Korean Diabetes J.
2010 Feb;34(1):47-54. 10.4093/kdj.2010.34.1.47.
The Effect of Glucose Fluctuation on Apoptosis and Function of INS-1 Pancreatic Beta Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Maryknoll Medical Center, Busan, Korea.
- 2Molecular Therapy Lab, Paik Memorial Institute for Clinical Research, Inje University, Busan, Korea. pjhdoc@chol.com
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2298045
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.1.47
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
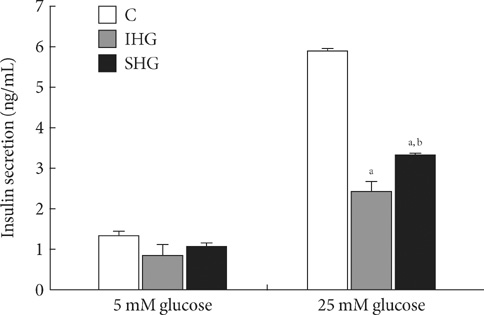
Blood glucose level continuously fluctuates within a certain range in the human body. In diabetes patients, the extent of such fluctuation is large, despite the strict control of blood glucose. Blood glucose fluctuation has been shown to mediate more adverse effects on vascular endothelial cells and diabetes complications than chronic hyperglycemia, which has been explained as due to oxidative stress. As few previous studies have reported the effects of chronic and intermittent hyperglycemia on the apoptosis and function of pancreatic beta cells, this study reported herein was performed to investigate such effects on these cells. METHODS: For chronic hyperglycemia, INS-1 cells were cultured for 5 days with changes of RPMI 1640 medium containing 33 mM glucose every 12 hours. For intermittent hyperglycemia, the medium containing 11 mM glucose was exchanged with the medium containing 33 mM glucose every 12 hours. Apoptosis was assessed by TUNEL assay Hoechst staining and cleaved caspase 3. Insulin secretory capacity was assessed, and the expression of Mn-SOD and Bcl-2 was measured by Western blotting. RESULTS: In comparison to the control group, INS-1 cells exposed to chronic hyperglycemia and intermittent hyperglycemia showed an increase in apoptosis. The apoptosis of INS-1 cells exposed to intermittent hyperglycemia increased significantly more than the apoptosis of INS-1 cells exposed to chronic hyperglycemia. In comparison to the control group, the insulin secretory capacity in the two hyperglycemic states was decreased, and more with intermittent hyperglycemia than with chronic hyperglycemia. The expression of Mn-SOD and Bcl-2 increased more with chronic hyperglycemia than with intermittent hyperglycemia. CONCLUSION: Intermittent hyperglycemia induced a higher degree of apoptosis and decreased the insulin secretory capacity more in pancreatic beta cells than chronic hyperglycemia. This activity may be mediated by the anti-oxidative enzyme Mn-SOD and the anti-apoptotic signal Bcl-2.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993. 329:977–986.2. Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, Matthews DR, Manley SE, Cull CA, Hadden D, Turner RC, Holman RR. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ. 2000. 321:405–412.3. Gerich JE. Clinical significance, pathogenesis, and management of postprandial hyperglycemia. Arch Intern Med. 2003. 163:1306–1316.4. Ceriello A, Hanefeld M, Leiter L, Monnier L, Moses A, Owens D, Tajima N, Tuomilehto J. Postprandial glucose regulation and diabetic complications. Arch Intern Med. 2004. 164:2090–2095.5. Heine RJ, Balkau B, Ceriello A, Del Prato S, Horton ES, Taskinen MR. What does postprandial hyperglycaemia mean? Diabet Med. 2004. 21:208–213.6. DECODE Study Group. the European Diabetes Epidemiology Group. Glucose tolerance and cardiovascular mortality: comparison of fasting and 2-hour diagnostic criteria. Arch Intern Med. 2001. 161:397–405.7. Meigs JB, Nathan DM, D'Agostino RB Sr, Wilson PW. Fasting and postchallenge glycemia and cardiovascular disease risk: the Framingham Offspring Study. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25:1845–1850.8. Brownlee M, Hirsch IB. Glycemic variability: a hemoglobin A1c-independent risk factor for diabetic complications. JAMA. 2006. 