J Rhinol.
2020 Nov;27(2):95-101. 10.18787/jr.2019.00302.
Histamine Induced Production of Chemokine CXCL8 Through H1R/PLC and NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Nasal Fibroblasts
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2508953
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2019.00302
Abstract
- Background and Objectives
Histamine has been suggested to play an important role during allergic and inflammatory reactions, affecting allergic rhinitis and chronic rhinosinusitis. CXCL8 is a pro-inflammatory chemokine and a critical factor that causes many airway inflammatory diseases including allergic rhinitis and chronic rhinosinusitis. Materials and Method: Histamine cytotoxicity was measured by MTT assay. Real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to identify histamine type 1 receptor in nasal fibroblasts. The fibroblasts were then treated with histamine with or without a histamine type 1 receptor antagonist and the CXCL8 protein was assessed using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The downstream signaling molecules, including phospholipase C and phospho-p50, were evaluated by western blot and immunofluorescent staining.
Results
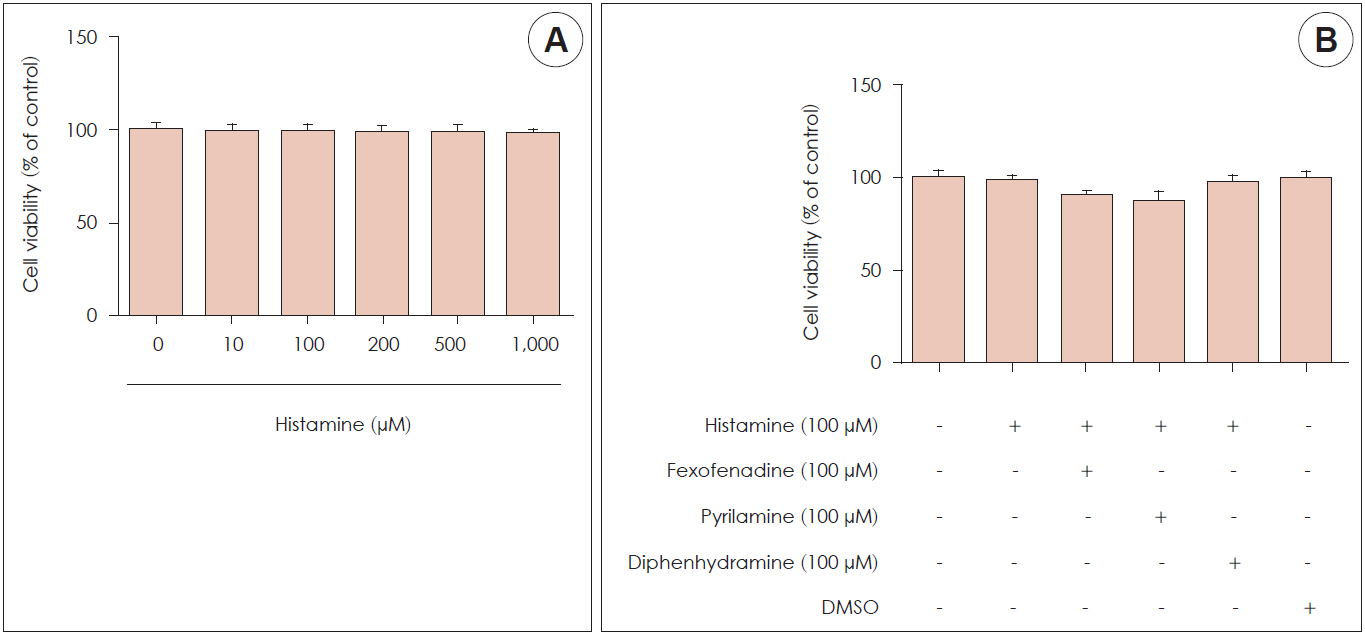
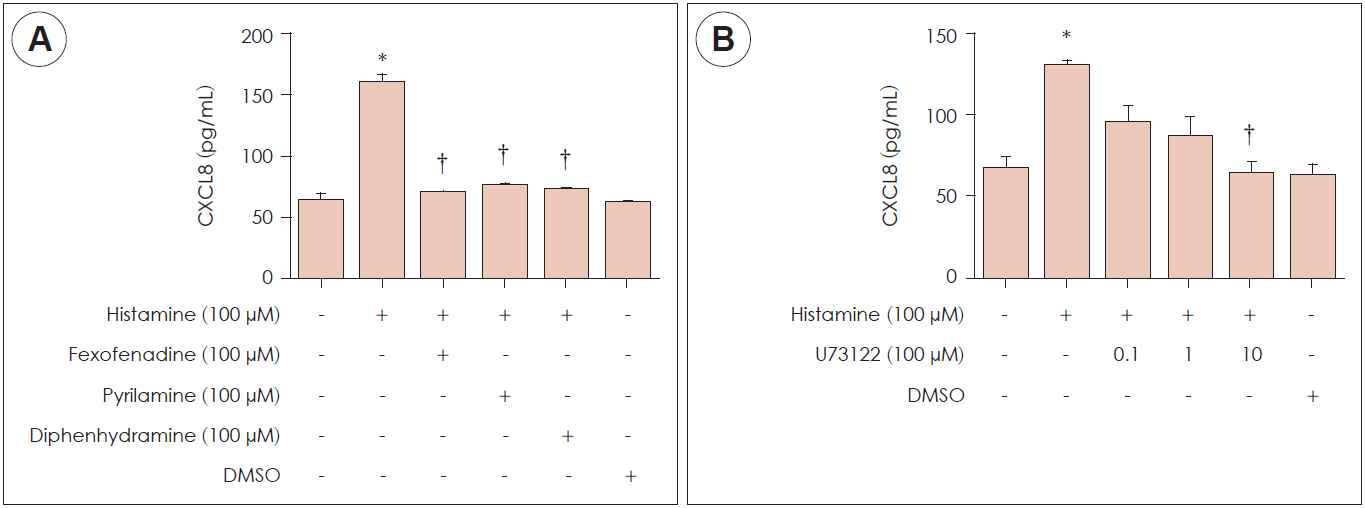
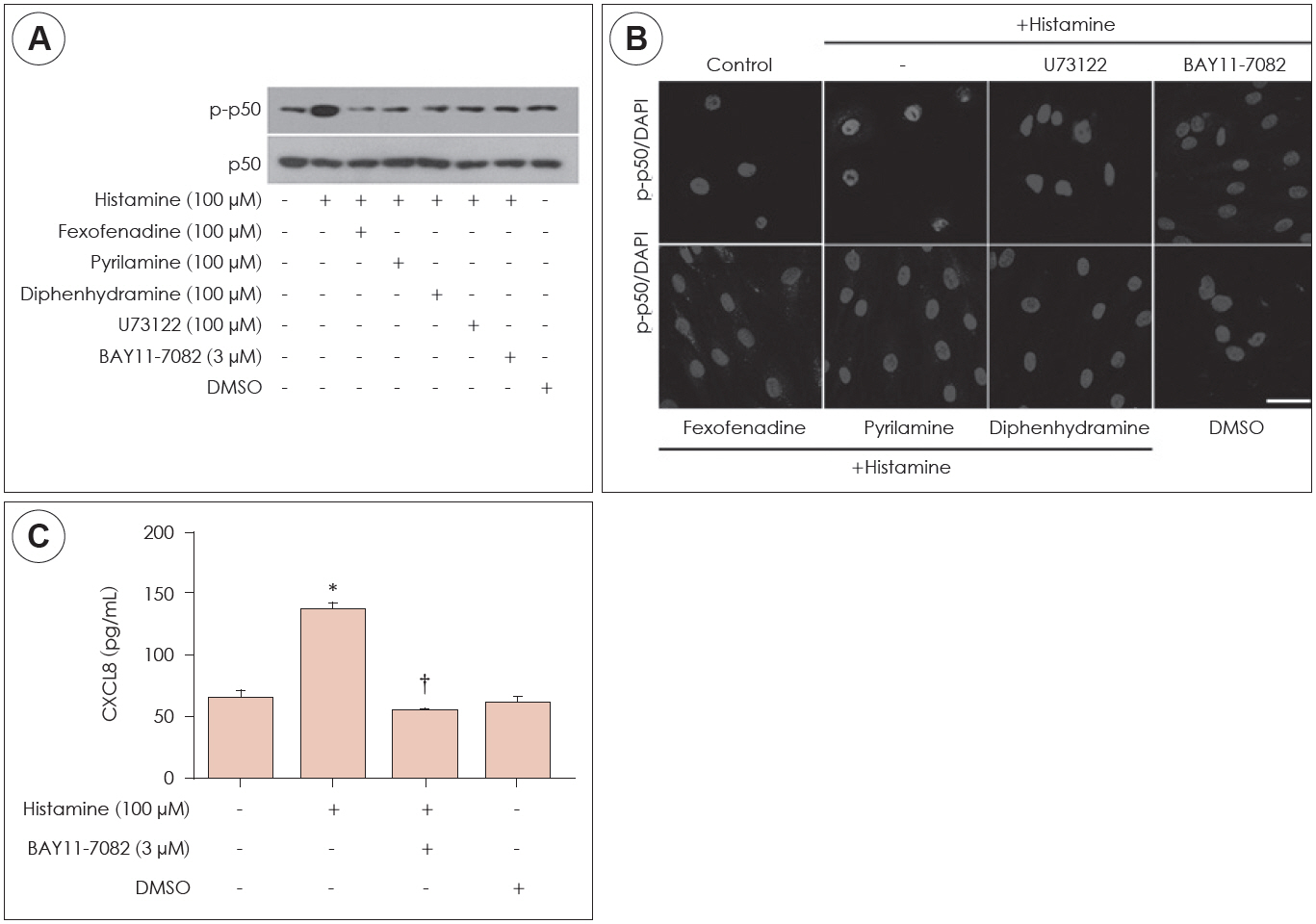
Histamine had no significant cytotoxic effect until the concentration reached 1,000 μM. Histamine type 1 receptor mRNA was expressed in nasal fibroblasts. CXCL8 protein expression level was significantly increased following histamine stimulation. However, the expression level of CXCL8 decreased when phospholipase C was inhibited by U73122. Histamine increased phospho-p50 expression as seen in western blot results. The BAY11-7082, NF-κB inhibitor significantly reduced CXCL8 production in histamine-stimulated nasal fibroblasts.
