Lab Anim Res.
2013 Sep;29(3):148-155. 10.5625/lar.2013.29.3.148.
Systemic administration of low dosage of tetanus toxin decreases cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in the mouse hippocampal dentate gyrus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Integrative Traditional & Western Medicine, Medical College, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China.
- 2Department of Neurobiology, and Institute of Medical Sciences, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea. mhwon@kangwon.ac.kr
- 3Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, and Institute of Neurodegeneration and Neuroregeneration, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Anatomy, College of Veterinary Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Oral Anatomy, College of Dentistry and Research institute of Oral Biology, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung, Korea.
- 6Department of Anatomy and Physiology, College of Pharmacy, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea.
- 7Department of Emergency Medicine, and Institute of Medical Sciences, Kangwon National University Hospital, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 8Division of Food Biotechnology, School of Biotechnology, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea. jongdai@cc.kangwon.ac.kr
- KMID: 2312107
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2013.29.3.148
Abstract
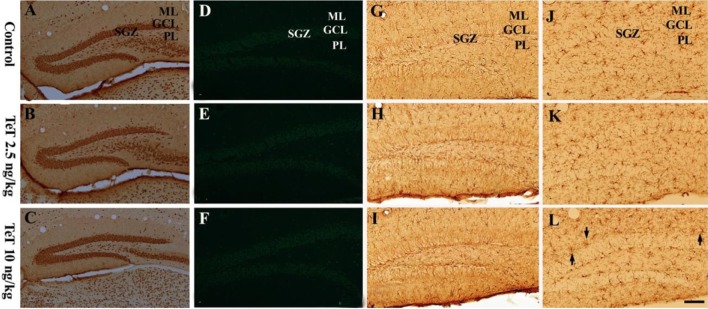
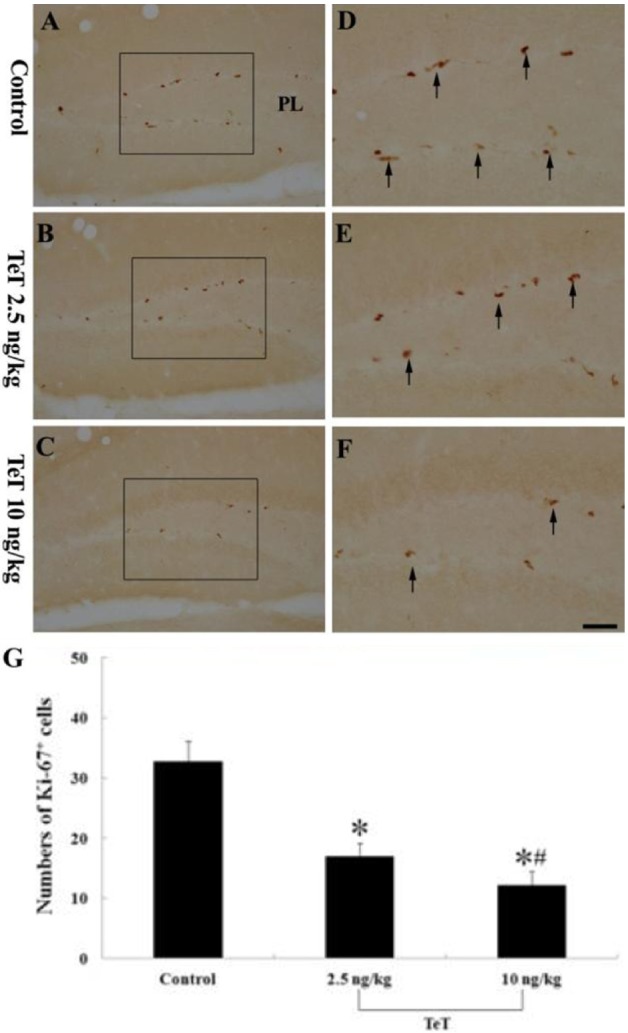
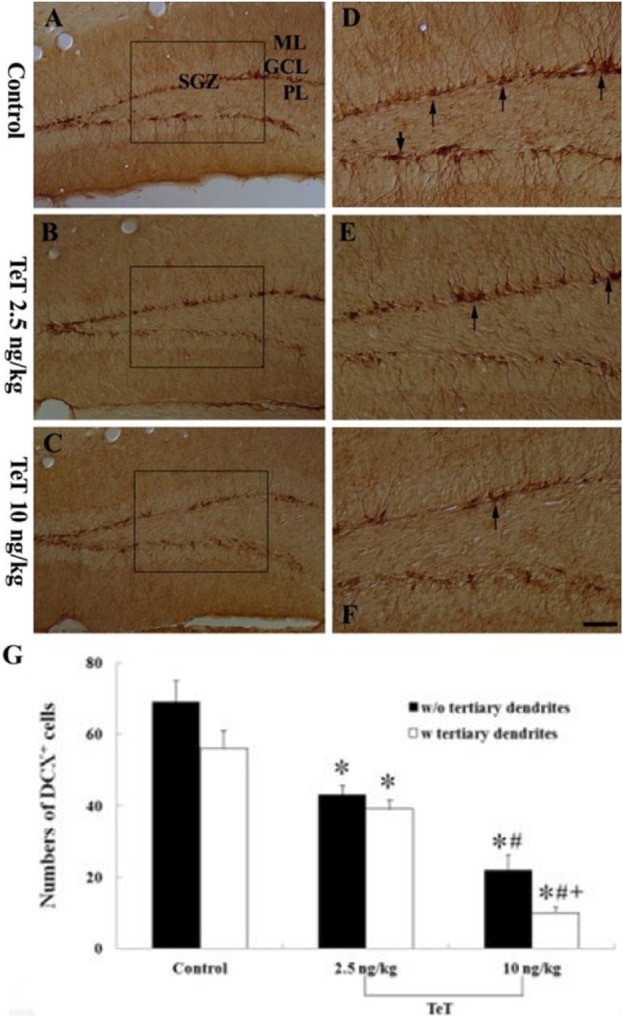
- In the present study, we investigated the effect of Tetaus toxin (TeT) on cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation using specific markers: 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU) as an exogenous marker for cell proliferation, Ki-67 as an endogenous marker for cell proliferation and doublecortin (DCX) as a marker for neuroblasts in the mouse hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG) after TeT treatment. Mice were intraperitoneally administered 2.5 and 10 ng/kg TeT and sacrificed 15 days after the treatment. In both the TeT-treated groups, no neuronal death occurred in any layers of the DG using neuronal nuclei (NeuN, a neuron nuclei maker) and Fluoro-Jade B (F-J B, a high-affinity fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal degeneration). In addition, no