295:1707–1708.9. Shiraiwa T, Kaneto H, Miyatsuka T, Kato K, Yamamoto K, Kawashima A, Kanda T, Suzuki M, Imano E, Matsuhisa M, Hori M, Yamasaki Y. Postprandial hyperglycemia is a better predictor of the progression of diabetic retinopathy than HbA1c in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:2806–2807.10. Cavalot F, Petrelli A, Traversa M, Bonomo K, Fiora E, Conti M, Anfossi G, Costa G, Trovati M. Postprandial blood glucose is a stronger predictor of cardiovascular events than fasting blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus, particularly in women: lessons from the San Luigi Gonzaga Diabetes Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006. 91:813–819.11. Quagliaro L, Piconi L, Assaloni R, Martinelli L, Motz E, Ceriello A. Intermittent high glucose enhances apoptosis related to oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: the role of protein kinase C and NAD(P)H-oxidase activation. Diabetes. 2003. 52:2795–2804.12. Ceriello A, Esposito K, Piconi L, Ihnat MA, Thorpe JE, Testa R, Boemi M, Giugliano D. Oscillating glucose is more deleterious to endothelial function and oxidative stress than mean glucose in normal and type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes. 2008. 57:1349–1354.13. Monnier L, Mas E, Ginet C, Michel F, Villon L, Cristol JP, Colette C. Activation of oxidative stress by acute glucose fluctuations compared with sustained chronic hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. JAMA. 2006. 295:1681–1687.14. Hou ZQ, Li HL, Gao L, Pan L, Zhao JJ, Li GW. Involvement of chronic stresses in rat islet and INS-1 cell glucotoxicity induced by intermittent high glucose. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008. 291:71–78.15. Federici M, Hribal M, Perego L, Ranalli M, Caradonna Z, Perego C, Usellini L, Nano R, Bonini P, Bertuzzi F, Marlier LN, Davalli AM, Carandente O, Pontiroli AE, Melino G, Marchetti P, Lauro R, Sesti G, Folli F. High glucose causes apoptosis in cultured human pancreatic islets of Langerhans: a potential role for regulation of specific Bcl family genes toward an apoptotic cell death program. Diabetes. 2001. 50:1290–1301.16. Kohnert KD, Augstein P, Zander E, Heinke P, Peterson K, Freyse EJ, Hovorka R, Salzsieder E. Glycemic variability correlates strongly with postprandial beta-cell dysfunction in a segment of type 2 diabetic patients using oral hypoglycemic agents. Diabetes Care. 2009. 32:1058–1062.17. Devaraj S, Hirany SV, Burk RF, Jialal I. Divergence between LDL oxidative susceptibility and urinary F(2)-isoprostanes as measures of oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes. Clin Chem. 2001. 47:1974–1979.18. Lenzen S, Drinkgern J, Tiedge M. Low antioxidant enzyme gene expression in pancreatic islets compared with various other mouse tissues. Free Radic Biol Med. 1996. 20:463–466.19. Carrington EM, McKenzie MD, Jansen E, Myers M, Fynch S, Kos C, Strasser A, Kay TW, Scott CL, Allison J. Islet beta-cells deficient in Bcl-xL develop but are abnormally sensitive to apoptotic stimuli. Diabetes. 2009. 58:2316–2323.20. Piro S, Anello M, Di Pietro C, Lizzio MN, Patanè G, Rabuazzo AM, Vigneri R, Purrello M, Purrello F. Chronic exposure to free fatty acids or high glucose induces apoptosis in rat pancreatic islets: possible role of oxidative stress. Metabolism. 2002. 51:1340–1347.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Padina arborescens extract protects high glucose-induced apoptosis in pancreatic beta cells by reducing oxidative stress
- Protective effect of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside against tacrolimus-induced pancreatic beta cell dysfunction
- Mitogenic Effects and Signaling Pathway of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I (IGF-I) in the Rat Beta Cell Line (INS-1)
- Decreased Expression and Induced Nucleocytoplasmic Translocation of Pancreatic and Duodenal Homeobox 1 in INS-1 Cells Exposed to High Glucose and Palmitate
- The Effects of Exendin-4 on IRS-2 Expression and Phosphorylation in INS-1 Cells