Lab Anim Res.
2016 Mar;32(1):24-33. 10.5625/lar.2016.32.1.24.
Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappa B in 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol-induced hepatic injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1BK21 Plus Team, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 500-757, Korea. toxkim@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2312151
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2016.32.1.24
Abstract
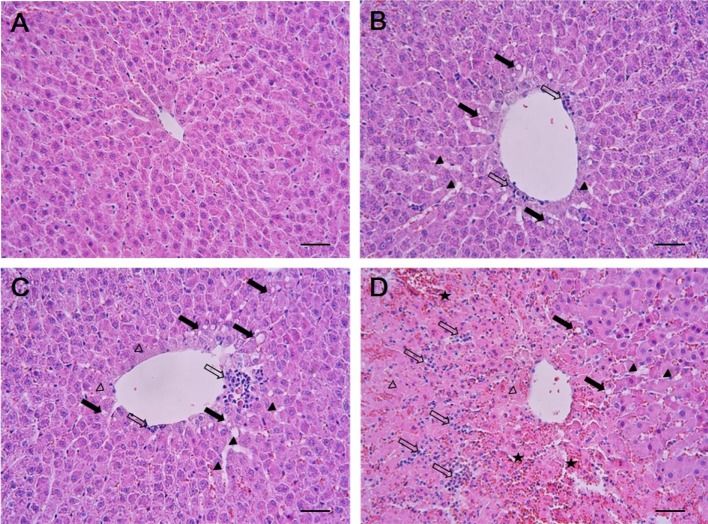
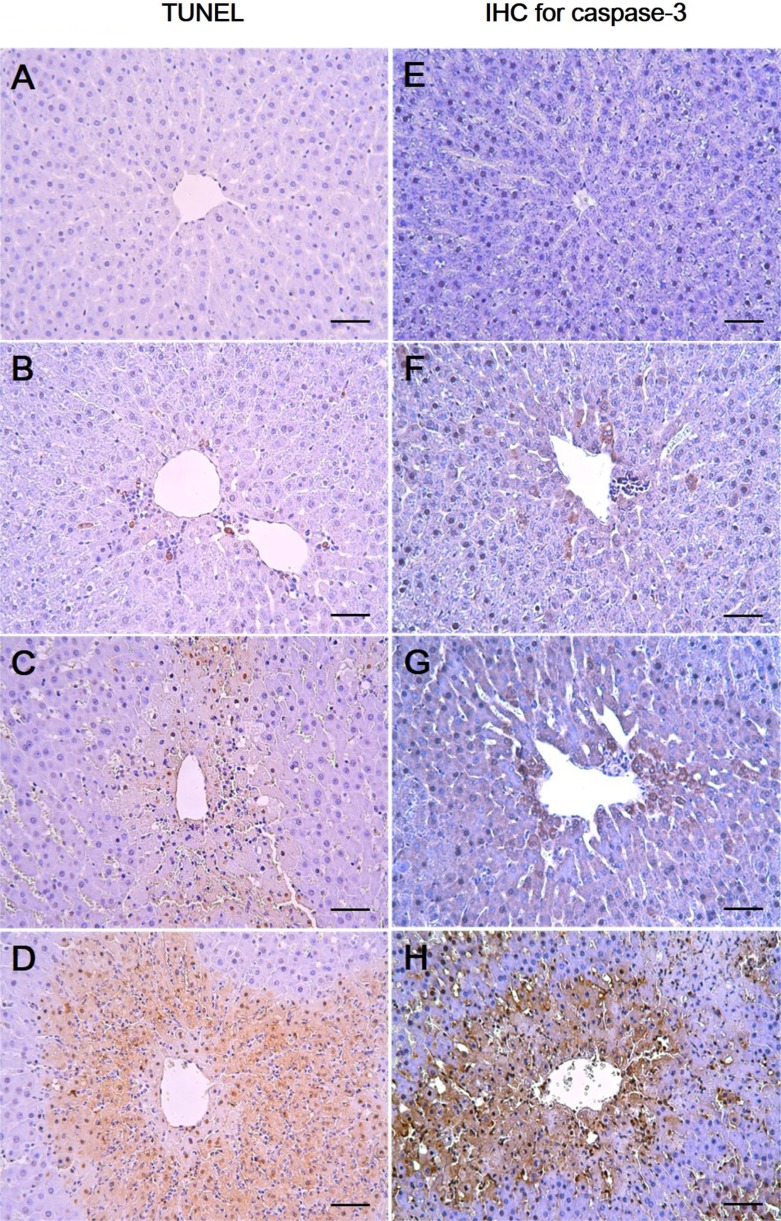
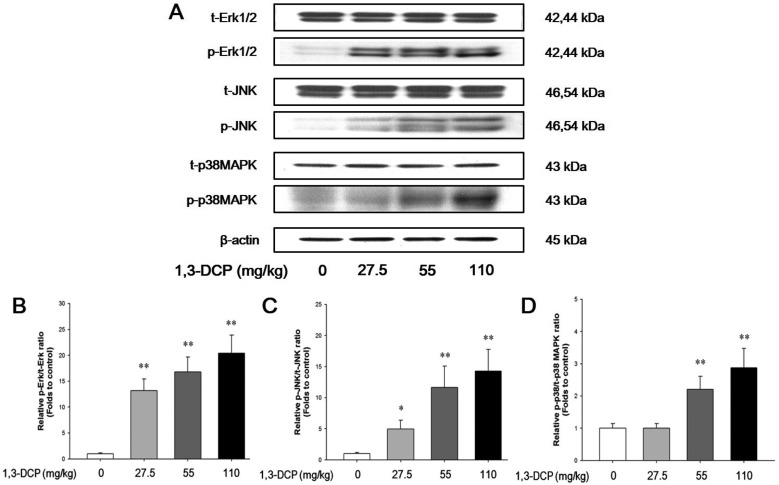
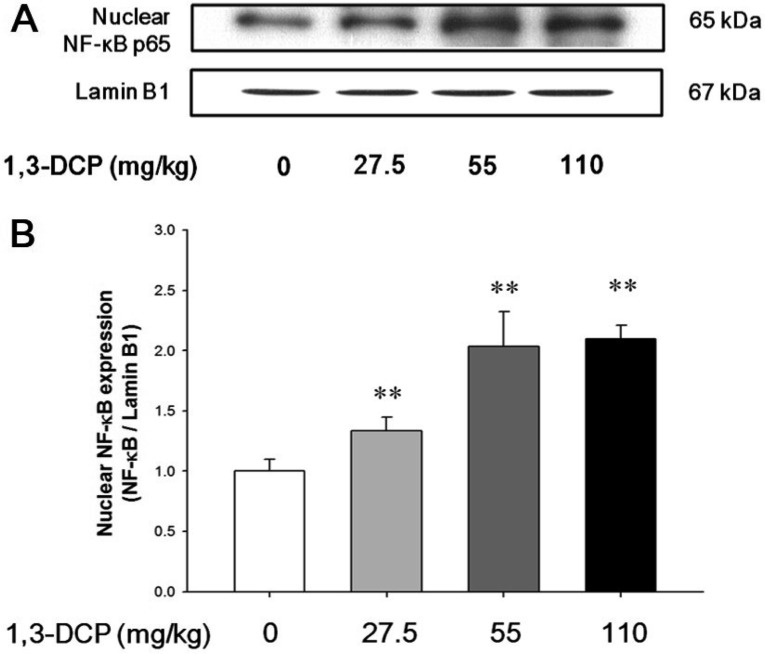
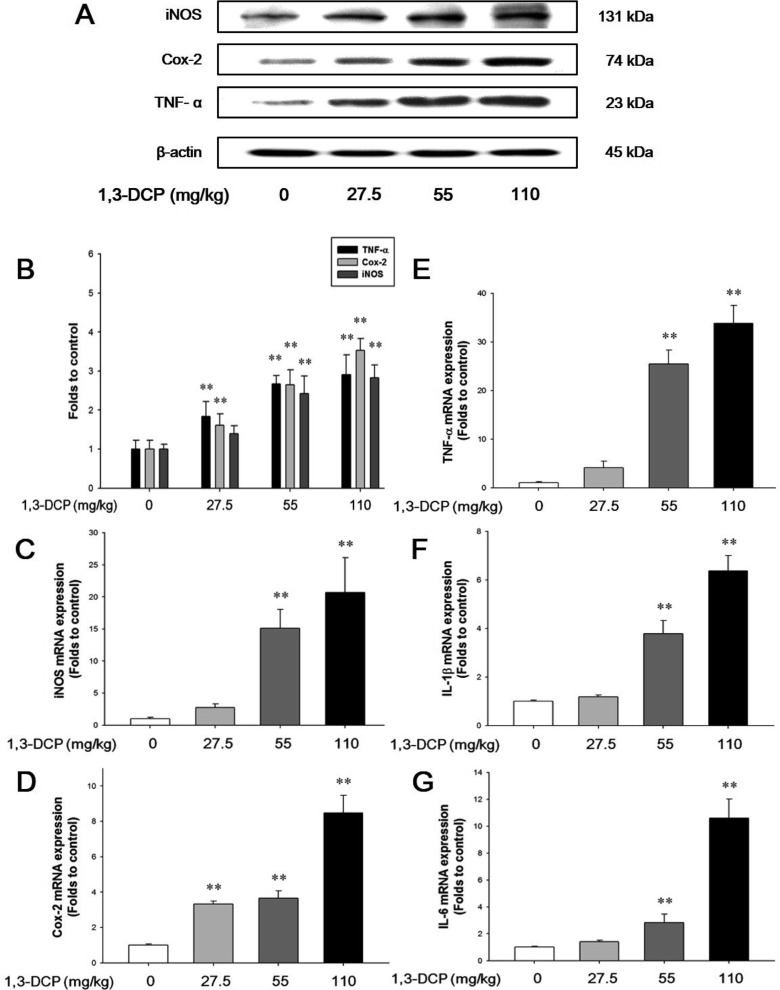
- In this study, the potential hepatotoxicity of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol and its hepatotoxic mechanisms in rats was investigated. The test chemical was administered orally to male rats at 0, 27.5, 55, and 110 mg/kg body weight. 1,3-Dichloro-2-propanol administration caused acute hepatotoxicity, as evidenced by an increase in serum aminotransferases, total cholesterol, and total bilirubin levels and a decrease in serum glucose concentration in a dose-dependent manner with corresponding histopathological changes in the hepatic tissues. The significant increase in malondialdehyde content and the significant decrease in glutathione content and antioxidant enzyme activities indicated that 