Conclusion
Histamine can induce the production of NF-κB controlled-chemokine CXCL8 by nasal fibroblasts, which supports a role for histamine in upper airway inflammatory diseases.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Modena BD, Dazy K, White AA. Emerging concepts: mast cell involvement in allergic diseases. Transl Res. 2016; 174:98–121.2. Stone KD, Prussin C, Metcalfe DD. IgE, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:S73–80.3. He SH, Zhang HY, Zeng XN, Chen D, Yang PC. Mast cells and basophils are essential for allergies: mechanisms of allergic inflammation and a proposed procedure for diagnosis. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2013; 34:1270–83.4. Siracusa MC, Kim BS, Spergel JM, Artis D. Basophils and allergic inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 132:789–801. quiz 788.5. Galli SJ, Tsai M, Piliponsky AM. The development of allergic inflammation. Nature. 2008; 454:445–54.6. Shimamura T, Shiroishi M, Weyand S, Tsujimoto H, Winter G, Katritch V, et al. Structure of the human histamine H1 receptor complex with doxepin. Nature. 2011; 475:65–70.7. Matsubara M, Ohmori K, Hasegawa K. Histamine H1 receptor-stimulated interleukin 8 and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production by bronchial epithelial cells requires extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling via protein kinase C. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2006; 139:279–93.8. Albrecht M, Dittrich AM. Expression and function of histamine and its receptors in atopic dermatitis. Mol Cell Pediatr. 2015; 2:16.9. Shirasaki H, Kanaizumi E, Seki N, Himi T. Localization and upregulation of the nasal histamine H1 receptor in perennial allergic rhinitis. Mediators Inflamm. 