significant change in glial activation in both the 2.5 and 10 ng/kg TeT-treated-groups was found by GFAP (a marker for astrocytes) and Iba-1 (a marker for microglia) immunohistochemistry. However, in the 2.5 ng/kg TeT-treated-group, the mean number of BrdU, Ki-67 and DCX immunoreactive cells, respectively, were apparently decreased compared to the control group, and the mean number of each in the 10 ng/kg TeT-treated-group was much more decreased. In addition, processes of DCX-immunoreactive cells, which projected into the molecular layer, were short compared to those in the control group. In brief, our present results show that low dosage (10 ng/kg) TeT treatment apparently decreased cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in the mouse hippocampal DG without distinct gliosis as well as any loss of adult neurons.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Colditz MJ, Catts VS, Al-menhali N, Osborne GW, Bartlett PF, Coulson EJ. p75 neurotrophin receptor regulates basal and fluoxetine-stimulated hippocampal neurogenesis. Exp Brain Res. 2010; 200(2):161–167. PMID: 19621217.
Article2. Helfer JL, Goodlett CR, Greenough WT, Klintsova AY. The effects of exercise on adolescent hippocampal neurogenesis in a rat model of binge alcohol exposure during the brain growth spurt. Brain Res. 2009; 1294:1–11. PMID: 19647724.
Article3. Li WL, Fraser JL, Yu SP, Zhu J, Jiang YJ, Wei L. The role of VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling in peripheral stimulation-induced cerebral neurovascular regeneration after ischemic stroke in mice. Exp Brain Res. 2011; 214(4):503–513. PMID: 21922279.
Article4. Shook BA, Manz DH, Peters JJ, Kang S, Conover JC. Spatiotemporal changes to the subventricular zone stem cell pool through aging. J Neurosci. 2012; 32(20):6947–6956. PMID: 22593063.
Article5. Crews FT, Boettiger CA. Impulsivity, frontal lobes and risk for addiction. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009; 93(3):237–247. PMID: 19410598.
Article6. Hong XP, Peng CX, Wei W, Tian Q, Liu YH, Cao FY, Wang Q, Wang JZ. Relationship of adult neurogenesis with tau phosphorylation and GSK-3â activity in subventricular zone. Neurochem Res. 2011; 36(2):288–296. PMID: 21061060.
Article7. Kalluri HS, Dempsey RJ. IGFBP-3 inhibits the proliferation of neural progenitor cells. Neurochem Res. 2011; 36(3):406–411. PMID: 21136151.
