J Lung Cancer.
2011 Jun;10(1):26-31. 10.6058/jlc.2011.10.1.26.
Mutational and Expressional Analysis of DOK2 Gene in Non-small Cell Lung Cancers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. suhulee@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2199891
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6058/jlc.2011.10.1.26
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Mounting evidence indicates that perturbation of tyrosine phosphorylation is implicated in the development of many human diseases, including cancers. Docking proteins (DOKs) are tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins that negatively regulate tyrosine kinase signaling and they are considered to be tumor suppressors. Deletion and the altered expression of the DOK2 gene have been studied in leukemias and lung cancers. However, the somatic mutation status of the DOK2 gene has not been studied in lung cancers. The aim of this study was to see whether alterations of DOK2 protein expression and somatic mutation of the DOK2 gene are present in human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
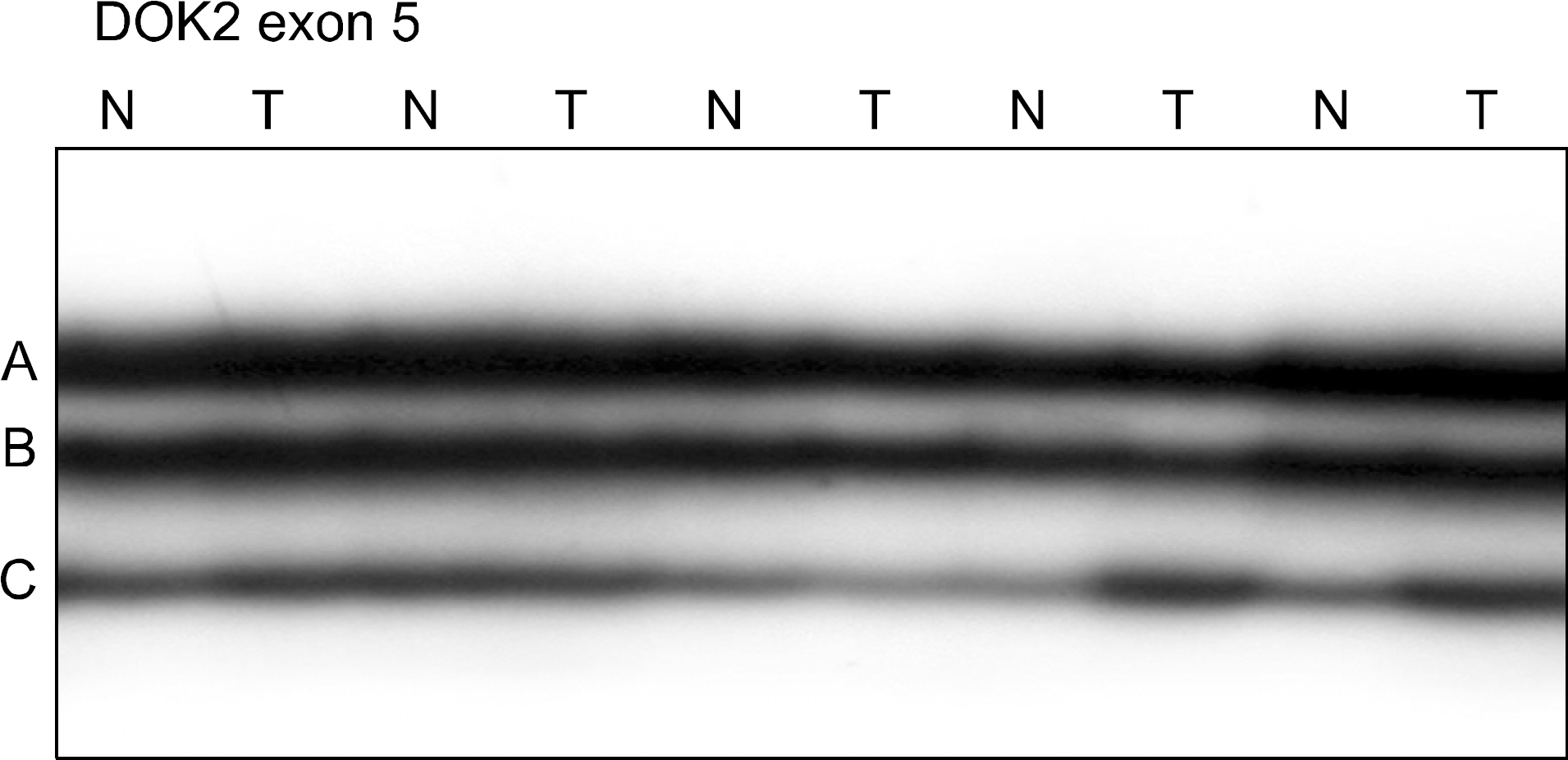
We analyzed DOK2 somatic mutation in 45 NSCLCs (23 adenocarcinomas (AD) and 22 squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) by single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP). We examined the DOK2 protein expression in 45 NSCLCs by immunohistochemistry.