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol-induced hepatic damage was mediated through oxidative stress, which caused a dose-dependent increase of hepatocellular apoptotic changes in the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end-labeling assay and immunohistochemical analysis for caspase-3. The phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases caused by 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol possibly involved in hepatocellular apoptotic changes in rat liver. Furthermore, 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol induced an inflammatory response through activation of nuclear factor-kappa B signaling that coincided with the induction of pro-inflammatory mediators or cytokines in a dose-dependent manner. Taken together, these results demonstrate that hepatotoxicity may be related to oxidative stress-mediated activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappa B-mediated inflammatory response.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Bilirubin
Blood Glucose
Body Weight
Caspase 3
Cholesterol
Cytokines
Glutathione
Humans
Liver
Male
Malondialdehyde
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases*
Oxidative Stress
Phosphorylation
Rats
Transaminases
Bilirubin
Caspase 3
Cholesterol
Cytokines
Glutathione
Malondialdehyde
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Transaminases
Figure
Reference
-
1. NTP. 1,3-Dichloro-2-propanol [CAS No. 96-23-1]. Review of toxicological literature, Research Triangle Park, NC. National Toxicology Program (NTP). 2005. Accessed 17 April 2015. Available from: URL: http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/chem_background/exsumpdf/dichloropropanol_508.pdf.2. Nyman PJ, Diachenko GW, Perfetti GA. Survey of chloropropanols in soy sauces and related products. Food Addit Contam. 2003; 20(10):909–915. PMID: 14594675.
Article3. Williams G, Leblanc JC, Setzer RW. Application of the margin of exposure (MoE) approach to substances in food that are genotoxic and carcinogenic: example: (CAS No. 96-23-1) 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol (DCP). Food Chem Toxicol. 2010; 48(S1):S57–S62. PMID: 20113855.4. Jersey GC, Breslin WJ, Zeilke GJ. Subchronic toxicity of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol in rats. Toxicologist. 1991; 11:353.5. Kim HY, Lee SB, Lim KT, Kim MK, Kim JC. subchronic inhalation toxicity study of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol in rats. Ann Occup Hyg. 2007; 51(7):633–643. PMID: 17921239.6. Andres S, Appel KE, Lampen A. Toxicology, occurrence and risk characterisation of the chloropropanols in food: 2-monochloro-1,3-propanediol, 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol and 2,3-dichloro-1-propanol. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013; 58:467–478. PMID: 23712097.