Article8. Lou SJ, Liu JY, Chang H, Chen PJ. Hippocampal neurogenesis and gene expression depend on exercise intensity in juvenile rats. Brain Res. 2008; 1210:48–55. PMID: 18423578.
Article9. Brinton RD, Wang JM. Therapeutic potential of neurogenesis for prevention and recovery from Alzheimer's disease: allopregnanolone as a proof of concept neurogenic agent. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2006; 3(3):185–190. PMID: 16842093.10. Bruel-Jungerman E, Rampon C, Laroche S. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity and memory: facts and hypotheses. Rev Neurosci. 2007; 18(2):93–114. PMID: 17593874.
Article11. Dayer AG, Ford AA, Cleaver KM, Yassaee M, Cameron HA. Short-term and long-term survival of new neurons in the rat dentate gyrus. J Comp Neurol. 2003; 460(4):563–572. PMID: 12717714.
Article12. Gage FH. Mammalian neural stem cells. Science. 2000; 287(5457):1433–1438. PMID: 10688783.
Article13. Tanapat P, Hastings NB, Reeves AJ, Gould E. Estrogen stimulates a transient increase in the number of new neurons in the dentate gyrus of the adult female rat. J Neurosci. 1999; 19(14):5792–5801. PMID: 10407020.
Article14. Yeh FL, Dong M, Yao J, Tepp WH, Lin G, Johnson EA, Chapman ER. SV2 mediates entry of tetanus neurotoxin into central neurons. PLoS Pathog. 2010; 6(11):e1001207. PMID: 21124874.
Article15. Behrensdorf-Nicol HA, Kegel B, Bonifas U, Silberbach K, Klimek J, Weiber K, Krämer B. Residual enzymatic activity of the tetanus toxin light chain present in tetanus toxoid batches used for vaccine production. Vaccine. 2008; 26(31):3835–3841. PMID: 18554757.
Article16. Goonetilleke A, Harris JB. Clostridial neurotoxins. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004; 75(Suppl 3):iii35–iii39. PMID: 15316043.
Article17. Indrawattana N, Sookrung N, Kulkeaw K, Seesuay W, Kongngoen T, Chongsa-nguan M, Tungtrongchitr A, Chaicumpa W. Human monoclonal ScFv that inhibits cellular entry and metalloprotease activity of tetanus neurotoxin. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2010; 28(1):85–93. PMID: 20527521.18. Kobayashi T, Kai N, Kobayashi K, Fujiwara T, Akagawa K, Onda M, Kobayashi K. Transient silencing of synaptic transmitter release from specific neuronal types by recombinant tetanus toxin light chain fused to antibody variable region. J Neurosci Methods. 2008; 175(1):125–132. PMID: 18775748.
Article19. Shapiro RE, Specht CD, Collins BE, Woods AS, Cotter RJ, Schnaar RL. Identification of a ganglioside recognition domain of tetanus toxin using a novel ganglioside photoaffinity ligand. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272(48):30380–30386. PMID: 9374528.
Article20. Mellanby J, George G. Tetanus toxin and experimental epilepsy in rats. Adv Cytopharmacol. 1979; 3:401–408. PMID: 573052.21. Rausch R, Babb TL. Hippocampal neuron loss and memory scores before and after temporal lobe surgery for epilepsy. Arch Neurol. 1993; 50(8):812–817. PMID: 8352666.
Article22. Huang Y, Shi X, Xu H, Yang H, Chen T, Chen S, Chen X. Chronic unpredictable stress before pregnancy reduce the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in hippocampus of offspring rats associated with impairment of memory. Neurochem Res. 2010; 35(7):1038–1049. PMID: 20309729.
Article23. Rajan KE, Singh HK, Parkavi A, Charles PD. Attenuation of 1-(m-chlorophenyl)-biguanide induced hippocampus-dependent memory impairment by a standardised extract of Bacopa monniera (BESEB CDRI-08). Neurochem Res. 2011; 36(11):2136–2144. PMID: 21735137.
Article24. Bagetta G, Corasaniti MT, Nisticó G, Bowery NG. Behavioural and neuropathological effects produced by tetanus toxin injected into the hippocampus of rats. Neuropharmacology. 1990; 29(8):765–770. PMID: 2274111.
Article25. Candelario-Jalil E, Alvarez D, Merino N, León OS. Delayed treatment with nimesulide reduces measures of oxidative stress following global ischemic brain injury in gerbils. Neurosci Res. 2003; 47(2):245–253. PMID: 14512150.
