Cancer Res Treat.
2005 Oct;37(5):313-317.
Pattern of Apoptosis by NS398, a Selective COX-2 Inhibitor, in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Lines
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Immunology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. ysung@knu.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
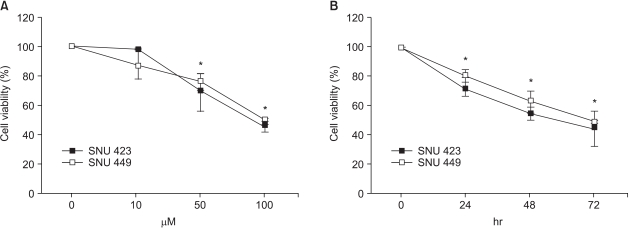
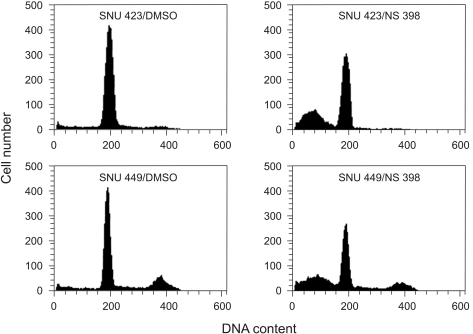
NS398, a selective COX-2 inhibitor, is known to inhibit the growth of COX-2 expressing hepatocellular carcinoma cells. The present study investigated whether the cytotoxic effect of NS398 was COX-2 dependent and whether caspases were involved in NS398-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The expressions of COX-2 in SNU 423 and SNU 449 hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines were examined using RT-PCR and Western blot. The cytotoxic effect of NS398 was measured using MTT in the presence or absence of caspase inhibitors. The distribution of the cell cycle and extent of apoptosis were analyzed using flow cytometry and a Cell Death Elisa kit, respectively. RESULTS: The expression of COX-2 was observed in SNU423 cells, but not in SNU 449 cells. NS398 treatment resulted in both dose-and time-dependent growth inhibitions, with increases in apoptotic cells in both cell lines. Treatment with the pan-caspase inhibitor, z-VAD- fmk, or the caspase-3 inhibitor, Ac-DMQD-CHO, showed no attenuation of the cytotoxic effect of NS398 in either cell line. CONCLUSIONS: This study demonstrated that the cytotoxic effect of NS398 was independent of COX-2 expression. Caspases were also shown not to be involved in NS398-induced apoptosis in either SNU 423 or SNU 449 Korean HCC cell lines. Our data suggests the feasibility of preventing hepatocellular carcinoma with the use of COX-2 inhibitors needs to be carefully evaluated.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Smith WL, Langenbach R. Why there are two cyclooxygenase isozymes. J Clin Invest. 2001; 107:1491–1495. PMID: 11413152.
Article2. Tsujii M, DuBois RN. Alterations in cellular adhesion and apoptosis in epithelial cells overexpressing prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2. Cell. 1995; 83:493–501. PMID: 8521479.
Article3. Tsujii M, Kawano S, Tsuji S, Sawaoka H, Hori M, DuBois RN. Cyclooxygenase regulates angiogenesis induced by colon cancer cells. Cell. 1998; 93:705–716. PMID: 9630216.
Article4. Jiang MC, Liao CF, Lee PH. Aspirin inhibits matrix etalloproteinase-2 activity, increases E-cadherin production, and inhibits in vitro invasion of tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001; 282:671–677. PMID: 11401513.5. Koga H, Sakisaka S, Ohishi M, Kawaguchi T, Taniguchi E, Sasatomi K, et al. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma: relevance to tumor dedifferentiation. Hepatology. 1999; 29:688–696. PMID: 10051469.
Article6. Bae SH, Jung ES, Park YM, Kim BS, Kim BK, Kim DG, et al. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in hepatocellular carcinoma and growth inhibition of hepatoma cell lines by a COX-2 inhibitor, NS-398. Clin Cancer Res. 2001; 7:1410–1418. PMID: 11350912.7. Sung YK, Hwang SY, Kim JO, Bae HI, Kim JC, Kim MK. The correlation between cyclooxygenase-2 expression and hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cells. 2004; 17:35–38. PMID: 15055524.8. Cheng J, Imanishi H, Amuro Y, Hada T. NS-398, a selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor, inhibited cell growth and induced cell cyle arrest in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Int J Cancer. 2002; 99:755–761. PMID: 12115513.9. Kern MA, Schubert D, Sahi D, Schoneweiss MM, Moll I, Haugg AM, et al. Proapoptotic and antiproliferative potential of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in human liver tumor cells. Hepatology. 2002; 36:885–894. PMID: 12297835.
Article10. Cheng AS, Chan HL, Leung WK, Wong N, Johnson PJ, Sung JJ. Specific COX-2 inhibitor, NS-398, suppresses cellular proliferation and induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2003; 23:113–119. PMID: 12792783.
Article11. Park MK, Hwang SY, Kim JO, Kwack MH, Kim JC, Kim MK, et al. NS398 inhibits the growth of Hep3B human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via caspase-independent apoptosis. Mol Cells. 2004; 17:45–50. PMID: 15055526.12. Sung YK, Hwang SY, Farooq M, Kim JC, Kim MK. Growth promotion of HepG2 hepatoma cells by antisense-mediated knockdown of glypican-3 is independent of insulin-like growth factor 2 signaling. Exp Mol Med. 2003; 35:257–262. PMID: 14508064.
Article13. Farooq M, Hwang SY, Park MK, Kim JC, Kim MK, Sung YK. Blocking endogenous glypican-3 expression releases Hep 3B cells from G1 arrest. Mol Cells. 2003; 15:356–360. PMID: 12872992.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cytotoxicity of COX-2 Inhibitor (Nimesulide) in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Line
- The Enhancement of Radiosensitivity by Celecoxib, Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitor, on Human Cancer Cells Expressing Differential Levels of Cyclooxygenase-2
- Growth inhibition of oral squamous cell carcinorma cell line induced by cox inhibitor
- Down-regulation of survivin in growth inhibition of hepatoma cells induced by a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor
- In Vitro Responses of SK-OV-3 Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines to Tamoxifen and Celecoxib