Anat Cell Biol.
2013 Dec;46(4):254-261. 10.5115/acb.2013.46.4.254.
Ascorbic acid insufficiency induces the severe defect on bone formation via the down-regulation of osteocalcin production
- Affiliations
-
- 1Labratory of Vitamin C and Immunology, Department of Anatomy, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kinglee@snu.ac.kr genius29@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Psychology, Boston College, Chestnut Hill, MA, USA.
- 4Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2046766
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2013.46.4.254
Abstract
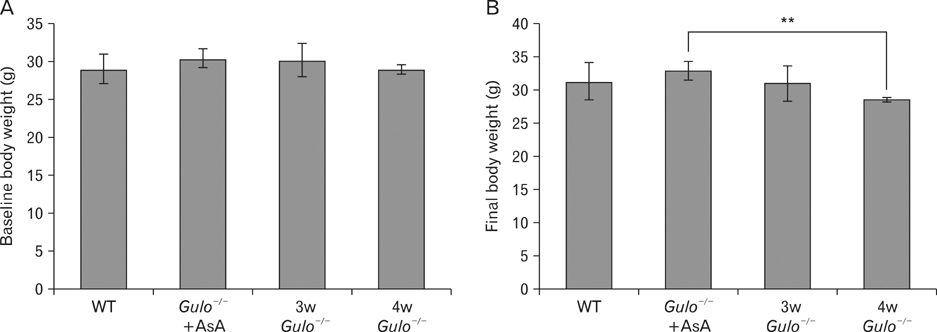
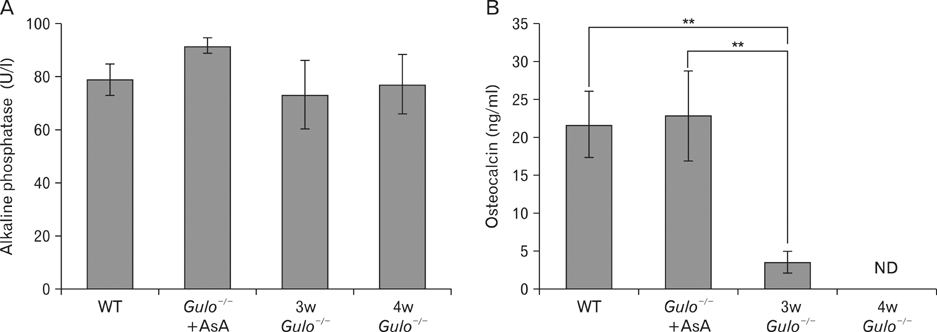
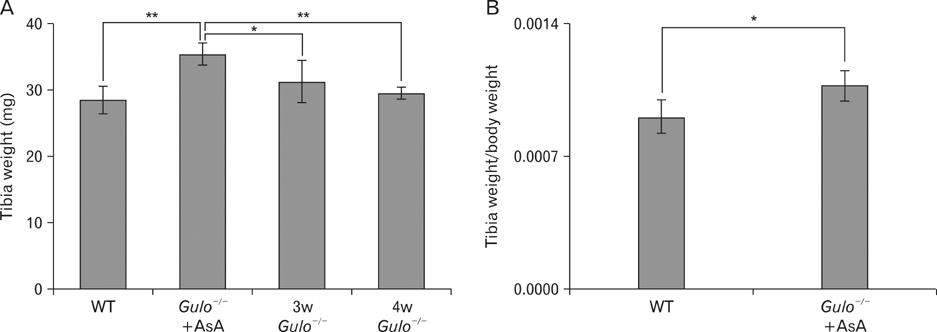
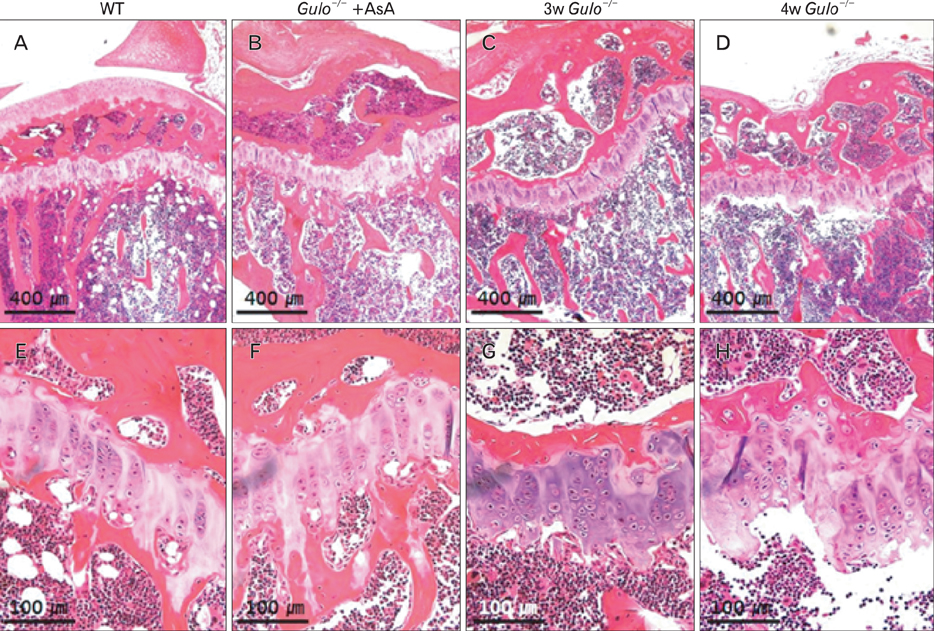
- The L-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase gene (Gulo) encodes an essential enzyme in the synthesis of ascorbic acid from glucose. On the basis of previous findings of bone abnormalities in Gulo-/- mice under conditions of ascorbic acid insufficiency, we investigated the effect of ascorbic acid insufficiency on factors related to bone metabolism in Gulo-/- mice. Four groups of mice were raised for 4 weeks under differing conditions of ascorbic acid insufficiency, namely, wild type; ascorbic acid-sufficient Gulo-/- mice, 3-week ascorbic acid-insufficient Gulo-/- mice, and 4-week ascorbic acid-insufficient Gulo-/- mice. Four weeks of ascorbic acid insufficiency resulted in significant weight loss in Gulo-/- mice. Interestingly, average plasma osteocalcin levels were significantly decreased in Gulo-/- mice after 3 weeks of ascorbic acid insufficiency. In addition, the tibia weight in ascorbic acid-sufficient Gulo-/- mice was significantly higher than that in the other three groups. Moreover, significant decreases in trabecular bone volume near to the growth plate, as well as in trabecular bone attachment to the growth plate, were evident in 3- or 4-week ascorbic acid-insufficient Gulo-/-. In summary, ascorbic acid insufficiency in Gulo-/- mice results in severe defects in normal bone formation, which are closely related to a decrease in plasma osteocalcin levels.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Nutrition and growth: assessing the impact of regional nutritional intake on childhood development and metacarpal parameters
Christian Moro, Jessica Covino
Anat Cell Biol. 2018;51(1):31-40. doi: 10.5115/acb.2018.51.1.31.
Reference