Article26. Schmued LC, Hopkins KJ. Fluoro-Jade B: a high affinity fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal degeneration. Brain Res. 2000; 874(2):123–130. PMID: 10960596.
Article27. Arushanyan EB, Beier EV. The hippocampus and cognitive impairments. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2008; 38(8):751–758. PMID: 18802776.
Article28. Leiva J, Palestini M, Infante C, Goldschmidt A, Motles E. Copper suppresses hippocampus LTP in the rat, but does not alter learning or memory in the morris water maze. Brain Res. 2009; 1256:69–75. PMID: 19133238.
Article29. Zhao H, Li Q, Zhang Z, Pei X, Wang J, Li Y. Long-term ginsenoside consumption prevents memory loss in aged SAMP8 mice by decreasing oxidative stress and up-regulating the plasticity-related proteins in hippocampus. Brain Res. 2009; 1256:111–122. PMID: 19133247.
Article30. Bergey GK, Bigalke H, Nelson PG. Differential effects of tetanus toxin on inhibitory and excitatory synaptic transmission in mammalian spinal cord neurons in culture: a presynaptic locus of action for tetanus toxin. J Neurophysiol. 1987; 57(1):121–131. PMID: 3031230.
Article31. Korolkiewicz R, Mlynarczyk M, Gasior M, Kleinrok Z. Influence of intracerebroventricular administration of tetanus toxin on experimental seizures and protection afforded by some antiepileptic drugs in mice. Pharmacol Res. 1998; 37(6):477–483. PMID: 9695121.
Article32. Shaw JA, Perry VH, Mellanby J. Tetanus toxin-induced seizures cause microglial activation in rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1990; 120(1):66–69. PMID: 2293095.
Article33. Shaw JA, Perry VH, Mellanby J. MHC class II expression by microglia in tetanus toxin-induced experimental epilepsy in the rat. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1994; 20(4):392–398. PMID: 7808590.
Article34. Bagetta G, Knott C, Nisticó G, Bowery NG. Tetanus toxin produces neuronal loss and a reduction in GABAA but not GABAB binding sites in rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1990; 109(1-2):7–12. PMID: 2156194.
Article35. Bagetta G, Corasaniti MT, Nisticó G, Bowery NG. High vulnerability of dentate granule cells to the neuropathological effects induced by intrahippocampal injection of tetanus toxin. Neuropharmacology. 1991; 30(7):803–808. PMID: 1922689.
Article36. Lee CL, Hannay J, Hrachovy R, Rashid S, Antalffy B, Swann JW. Spatial learning deficits without hippocampal neuronal loss in a model of early-onset epilepsy. Neuroscience. 2001; 107(1):71–84. PMID: 11744248.
Article37. Deng W, Aimone JB, Gage FH. New neurons and new memories: how does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010; 11(5):339–350. PMID: 20354534.
Article38. Lafenetre P, Leske O, Wahle P, Heumann R. The beneficial effects of physical activity on impaired adult neurogenesis and cognitive performance. Front Neurosci. 2011; 5:51. PMID: 21559064.
Article39. Dupret D, Revest JM, Koehl M, Ichas F, De Giorgi F, Costet P, Abrous DN, Piazza PV. Spatial relational memory requires hippocampal adult neurogenesis. PLoS One. 2008; 3(4):e1959. PMID: 18509506.
Article40. Nam SM, Yoo DY, Kim W, Yoo M, Kim DW, Won MH, Hwang IK, Yoon YS. Effects of S-allyl-L-cysteine on cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in the mouse dentate gyrus. J Vet Med Sci. 2011; 73(8):1071–1075. PMID: 21467757.41. Lafenêtre P, Leske O, Ma-Högemeie Z, Haghikia A, Bichler Z, Wahle P, Heumann R. Exercise can rescue recognition memory impairment in a model with reduced adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Front Behav Neurosci. 2010; 3:34. PMID: 20204139.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Vanillin and 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol attenuate cognitive impairment and the reduction of cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in the dentate gyrus in a mouse model of scopolamine-induced amnesia
- The high dosage of earthworm (Eisenia andrei) extract decreases cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in the mouse hippocampal dentate gyrus
- Temporal Change of Calbindin-D28k Immunoreactivity in the Dentate Gyrus of Voluntary Running Mouse
- Bacopa monnieri extract improves novel object recognition, cell proliferation, neuroblast differentiation, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein in the dentate gyrus
- Sirtuin-2 inhibition affects hippocampal functions and sodium butyrate ameliorates the reduction in novel object memory, cell proliferation, and neuroblast differentiation