Nutr Res Pract.
2008 Jun;2(2):74-79.
Zinc deficiency decreased cell viability both in endothelial EA.hy926 cells and mouse aortic culture ex vivo and its implication for anti-atherosclerosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Andong National University, Gyungpook 760-749, Korea. iskwun@andong.ac.kr
- 2Gyeongbuk Institute for BioIndustry, Andong, Gyungpook, Korea.
- 3Division of Vascular Health, Rowett Research Institute, Aberdeen, UK.
Abstract
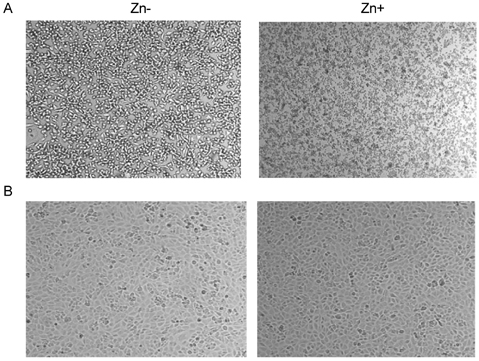
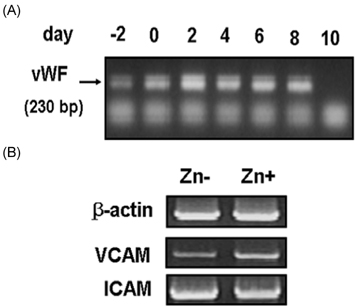
- Zinc plays a protective role in anti-atherosclerosis but the clear mechanism has not been proposed yet. In the present study, we evaluated whether zinc modulates atherosclerotic markers, VACM-1 and ICAM-1 and cell viability both in endothelial cells in vitro and mouse aortic cell viability ex vivo. In study 1, as in vitro model, endothelial EA.hy926 cells were treated with TNFalpha for 5 hours for inducing oxidative stress, and then treated with Zn-adequacy (15 micrometer Zn) or Zn-deficiency (0 micrometer Zn) for 6 hours. Pro-atherosclerosis factors, VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 mRNA expression and cell viability was measured. In study 2, as ex vivo model, mouse aorta ring was used. Mourse aorta was removed and cut in ring then, cultured in a 96-well plate. Aortic ring was treated with various TNFalpha (0-30 mg/ml) and intracellular zinc chelator, N, N, N', N', -tetrakis (2-pyridylmethyl) ethylenediamine (TPEN, 0-30 microM) for cellular zinc depletion for 2 days and then cell viability was measured. The results showed that in in vitro study, Zn-adequate group induced more VCAM-1 & ICAM-1 mRNA expression than Zn-deficient group during 6-hour zinc treatment post-5 hour TNF-alpha treatment, unexpectedly. These results might be cautiously interpreted that zinc would biologically induce the early expression of anti-oxidative stress through the increased adhesion molecule expression for reducing atherosclerotic action, particularly under the present 6-hour zinc treatment. In ex vivo, mouse aortic ring cell viability was decreased as TNF-alpha and TPEN levels increased, which suggests that mouse aortic blood vessel cell viability was decreased, when oxidative stress increases and cellular zinc level decreases. Taken together, it can be suggested that zinc may have a protective role in anti-atherosclerosis by cell viability in endothelial cells and aorta tissue. Further study is needed to clarify how pro-atherosclerosis molecule expression is modulated by zinc.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Aorta
Atherosclerosis
Blood Vessels
Cell Survival
Endothelial Cells
Ethylenediamines
Glycosaminoglycans
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1
Mice
Oxidative Stress
RNA, Messenger
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1
Zinc
Ethylenediamines
Glycosaminoglycans
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1
RNA, Messenger
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1
Zinc
Figure
Reference
-
1. Alexander RW. Hypertension and the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: oxidative stress and the mediation of arterialinflammatory response: a new perspective. Hypertension. 1995. 25:155–161.
Article2. Beattie JH, Kwun IS. Is zinc deficiency a risk factor for atherosclerosis? Br J Nutr. 2004. 91:177–181.
Article3. Berger M, Rubinraut E, Barshack I, Roth A, Keren G, George J. Zinc reduces intimal hyperplasia in the rat carotid injury model. Atherosclerosis. 2004. 175:229–234.
Article4. Choi JS, Choi YJ, Park SH, Kang JS, Kang YH. Flavones mitigate tumor necrosis factor-a-induced adhesion molecular upregulation in cultured human endothelial cells: role of nuclear factor-κB. J Nutr. 2004. 134:10103–11019.5. Clair J, Talwalkar R, McClainC J, Hennig B. Selective removal of zinc from cell culture media. Journal of Trace Elements in Experimental Medicine. 1995. 7:143–151.6. Clegg MS, Hanna LA, Niles BJ, Momma TY, Keen CL. Zinc deficiency-induced cell death. IUBMB Life. 2005. 57:661–669.
