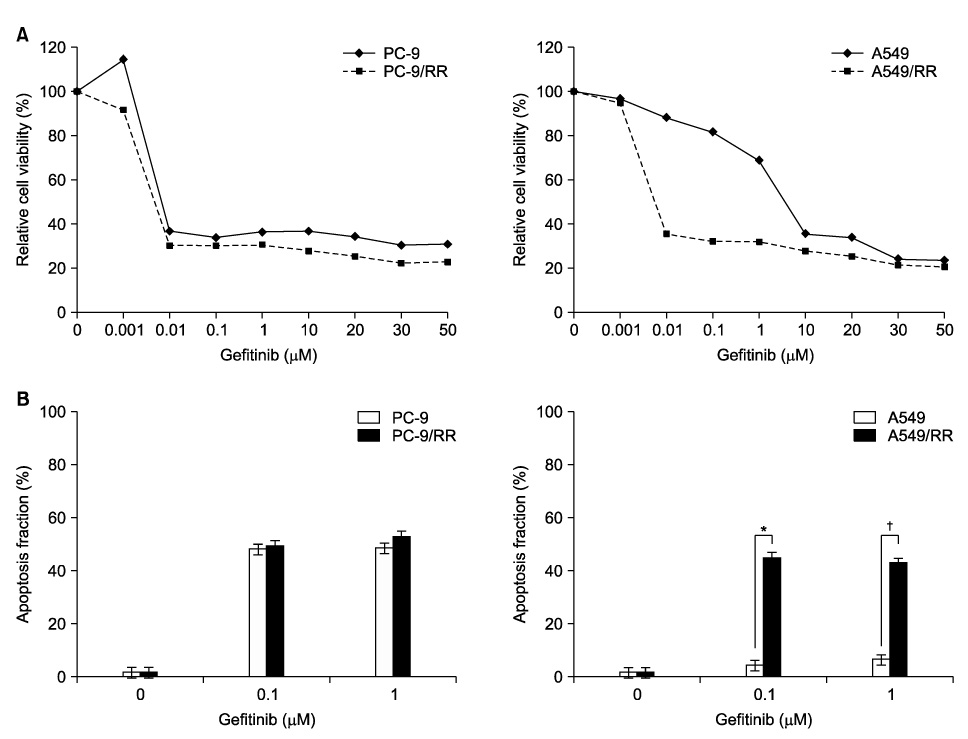
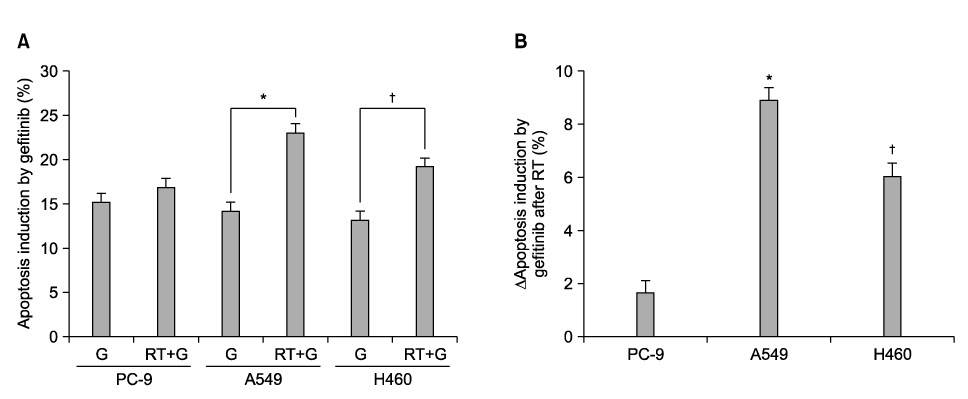
PC-9 cells having mutated EGFR and their radiation-resistant cells showed no significant difference in cell viability. However, radiation-resistant A549 cells were more sensitive to gefitinib than were their parental cells. This was attributable to an increased induction of apoptosis. Gefitinib-induced apoptosis increased significantly after radiation in cells with wild type EGFR including A549 and NCI-H460, but not in PC-9 cells with mutated EGFR. Caspase 3 activation and PARP cleavage accompanied these findings.