Article7. Shiozaki T, Mizobata Y, Sugimoto H, Yoshioka T, Sugimoto T. Fulminant hepatitis following exposure to dichlorohydrin--report of two cases. Hum Exp Toxicol. 1994; 13(4):267–270. PMID: 8204313.8. RTECS. 1,3-Dichloro-2-propanol: toxicity, carcinogenicity, tumorigenicity, mutagenicity, and teratogenicity. Registry of Toxic Effects of Chemical Substances (RTECS) No. UB1400000. 2000. accessed 17 April 2015. Available from: URL: http://www.cdc.gov/niosh-rtecs/ub155cc0.html.9. Lee JC, Shin IS, Ahn TH, Kim KH, Moon C, Kim SH, Shin DH, Park SC, Kim YB, Kim JC. Developmental toxic potential of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol in Sprague-Dawley rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2009; 53(1):63–69. PMID: 19047007.
Article10. Lu J, Huang G, Hu S, Wang Z, Guan S. 1,3-Dichloro-2-propanol induced hyperlipidemia in C57BL/6J mice via AMPK signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014; 64:403–409. PMID: 24333398.
Article11. Hammond AH, Garle MJ, Fry JR. Toxicity of dichloropropanols in rat hepatocyte cultues. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 1996; 1(1):39–43. PMID: 21781661.
Article12. Hammond AH, Fry JR. Involvement of cytochrome P4502E1 in the toxicity of dichloropropanol to rat hepatocyte cultures. Toxicology. 1997; 118(2-3):171–179. PMID: 9129171.
Article13. Katoh T, Haratake J, Nakano S, Kikuchi M, Yoshikawa M, Arashidani K. Dose-dependent effects of dichloropropanol on liver histology and lipid peroxidation in rats. Ind Health. 1998; 36(4):318–323. PMID: 9810144.
Article14. Hammond AH, Fry JR. Effect of cyanamide on toxicity and glutathione depletion in rat hepatocyte cultures: differences between two dichloropropanol isomers. Chem Biol Interact. 1999; 122(2):107–115. PMID: 10528996.
Article15. Kuroda Y, Fueta Y, Kohshi K, Nakao H, Imai H, Katoh T. Toxicity of dichloropropanols. J UOEH. 2002; 24(3):271–280. PMID: 12235957.
Article16. Park SY, Kim YH, Kim YH, Lee SJ. 1,3-Dichloro-2-propanol induces apoptosis via both calcium and ROS in mouse melanoma cells. Biotechnol Lett. 2010; 32(1):45–51. PMID: 19731046.
Article17. Lee IC, Ko JW, Lee SM, Kim SH, Shin IS, Moon OS, Yoon WK, Kim HC, Kim JC. Time-course and molecular mechanism of hepatotoxicity induced by 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015; 40(1):191–198. PMID: 26143167.
Article18. Haratake J, Furuta A, Iwasa T, Wakasugi C, Imazu K. Submassive hepatic necrosis induced by dichloropropanol. Liver. 1993; 13(3):123–129. PMID: 8336524.
Article19. Moron MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B. Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979; 582(1):67–78. PMID: 760819.
Article20. Berton TR, Conti CJ, Mitchell DL, Aldaz CM, Lubet RA, Fischer SM. The effect of vitamin E acetate on ultraviolet-induced mouse skin carcinogenesis. Mol Carcinog. 1998; 23(3):175–184. PMID: 9833778.
Article21. Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951; 193(1):265–275. PMID: 14907713.
Article22. Kim JW, Park S, Lim CW, Lee K, Kim B. The role of air pollutants in initiating liver disease. Toxicol Res. 2014; 30(2):65–70. PMID: 25071914.
Article23. Seo Y, Bazarsad D, Choe SY. Effect of acer tegmentosum maxim. Extracts on acute hepatitis and fatty liver in rats. J Biomed Res. 2012; 13(2):165–170.
Article24. Tak PP, Firestein GS. NF-kappaB: a key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest. 2001; 107(1):7–11. PMID: 11134171.25. Leclercq IA, Farrell GC, Sempoux C, dela Peña A, Horsmans Y. Curcumin inhibits NF-kappaB activation and reduces the severity of experimental steatohepatitis in mice. J Hepatol. 2004; 41(6):926–934. PMID: 15582125.26. Reyes-Gordillo K, Segovia J, Shibayama M, Vergara P, Moreno MG, Muriel P. Curcumin protects against acute liver damage in the rat by inhibiting NF-kappaB, proinflammatory cytokines production and oxidative stress. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007; 1770(6):989–996. PMID: 17383825.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of 5´-AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Activators in Regulating Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling
- Molecular Mechanisms of Neutrophil Activation in Acute Lung Injury
- Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling in Inflammation-related Carcinogenesis
- p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB are required for LPS-induced RANTES production in immortalized murine microglia (BV-2)
- A Role of Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases and Inflammatory Responses in Gender Differences in Kidney Ischemia Injury