2012; 2012:951316.10. Humphrey JD, Dufresne ER, Schwartz MA. Mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio. 2014; 15:802–12.11. Park SK, Jin YD, Park YK, Yeon SH, Xu J, Han RN, et al. IL-25-induced activation of nasal fibroblast and its association with the remodeling of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Plos One. 2017; 12(8):e0181806.12. Brechard S, Bueb JL, Tschirhart EJ. Interleukin-8 primes oxidative burst in neutrophil-like HL-60 through changes in cytosolic calcium. Cell Calcium. 2005; 37:531–40.13. Turner MD, Nedjai B, Hurst T, Pennington DJ. Cytokines and chemokines: At the crossroads of cell signalling and inflammatory disease. Bba-Mol Cell Res. 2014; 1843:2563–82.14. Agache I, Akdis CA. Endotypes of allergic diseases and asthma: An important step in building blocks for the future of precision medicine. Allergol Int. 2016; 65:243–52.15. Xi X, McMillan DH, Lehmann GM, Sime PJ, Libby RT, Huxlin KR, et al. Ocular fibroblast diversity: implications for inflammation and ocular wound healing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:4859–65.16. Stamegna JC, Girard SD, Veron A, Sicard G, Khrestchatisky M, Feron F, et al. A unique method for the isolation of nasal olfactory stem cells in living rats. Stem Cell Res. 2014; 12:673–9.17. Amin K. The role of mast cells in allergic inflammation. Resp Med. 2012; 106:9–14.18. Jundi K, Greene CM. Transcription of Interleukin-8: How Altered Regulation Can Affect Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. Biomolecules. 2015; 5:1386–98.19. Duque GA, Descoteaux A. Macrophage cytokines: involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front Immunol. 