CONCLUSION
The data suggest that gefitinib-induced apoptosis could increase after radiation in cells with wild type EGFR, but not in cells with mutated EGFR.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Apoptosis
Asian Continental Ancestry Group
Blotting, Western
Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung
Caspase 3
Cell Line
Cell Proliferation
Cell Survival
Flow Cytometry
Humans
Parents
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Quinazolines
Radiation, Ionizing
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Erlotinib Hydrochloride
Caspase 3
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Quinazolines
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jänne PA, Johnson BE. Effect of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase domain mutations on the outcome of patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. 12:4416s–4420s.2. Engelman JA, Jänne PA. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. 14:2895–2899.3. Haasbeek CJ, Slotman BJ, Senan S. Radiotherapy for lung cancer: clinical impact of recent technical advances. Lung Cancer. 2009. 64:1–8.4. Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N, Shin DM, Cohen RB, et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2006. 354:567–578.5. She Y, Lee F, Chen J, Haimovitz-Friedman A, Miller VA, Rusch VR, et al. The epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 selectively potentiates radiation response of human tumors in nude mice, with a marked improvement in therapeutic index. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. 9:3773–3778.6. Park JS, Jun HJ, Cho MJ, Cho KH, Lee JS, Zo JI, et al. Radiosensitivity enhancement by combined treatment of celecoxib and gefitinib on human lung cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. 12:4989–4999.7. Shibuya K, Komaki R, Shintani T, Itasaka S, Ryan A, Jurgensmeier JM, et al. Targeted therapy against VEGFR and EGFR with ZD6474 enhances the therapeutic efficacy of irradiation in an orthotopic model of human non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007. 69:1534–1543.8. Tanaka T, Munshi A, Brooks C, Liu J, Hobbs ML, Meyn RE. Gefitinib radiosensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells by suppressing cellular DNA repair capacity. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. 14:1266–1273.9. Schmidt-Ullrich RK, Mikkelsen RB, Dent P, Todd DG, Valerie K, Kavanagh BD, et al. Radiation-induced proliferation of the human A431 squamous carcinoma cells is dependent on EGFR tyrosine phosphorylation. Oncogene. 1997. 15:1191–1197.10. Dittmann K, Mayer C, Fehrenbacher B, Schaller M, Raju U, Milas L, et al. Radiation-induced epidermal growth factor receptor nuclear import is linked to activation of DNA-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 2005. 280:31182–31189.11. Das AK, Sato M, Story MD, Peyton M, Graves R, Redpath S, et al. Non-small-cell lung cancers with kinase domain mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor are sensitive to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 2006. 66:9601–9608.12. Das AK, Chen BP, Story MD, Sato M, Minna JD, Chen DJ, et al. Somatic mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) abrogate EGFR-mediated radioprotection in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007. 67:5267–5274.13. Reardon DB, Contessa JN, Mikkelsen RB, Valerie K, Amir C, Dent P, et al. Dominant negative EGFR-CD533 and inhibition of MAPK modify JNK1 activation and enhance radiation toxicity of human mammary carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 1999. 18:4756–4766.14. Suy S, Anderson WB, Dent P, Chang E, Kasid U. Association of Grb2 with Sos and Ras with Raf-1 upon gamma irradiation of breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 1997. 15:53–61.15. Withers HR, Taylor JM, Maciejewski B. The hazard of accelerated tumor clonogen repopulation during radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 1988. 27:131–146.16. Dent P, Yacoub A, Contessa J, Caron R, Amorino G, Valerie K, et al. Stress and radiation-induced activation of multiple intracellular signaling pathways. Radiat Res. 2003. 159:283–300.17. Contessa JN, Hampton J, Lammering G, Mikkelsen RB, Dent P, Valerie K, et al. Ionizing radiation activates Erb-B receptor dependent Akt and p70 S6 kinase signaling in carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2002. 21:4032–4041.18. Toulany M, Dittmann K, Kruger M, Baumann M, Rodemann HP. Radioresistance of K-Ras mutated human tumor cells is mediated through EGFR-dependent activation of PI3K-AKT pathway. Radiother Oncol. 2005. 76:143–150.19. Huang SM, Li J, Armstrong EA, Harari PM. Modulation of radiation response and tumor-induced angiogenesis after epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition by ZD1839 (Iressa). Cancer Res. 2002. 62:4300–4306.20. Ochs JS. Rationale and clinical basis for combining gefitinib (IRESSA, ZD1839) with radiation therapy for solid tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. 58:941–949.21. Burdak-Rothkamm S, Rübe CE, Nguyen TP, Ludwig D, Feldmann K, Wiegel T, et al. Radiosensitivity of tumor cell lines after pretreatment with the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 (Iressa). Strahlenther Onkol. 2005. 181:197–204.22. Colquhoun AJ, Mchugh LA, Tulchinsky E, Kriajevska M, Mellon JK. Combination treatment with ionising radiation and gefitinib ('Iressa', ZD1839), an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor, significantly inhibits bladder cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 2007. 48:351–360.23. Harari PM. Stepwise progress in epidermal growth factor receptor/radiation studies for head and neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007. 69:2 Suppl. S25–S27.24. Thariat J, Yildirim G, Mason KA, Garden AS, Milas L, Ang KK. Combination of radiotherapy with EGFR antagonists for head and neck carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol. 2007. 12:99–110.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of leptomeningeal metastasis from adenocarcinoma of the lung improved by treatment with Gefitinib
- Enhancement of Sensitivity of Human Lung Cancer Cell Line to TRAIL and Gefitinib by IGF-1R Blockade
- Overcoming the Intrinsic Gefitinib-resistance via Downregulation of AXL in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Radiation Recall Dermatitis Induced by Gefitinib
- The Effectiveness of Gefitinib on Spinal Metastases of Lung Cancer: Report of Two Cases