J Breast Cancer.
2016 Mar;19(1):45-52. 10.4048/jbc.2016.19.1.45.
Silibinin-Induced Apoptosis and Downregulation of MicroRNA-21 and MicroRNA-155 in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cell & Molecular Biology, School of Biology, College of Science, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran. motamed2@khayam.ut.ac.ir
- 2Department of Genetics, College of Science, Rasht Branch, Islamic Azad University, Rasht, Iran.
- 3National Cell Bank of Iran, Pasteur Institute of Iran, Tehran, Iran.
- 4Cancer Epigenetics Group, Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research & School of Anatomy, Physiology and Human Biology, The University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia.
- KMID: 2176320
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2016.19.1.45
Abstract
- PURPOSE
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have received much attention owing to their aberrant expression in various stages of cancer. In many biological processes, miRNAs negatively regulate gene expression, and may be useful in therapeutic strategies. The present study evaluated the effects of silibinin (silybin), a natural flavonoid, on miRNA expression and attempted to elucidate therapeutic targets in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
METHODS
The rates of cell proliferation and apoptosis were determined in silibinin-treated and untreated MCF-7 cells. Furthermore, the expression levels of miR-21 and miR-155 were measured in MCF-7 cells after incubation with silibinin (100 µg/mL), and the putative targets of the miRNAs within the apoptotic pathways were predicted using bioinformatic approaches. The expression levels of some of these targets were evaluated by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
RESULTS
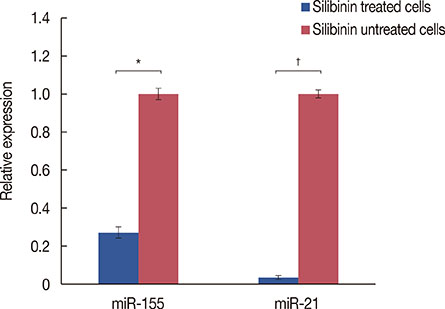
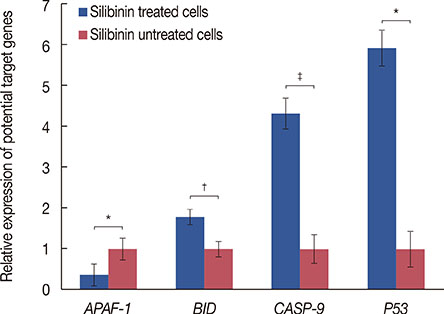
Silibinin induced apoptosis in MCF-7 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. qRT-PCR analysis revealed a decrease in miR-21 and miR-155 expression levels in silibinin-treated cells relative to the levels in the untreated cells. Potential miR-21 and miR-155 targets within the apoptotic pathways, such as CASP-9, BID, APAF-1, CASP-3, CASP-8, and PDCD4, were predicted by in silico analysis. qRT-PCR analysis showed upregulation of some of these potential targets including caspase-9 (CASP-9) and BID after silibinin treatment for 48 hours.
CONCLUSION
Our results suggest a correlation between the expression of miR-21 and miR-155, and MCF-7 cell proliferation. The antiproliferative activity of silibinin may partly be attributable to the downregulation of miR-21 and miR-155, and the upregulation of their apoptotic targets. Furthermore, the upregulation of CASP-9 and BID indicates that silibinin induces apoptosis through both the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tiwari P, Kumar A, Balakrishnan S, Kushwaha HS, Mishra KP. Silibinin-induced apoptosis in MCF7 and T47D human breast carcinoma cells involves caspase-8 activation and mitochondrial pathway. Cancer Invest. 2011; 29:12–20.
Article2. Noh EM, Yi MS, Youn HJ, Lee BK, Lee YR, Han JH, et al. Silibinin enhances ultraviolet B-induced apoptosis in mcf-7 human breast cancer cells. J Breast Cancer. 2011; 14:8–13.
Article3. Ranji N, Sadeghizadeh M, Karimipoor M, Shokrgozar MA, Ebrahimzadeh-Vesal R. AKT family and miRNAs expression in IL-2 induced CD4(+)T cells. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2014; 17:886–894.4. Blondal T, Jensby Nielsen S, Baker A, Andreasen D, Mouritzen P, Wrang Teilum M, et al. Assessing sample and miRNA profile quality in serum and plasma or other biofluids. Methods. 2013; 59:S1–S6.
Article5. Ranji N, Sadeghizadeh M, Shokrgozar MA, Bakhshandeh B, Karimipour M, Amanzadeh A, et al. MiR-17-92 cluster: an apoptosis inducer or proliferation enhancer. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013; 380:229–238.
Article6. Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z, Kong D, Ali S. Implication of microRNAs in drug resistance for designing novel cancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat. 2010; 13:57–66.
Article7. Yang H, Kong W, He L, Zhao JJ, O'Donnell JD, Wang J, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214 induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN. Cancer Res. 2008; 68:425–433.
Article8. Rothé F, Ignatiadis M, Chaboteaux C, Haibe-Kains B, Kheddoumi N, Majjaj S, et al. Global microRNA expression profiling identifies MiR-210 associated with tumor proliferation, invasion and poor clinical outcome in breast cancer. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e20980.