2014; 5:1–12.20. Raghuwanshi SK, Su YJ, Singh V, Haynes K, Richmond A, Richardson RM. The Chemokine Receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2 Couple to Distinct G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinases To Mediate and Regulate Leukocyte Functions. Journal of Immunology. 2012; 189:2824–32.21. Wilgus TA, Roy S, McDaniel JC. Neutrophils and Wound Repair: Positive Actions and Negative Reactions. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2013; 2:379–88.22. Lee S, Lane AP. Chronic rhinosinusitis as a multifactorial inflammatory disorder. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2011; 13:159–68.23. Ural A, Tezer MS, Yucel A, Atilla H, Ileri F. Interleukin-4, interleukin-8 and E-selectin levels in intranasal polyposis patients with and without allergy: a comparative study. J Int Med Res. 2006; 34:520–4.24. Cho SH, Kim DW, Gevaert P. Chronic Rhinosinusitis without Nasal Polyps. J Aller Cl Imm-Pract. 2016; 4:575–82.25. Cho JS, Han IH, Lee HR, Lee HM. Prostaglandin E2 Induces IL-6 and IL-8 Production by the EP Receptors/Akt/NF-kappa B Pathways in Nasal Polyp-Derived Fibroblasts. Allergy Asthma Immun. 2014; 6:449–57.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Histamine Promotes the Release of Interleukin-6 via the H1R/p38 and NF-kappaB Pathways in Nasal Fibroblasts
- Galangin Regulates Mucin 5AC Gene Expression via the Nuclear Factor-κB Inhibitor α/Nuclear Factor-κB p65 Pathway in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- Regulation of RANTES and MCP Expression in Human Nasal Mucosal Fibroblasts
- Kaempferol Regulates the Expression of Airway MUC5AC Mucin Gene via IκBα-NF-κB p65 and p38-p44/42-Sp1 Signaling Pathways
- Eriodictyol Inhibits the Production and Gene Expression of MUC5AC Mucin via the IκBα-NF-κB p65 Signaling Pathway in Airway Epithelial Cells