Article7. Collins PW, Macey MG, Cahill MR, Newland AC. Von Willebrand factor release and P-selectin expression is stimulated by thrombin and trypsin but not IL-1 in cultured human endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost. 1993. 70:346–350.
Article8. Costarelli L, Muti E, Malavolta M, Giacconi R, Cipriano C, Sartini D, Emanuelli M, Silvestrini M, Provinciali L, Gobbi B, Mocchegiani E. Modulation of genes involved in Zinc homeostasis in old low-grade atherosclerotic patients under effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Rejuvenation Res. 2008. 11:287–291.
Article9. Desai A, ZhaoY , Warren JS. Development of atherosclerosis in Balb/c apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2008. (Epub ahead of print).
Article10. Formigari A, Irato P, Santon A. Zinc, antioxidant systems an dmetallothionein in metal mediated-apoptosis: Biochemical and cytochemical aspects. Com Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2007. (Epub ahead of print).11. Hennig B, Wang Y, Ramasamy S, McClain CJ. Zinc deficiency alters barrier function of cultured porcine endothelial cells. J Nutr. 1992. 122:1242–1247.
Article12. Hennig B, Meerarani P, Ramadass P, Toborek M, Malecki N, Slim R, McClain CJ. Zinc nutrition and apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells: implications in atherosclerosis. Nutrition. 1999. 1:744–748.
Article13. Henriksen PA, Sallenave JM. Medicine in focus Human neutrophil elastase: Mediator and therapeutic target in atherosclerosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. 40:1095–1100.
Article14. Kharbanda R, MacAllister RJ. The Atherosclerosis time-line and the role of the endothelium. Endocr Metab Agents. 2005. 5:47–52.
Article15. Kunsch C, Medford RM. Oxidative stress as a regulator of gene expression in the vasculature. Circ Res. 1999. 85(8):753–766.
Article16. Ling S, Nheu L, Dai A, Guo Z, Komesaroff P. Effects of four medicinal herbs on human vascular endothelial cells in culture. Int J Cardiol. 2007. (Epub ahead of print).
Article17. McClain C, Morris P, Hennig B. Zinc and endothelial function. Nutrition. 1995. 11:117–120.18. Minqin R, En H, Beck K, Rajendran R, Wu BJ, Halliwell B, Watt F, Stocker R. Nuclear microprobe investigation into the trace elemental contents of carotid artery walls of apolipoprotein E deficient mice. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B. 2007. 260:240–244.
Article19. Meerarani P, Ramadass P, Toborek M, Bauer HC, Bauer H, Hennig B. Zinc protect against apoptosis of endothelial cells induced by linoleic acid and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000. 71:81–87.
Article20. Papagianni A, Kalovoulos M, Kirmizis D, Vainas A, Belechri A, Alexopoulos E, Memmos D. Carotid atherosclerosis is associated with inflammation and endothelial cell adhesion molecules in chronic haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003. 18:113–119.
Article21. Reiterer G, Toborek M, Hennig B. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptors and γ require zinc for their anti-inflammatoryproperties in porcine vascular endothelial cells. J Nutr. 2004. 134:1711–1715.
Article22. Ren M, Watt F, Huat BTK, Halliwell B. Correlation of iron and zinc levels with lesion depth in newly formed atherosclerotic lesions. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003. 34:746–752.
Article23. Theilmeier G, Michiels C, Spaepen E, Vreys I, Collen D, Vermylen J, Hoylaerts MF. Endothelial von Willebrand factor recruits platelets to atherosclerosis-prone sites in response to hypercholesterolemia. Blood. 2008. 99:4486–4493.
Article24. Watt F, Rajendran R, Ren MQ, Tan BKH, Halliwell B. A nuclear microscopy study of trace elements Ca, Fe, Zn and Cu in atherosclerosis. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res. 2006. 249:646–652.
Article25. Yang H, Roberts LJ, Shi MJ, Zhou LC, Ballard BR, Richardson A, Guo ZM. Retardation of atherosclerosis by overexpression of catalase or both Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase and catalase in mice lacking apolipoprotein. E. Circ Res. 2004. 95:1075–1081.
Article26. Zheng HT, Zhou LN, Huang CJ, Hua X, Jian R, Su BH, Fanga F. Selenium inhibits high glucose and high insulin-induced adhesion molecule expression in vascular endothelial cells. Arch Med Res. 2008. 39:373–379.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Inhibitory Effect of an Urotensin II Receptor Antagonist on Proinflammatory Activation Induced by Urotensin II in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells
- In Vitro Culture of Endothelial Cell and Smooth Muscle Cell for Studying Vascular Diseases
- The function of zinc in the primary vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in rats
- Flow Cytometric Analysis of Endothelial Cell Viability in Arterial Allograft
- An Effective Isolation of the Vascular Endothelial and Smooth Muscle Cells from the Mouse Aorta