Article9. Witkos TM, Koscianska E, Krzyzosiak WJ. Practical aspects of microRNA target prediction. Curr Mol Med. 2011; 11:93–109.
Article10. Kim S, Lee HS, Lee SK, Kim SH, Hur SM, Kim JS, et al. 12-O-Tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced growth arrest is increased by silibinin by the down-regulation of cyclin B1 and cdc2 and the up-regulation of p21 expression in MDA-MB231 human breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 2010; 17:1127–1132.
Article11. Cufí S, Bonavia R, Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Corominas-Faja B, Cuyàs E, et al. Silibinin suppresses EMT-driven erlotinib resistance by reversing the high miR-21/low miR-200c signature in vivo. Sci Rep. 2013; 3:2459.
Article12. Zhu S, Wu H, Wu F, Nie D, Sheng S, Mo YY. MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis. Cell Res. 2008; 18:350–359.
Article13. Zadeh MM, Ranji N, Motamed N. Deregulation of miR-21 and miR-155 and their putative targets after silibinin treatment in T47D breast cancer cells. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015; 18:1209–1214.14. Gao J, Zhang Q, Xu J, Guo L, Li X. Clinical significance of serum miR-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA. Chin J Cancer Res. 2013; 25:743–748.15. Walter BA, Gómez-Macias G, Valera VA, Sobel M, Merino MJ. miR-21 expression in pregnancy-associated breast cancer: a possible marker of poor prognosis. J Cancer. 2011; 2:67–75.
Article16. Yan LX, Wu QN, Zhang Y, Li YY, Liao DZ, Hou JH, et al. Knockdown of miR-21 in human breast cancer cell lines inhibits proliferation, in vitro migration and in vivo tumor growth. Breast Cancer Res. 2011; 13:R2.17. Zhang CM, Zhao J, Deng HY. MiR-155 promotes proliferation of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells through targeting tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1. J Biomed Sci. 2013; 20:79.
Article18. Jiang S, Zhang HW, Lu MH, He XH, Li Y, Gu H, et al. MicroRNA-155 functions as an OncomiR in breast cancer by targeting the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 gene. Cancer Res. 2010; 70:3119–3127.
Article19. Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A, Lindow M, Krogh A, Lund AH. Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283:1026–1033.
Article20. Sayed D, Abdellatif M. AKT-ing via microRNA. Cell Cycle. 2010; 9:3213–3217.
Article21. Lankat-Buttgereit B, Göke R. The tumour suppressor Pdcd4: recent advances in the elucidation of function and regulation. Biol Cell. 2009; 101:309–317.
Article22. Gasparini P, Lovat F, Fassan M, Casadei L, Cascione L, Jacob NK, et al. Protective role of miR-155 in breast cancer through RAD51 targeting impairs homologous recombination after irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111:4536–4541.
Article23. Higgs G, Slack F. The multiple roles of microRNA-155 in oncogenesis. J Clin Bioinforma. 2013; 3:17.
Article24. Fu WN, Bertoni F, Kelsey SM, McElwaine SM, Cotter FE, Newland AC, et al. Role of DNA methylation in the suppression of Apaf-1 protein in human leukaemia. Oncogene. 2003; 22:451–455.
Article25. Kim HE, Jiang X, Du F, Wang X. PHAPI, CAS, and Hsp70 promote apoptosome formation by preventing Apaf-1 aggregation and enhancing nucleotide exchange on Apaf-1. Mol Cell. 2008; 30:239–247.
Article26. Klener P Jr, Andera L, Klener P, Necas E, Zivný J. Cell death signalling pathways in the pathogenesis and therapy of haematologic malignancies: overview of therapeutic approaches. Folia Biol (Praha). 2006; 52:119–136.27. Anto RJ, Mukhopadhyay A, Denning K, Aggarwal BB. Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) induces apoptosis through activation of caspase-8, BID cleavage and cytochrome c release: its suppression by ectopic expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl. Carcinogenesis. 2002; 23:143–150.
Article28. Kang MH, Reynolds CP. Bcl-2 inhibitors: targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2009; 15:1126–1132.
Article29. Ma X, Choudhury SN, Hua X, Dai Z, Li Y. Interaction of the oncogenic miR-21 microRNA and the p53 tumor suppressor pathway. Carcinogenesis. 2013; 34:1216–1223.
Article30. Osada H, Takahashi T. MicroRNAs in biological processes and carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2007; 28:2–12.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Silibinin Enhances Ultraviolet B-Induced Apoptosis in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells
- LncRNA Taurine-Upregulated Gene 1 Promotes Cell Proliferation by Inhibiting MicroRNA-9 in MCF-7 Cells
- Prolactin Inhibits BCL6 Expression in Breast Cancer Cells through a MicroRNA-339-5p-Dependent Pathway
- Apoptotic Effects of 6-Gingerol in Human Breast Cancer Cells
- Effects of retinoic acid isomers on apoptosis and enzymatic antioxidant system in human breast cancer cells