RESULTS
SSCP analysis revealed no evidence of somatic mutation in the DNA sequences encoding the DOK2 gene in the 45 NSCLCs. Among the informative cases, 27% and 21% of the ADs and SCCs showed allelic loss in the DOK2 locus, respectively. On the immunohistochemistry, DOK2 protein was expressed in the normal bronchial epithelial cells, while it was lost in 10 (22%) of the NSCLCs.
CONCLUSION
Our data indicates that DOK2 is altered in NSCLC at the expressional level, but not at the mutational level. The data also suggests that loss of the expression of DOK2 might play roles in NSCLC development by possibly altering tyrosine kinase signaling.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma
Base Sequence
Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung
Carcinoma, Squamous Cell
Epithelial Cells
Gene Expression
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Leukemia
Loss of Heterozygosity
Lung
Lung Neoplasms
Phosphorylation
Polymorphism, Single-Stranded Conformational
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Proteins
Tyrosine
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Proteins
Tyrosine
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gschwind A, Fischer OM, Ullrich A. The discovery of receptor tyrosine kinases: targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004; 4:361–370.
Article2. Neel BG, Tonks NK. Protein tyrosine phosphatases in signal transduction. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997; 9:193–204.
Article3. Krause DS, Van Etten RA. Tyrosine kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:172–187.
Article4. Blume-Jensen P, Hunter T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature. 2001; 411:355–365.
Article5. Di Cristofano A, Carpino N, Dunant N, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of p56dok-2 defines a new family of RasGAP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:4827–4830.6. Suzu S, Tanaka-Douzono M, Nomaguchi K, et al. p56(dok-2) as a cytokine-inducible inhibitor of cell proliferation and signal transduction. EMBO J. 2000; 19:5114–5122.
Article7. Grimm J, Sachs M, Britsch S, et al. Novel p62dok family members, dok-4 and dok-5, are substrates of the c-Ret receptor tyrosine kinase and mediate neuronal differentiation. J Cell Biol. 2001; 154:345–354.
Article8. Dong S, Corre B, Foulon E, et al. T cell receptor for antigen induces linker for activation of T cell-dependent activation of a negative signaling complex involving Dok-2, SHIP-1, and Grb-2. J Exp Med. 2006; 203:2509–2518.
Article9. Gé rard A, Favre C, Garç on F, et al. Functional interaction of RasGAP-binding proteins Dok-1 and Dok-2 with the Tec protein tyrosine kinase. Oncogene. 2004; 23:1594–1598.
Article10. Cong F, Yuan B, Goff SP. Characterization of a novel member of the DOK family that binds and modulates Abl signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 1999; 19:8314–8325.
Article11. Jones N, Dumont DJ. Recruitment of Dok-R to the EGF receptor through its PTB domain is required for attenuation of Erk MAP kinase activation. Curr Biol. 1999; 9:1057–1060.
Article12. Niki M, Di Cristofano A, Zhao M, et al. Role of Dok-1 and Dok-2 in leukemia suppression. J Exp Med. 2004; 200:1689–1695.
Article13. Mashima R, Hishida Y, Tezuka T, Yamanashi Y. The roles of Dok family adapters in immunoreceptor signaling. Immunol Rev. 2009; 232:273–285.
Article14. Yasuda T, Shirakata M, Iwama A, et al. Role of Dok-1 and Dok-2 in myeloid homeostasis and suppression of leukemia. J Exp Med. 2004; 200:1681–1687.
Article15. Berger AH, Niki M, Morotti A, et al. Identification of DOK genes as lung tumor suppressors. Nat Genet. 2010; 42:216–223.
Article16. Berger AH, Pandolfi PP. Haplo-insufficiency: a driving force in cancer. J Pathol. 2011; 223:137–146.
Article17. Lee SH, Shin MS, Park WS, et al. Alterations of Fas (Apo-1/CD95) gene in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 1999; 18:3754–3760.
Article18. Lee JW, Soung YH, Kim SY, et al. PIK3CA gene is frequently mutated in breast carcinomas and hepatocellular carcinomas. Oncogene. 2005; 24:1477–1480.
Article19. Lee JW, Jeong EG, Soung YH, et al. Decreased expression of tumour suppressor Bax-interacting factor-1 (Bif-1), a Bax activator, in gastric carcinomas. Pathology. 2006; 38:312–315.
Article20. Sherr CJ. Principles of tumor suppression. Cell. 2004; 116:235–246.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mutational and Expressional Analysis of ATG5 Gene in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers
- Mutational Analysis of Pro-apoptotic BNIP3 Gene in Non- Small Cell Lung Cancers
- Mutational Analysis of PUMA Gene in Non-small Cell Lung Cancers
- Pro-apoptotic Cytochrome c Gene Mutation is Rare in Non-small Cell Lung Cancers
- Mutational Analysis of Pro-apoptotic BAD Gene in Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer