Cancer Res Treat.
2007 Mar;39(1):22-29.
Enhancement of Plasmacytoma Cell Growth by Ascorbic Acid is Mediated Via Glucose 6-phosphate Dehydrogenase
- Affiliations
-
- 1Korea Institute of Toxicology, Daejeon, Korea. wskoh@kitox.re.kr
- 2Cancer Center, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3The Center for Improvement of Human Functioning International, Wichita, KS 67219, USA.
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: We investigated the mechanism by which some types of cancer cells grow faster in the presence of ascorbic acid supplementation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Adj.PC-5, a mouse plasmacytoma cell, is known to show ascorbic acid-dependent growth and was chosen as a test system. The growth of cancer cells was measured by the colony number on soft agar or the cellular proliferation in suspension culture. The ascorbate level was measured by a high performance liquid chromatography system with an electrochemical detector. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase was analyzed both on the specific enzyme activity level and on the transcription level by performing Northern blot analysis.
RESULTS
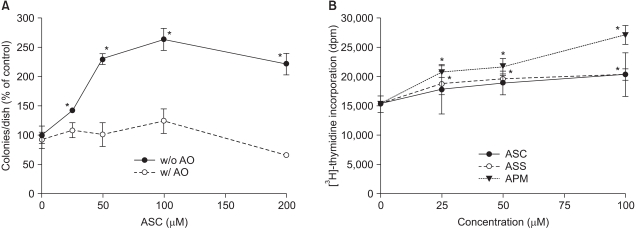
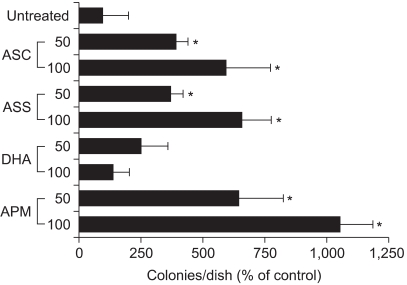
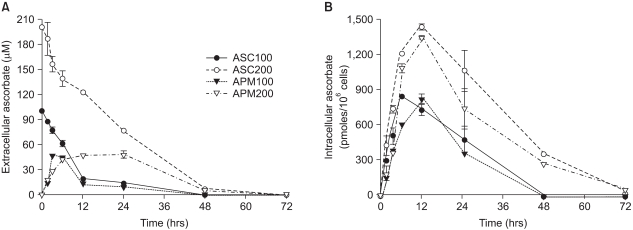
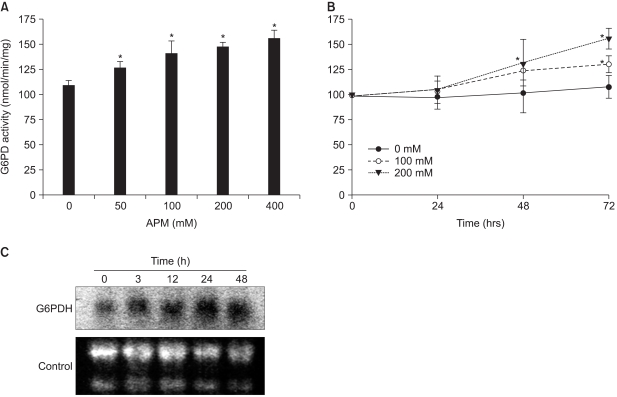
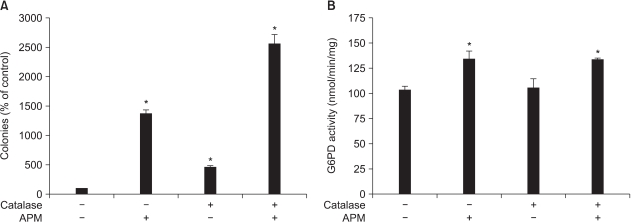
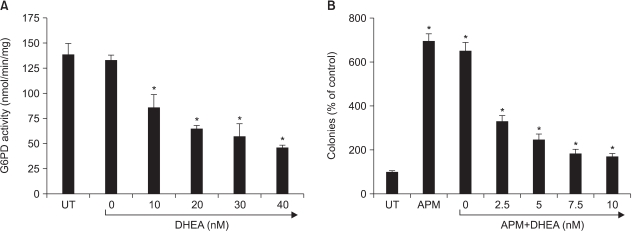
Ascorbyl 2-phosphate among the ascorbate derivatives was the most efficient in stimulating cell growth. The intracellular and extracellular ascorbate concentrations following treatment with either ascorbate or ascorbyl 2-phosphate suggest that the superiority of ascorbyl 2-phosphate for stimulating cell growth may be due to its slow conversion to ascorbate in the culture medium. The steady transformation to ascorbate ensures sustained levels of ascorbate in the culture medium and thereby maximizes the growth stimulatory effect of ascorbate. Ascorbyl 2-phosphate markedly enhanced, in a concentration-and time-dependent manner, mRNA synthesis as well as the enzymatic activity of glucose 6- phosphate dehydrogenase, which is known to be a rate- limiting enzyme in cell growth. On the other hand, simultaneous addition of dehydroisoandrosterone, a well- known inhibitor of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase, to the culture medium abrogated the growth stimulation by ascorbyl 2-phosphate, and it also reduced the glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity proportionately.
CONCLUSIONS
The results from this study suggest that enhanced glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity may at least in part explain the stimulation of cell growth by ascorbate or ascorbyl 2-phosphate.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Elmore AR. Final report of the safety assessment of L-Ascorbic Acid, Calcium Ascorbate, Magnesium Ascorbate, Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate, Sodium Ascorbate, and Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate as used in cosmetics. Int J Toxicol. 2005; 24(Suppl 2):51–111. PMID: 16154915.2. Casciari JJ, Riordan NH, Schmidt TL, Meng XL, Jackson JA, Riordan HD. Cytotoxicity of ascorbate, lipoic acid, and other antioxidants in hollow fibre in vitro tumours. Br J Cancer. 2001; 84:1544–1550. PMID: 11384106.
Article3. Koh WS, Lee SJ, Lee H, Park C, Park MH, Kim WS, et al. Differential effects and transport kinetics of ascorbate derivatives in leukemic cell lines. Anticancer Res. 1998; 18:2487–2493. PMID: 9703897.4. Park CH, Amare M, Hoogstraten B. Analysis of the growth enhancing effect of L-ascorbic acid on human leukemic cells in culture. Exp Hematol. 1980; 8:853–859. PMID: 16398016.5. Park CH, Bergsagel DE, McCulloch EA. Ascorbic acid: a culture requirement for colony formation by mouse plasmacytoma cells. Science. 1971; 174:720–722. PMID: 5123422.
Article6. Venezian R, Shenker BJ, Datar S, Leboy PS. Modulation of chondrocyte proliferation by ascorbic acid and BMP-2. J Cell Physiol. 1998; 174:331–341. PMID: 9462695.
Article7. Nowak G, Schnellmann RG. L-ascorbic acid regulates growth and metabolism of renal cells: improvements in cell culture. Am J Physiol. 1996; 271:C2072–C2080. PMID: 8997210.
Article8. Deutsch JC. Ascorbic acid oxidation by hydrogen peroxide. Anal Biochem. 1998; 255:1–7. PMID: 9448835.
Article9. Mendiratta S, Qu Z, May JM. Erythrocyte defenses against hydrogen peroxide: the role of ascorbic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998; 1380:389–395. PMID: 9555101.
Article10. Yoshimoto K, Nakamura T, Ichihara A. Reciprocal effects of epidermal growth factor on key lipogenic enzymes in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Induction of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and suppression of malic enzyme and lipogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1983; 258:12355–12360. PMID: 6355085.
Article11. Baba M, Yamamoto R, Iishi H, Tatsuta M, Wada A. Role of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase on enhanced proliferation of pre-neoplastic and neoplastic cells in rat liver induced by N-nitrosomorpholine. Int J Cancer. 1989; 43:892–895. PMID: 2565888.
Article12. Deshpande N, Mitchell I, Millis R. Enzyme studies in human breast tumours. Eur J Cancer. 1977; 13:1261–1267. PMID: 145367.
Article13. Heyden G. Histochemical investigation of malignant cells. Histochemistry. 1974; 39:327–334. PMID: 4859353.
Article14. Shepherd A, Cleary MP. Metabolic alterations after dehydroepiandrosterone treatment in Zucker rats. Am J Physiol. 1984; 246:E123–E128. PMID: 6230014.
Article15. Tian WN, Braunstein LD, Pang J, Stuhlmeier KM, Xi QC, Tian X, et al. Importance of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity for cell growth. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:10609–10617. PMID: 9553122.
Article16. Park CH, Bergsagel DE, McCulloch EA. Mouse myeloma tumor stem cells: a primary cell culture assay. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971; 46:411–422. PMID: 5115909.17. Kornberg A, Horecker BL. Colowick SP, Kaplan NO, editors. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Methods of enzymology. 1955. New York: Academic Press;p. 323.18. Dunnett CW. A multiple comparison procedure for comparing several treatments with a control. J Am Statist Assoc. 1955; 50:1096–1121.
Article19. Arakawa N, Nemoto S, Suzuki E, Otsuka M. Role of hydrogen peroxide in the inhibitory effect of ascorbate on cell growth. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 1994; 40:219–227. PMID: 7965211.
Article20. Miwa N, Yamazaki H, Nagaoka Y, Kageyama K, Onoyama Y, Matsui-Yuasa I, et al. Altered production of the active oxygen species is involved in enhanced cytotoxic action of acylated derivatives of ascorbate to tumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988; 972:144–151. PMID: 3191161.
Article21. May JM. Ascorbate function and metabolism in the human erythrocyte. Front Biosci. 1998; 3:d1–d10. PMID: 9405334.
Article22. Kuo SM, MacLean ME, McCormick K, Wilson JX. Gender and sodium-ascorbate transporter isoforms determine ascorbate concentrations in mice. J Nutr. 2004; 134:2216–2221. PMID: 15333707.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Jaundice and Hemolytic Anemia Appearing within the First 24 Hour of Life due to Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency
- The Effect of Ascorbic Acid and its Derivative on Cultured Rabbit Keratocytes
- A Case of Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase Riley Causing Hemolytic Anemia
- Ascorbic acid insufficiency induces the severe defect on bone formation via the down-regulation of osteocalcin production
- Effects of Topically Applied Na-Hyaluronan on Epithelial Healing and Aqueous Composition in Experimental Corneal Alkali Wounds