Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2016 Jan;8(1):63-68. 10.4168/aair.2016.8.1.63.
Alternaria Induces Production of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in Nasal Fibroblasts Through Toll-like Receptor 2
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, School of medicine, Catholic University of Daegu, Daegu, Korea. hsseung@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2166653
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2016.8.1.63
Abstract
- PURPOSE
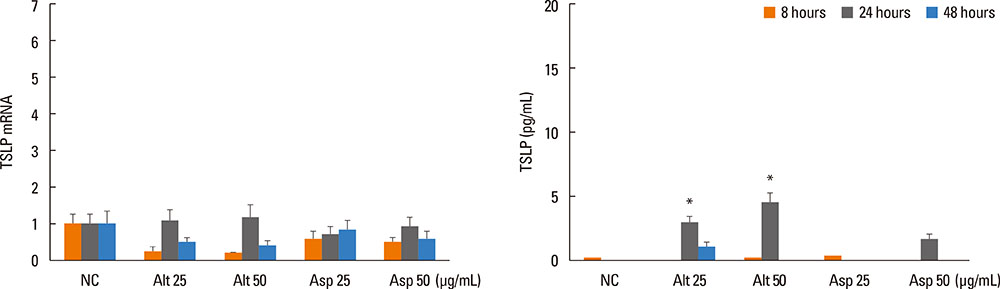
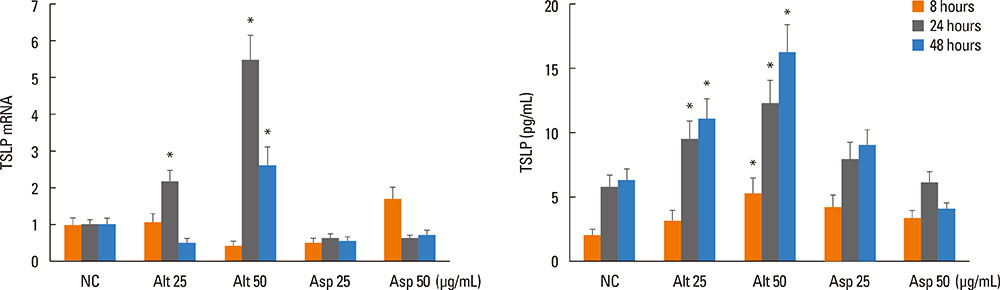
Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps is a chronic inflammatory disease with markedly increased eosinophils, Th2-type lymphocytes, fibroblasts, and goblet cells. Fungi are commonly associated with airway inflammatory diseases, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) is important in the development of Th2 inflammatory responses. The aim of this study was to investigate the interaction between airborne fungi and nasal fibroblasts in TSLP mRNA and protein expression.
METHODS
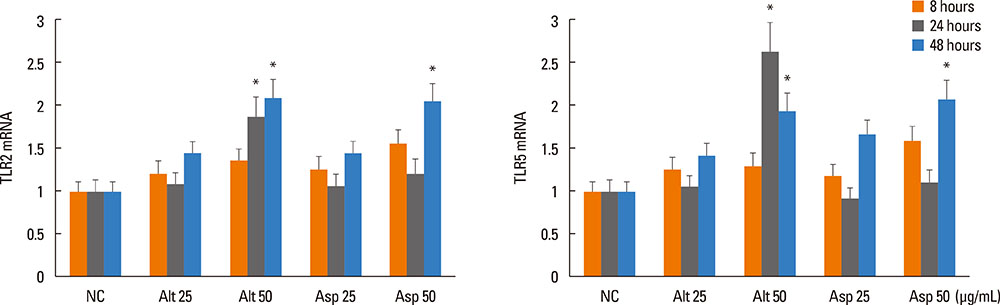
Inferior turbinate and nasal polyp fibroblasts were stimulated with Alternaria and Aspergillus, respectively, for 48 hours, and TSLP mRNA and protein expressions were measured. The reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction was performed for the Toll-like receptor (TLR) mRNA expression of the nasal fibroblasts. To determine the role of TLR in the induction of TSLP, the fibroblasts were transfected with siRNA against TLR2 and TLR5.
RESULTS
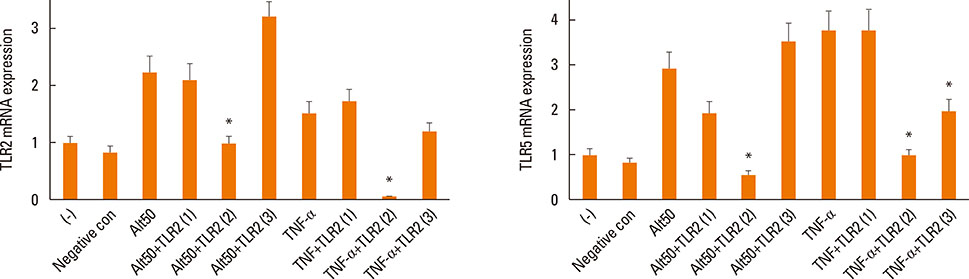
Alternaria induced TSLP mRNA and protein expression in both inferior turbinate and nasal polyp fibroblasts. The nasal polyp fibroblasts responded more strongly to the fungi. TLR2 and TLR5 mRNA expressions were significantly increased with fungal stimulation and TSLP production was significantly inhibited by siRNA against TLR2.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study show that TSLP expression could be induced in nasal fibroblasts by exposure to Alternaria and that TLR2 may be involved in the process. The promotion of TSLP production in nasal fibroblasts by airborne fungi may facilitate the development or exacerbation of Th2-type nasal inflammation, especially in CRS with nasal polyps.
MeSH Terms
-
Alternaria*
Aspergillus
Eosinophils
Fibroblasts*
Fungi
Goblet Cells
Inflammation
Lymphocytes
Nasal Polyps
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA, Messenger
RNA, Small Interfering
Toll-Like Receptor 2*
Toll-Like Receptors*
Turbinates
RNA, Messenger
RNA, Small Interfering
Toll-Like Receptor 2
Toll-Like Receptors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zhang K, Shan L, Rahman MS, Unruh H, Halayko AJ, Gounni AS. Constitutive and inducible thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression in human airway smooth muscle cells: role in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007; 293:L375–L382.2. Ziegler SF. The role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) in allergic disorders. Curr Opin Immunol. 2010; 22:795–799.3. Liu YJ. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin: master switch for allergic inflammation. J Exp Med. 2006; 203:269–273.4. Ying S, O'Connor B, Ratoff J, Meng Q, Fang C, Cousins D, et al. Expression and cellular provenance of thymic stromal lymphopoietin and chemokines in patients with severe asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Immunol. 2008; 181:2790–2798.5. Kimura S, Pawankar R, Mori S, Nonaka M, Masuno S, Yagi T, et al. Increased expression and role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in nasal polyposis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011; 3:186–193.6. Teran LM, Mochizuki M, Bartels J, Valencia EL, Nakajima T, Hirai K, et al. Th1- and Th2-type cytokines regulate the expression and production of eotaxin and RANTES by human lung fibroblasts. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999; 20:777–786.7. Nomura K, Kojima T, Fuchimoto J, Obata K, Keira T, Himi T, et al. Regulation of interleukin-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin in human nasal fibroblasts by proinflammatory cytokines. Laryngoscope. 2012; 122:1185–1192.8. Kouzaki H, O'Grady SM, Lawrence CB, Kita H. Proteases induce production of thymic stromal lymphopoietin by airway epithelial cells through protease-activated receptor-2. J Immunol. 2009; 183:1427–1434.9. Shin SH, Lee YH. Airborne fungi induce nasal polyp epithelial cell activation and toll-like receptor expression. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010; 153:46–52.10. Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, et al. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology. 2012; 50:1–12.11. Fukumoto A, Nonaka M, Ogihara N, Pawankar R. Induction of TARC production by lipopolysaccharide and interleukin-4 in nasal fibroblasts. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2008; 145:291–297.12. Shin SH, Ye MK, Kim JK. Effects of fungi and eosinophils on mucin gene expression in rhinovirus-infected nasal epithelial cells. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:149–155.13. Shin SH, Ye MK, Lee YH. Fungus culture of the nasal secretion of chronic rhinosinusitis patients: seasonal variations in Daegu, Korea. Am J Rhinol. 2007; 21:556–559.14. Janssens S, Beyaert R. Role of toll-like receptors in pathogen recognition. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2003; 16:637–646.15. Chen K, Huang J, Gong W, Iribarren P, Dunlop NM, Wang JM. Tolllike receptors in inflammation, infection and cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 2007; 7:1271–1285.16. Dong Z, Yang Z, Wang C. Expression of TLR2 and TLR4 messenger RNA in the epithelial cells of the nasal airway. Am J Rhinol. 2005; 19:236–239.17. Gantner BN, Simmons RM, Canavera SJ, Akira S, Underhill DM. Collaborative induction of inflammatory responses by dectin-1 and Toll-like receptor 2. J Exp Med. 2003; 197:1107–1117.18. Ozawa T, Koyama K, Ando T, Ohnuma Y, Hatsushika K, Ohba T, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin secretion of synovial fibroblasts is positively and negatively regulated by Toll-like receptors/nuclear factor-κB pathway and interferon-γ/dexamethasone. Mod Rheumatol. 2007; 17:459–463.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Panonychus citri Can Induce T-helper Type 2 Immune Responses via the Release of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and IL-4
- Increased Expression and Role of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in Nasal Polyposis
- Nucleic Acid Recognition and Signaling by Toll-like Receptor 9: Compartment-dependent Regulation
- IL-17 and Toll-like Receptor 2 or Toll-like Receptor 4 Combined Engagement Upregulates RANKL and IL-6 in Human Rheumatoid Synovial Fibroblasts
- Histamine Induced Production of Chemokine CXCL8 Through H1R/PLC and NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Nasal Fibroblasts