-
1. Peterkofsky B. Ascorbate requirement for hydroxylation and secretion of procollagen: relationship to inhibition of collagen synthesis in scurvy. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991; 54:6 Suppl. 1135S–1140S.2. Fain O. Musculoskeletal manifestations of scurvy. Joint Bone Spine. 2005; 72:124–128.3. Niyibizi C, Eyre DR. Structural characteristics of cross-linking sites in type V collagen of bone: chain specificities and heterotypic links to type I collagen. Eur J Biochem. 1994; 224:943–950.4. Cummine J, Armstrong L, Nade S. Osteogenesis after bone and bone marrow transplantation: studies of cellular behaviour using combined myelo-osseous grafts in the subscorbutic guinea pig. Acta Orthop Scand. 1983; 54:235–241.5. Bourne G. The effect of graded doses of vitamin C upon the regeneration of bone in guinea-pigs on a scorbutic diet. J Physiol. 1942; 101:327–336.6. Léone J, Delhinger V, Maes D, Scheer C, Pennaforte JL, Eschard JP, Etienne JC. Rheumatic manifestations of scurvy: a report of two cases. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1997; 64:428–431.7. Shetty AK, Buckingham RB, Killian PJ, Girdany D, Meyerowitz R. Hemarthrosis and femoral head destruction in an adult diet faddist with scurvy. J Rheumatol. 1988; 15:1878–1880.8. Wapnick AA, Lynch SR, Seftel HC, Charlton RW, Bothwell TH, Jowsey J. The effect of siderosis and ascorbic acid depletion on bone metabolism, with special reference to osteoporosis in the Bantu. Br J Nutr. 1971; 25:367–376.9. Hall SL, Greendale GA. The relation of dietary vitamin C intake to bone mineral density: results from the PEPI study. Calcif Tissue Int. 1998; 63:183–189.10. Sahni S, Hannan MT, Gagnon D, Blumberg J, Cupples LA, Kiel DP, Tucker KL. High vitamin C intake is associated with lower 4-year bone loss in elderly men. J Nutr. 2008; 138:1931–1938.11. Ohta Y, Nishikimi M. Random nucleotide substitutions in primate nonfunctional gene for L-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase, the missing enzyme in L-ascorbic acid biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999; 1472:408–411.12. Nishikimi M, Fukuyama R, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Yagi K. Cloning and chromosomal mapping of the human nonfunctional gene for L-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase, the enzyme for L-ascorbic acid biosynthesis missing in man. J Biol Chem. 1994; 269:13685–13688.13. Nishikimi M, Kawai T, Yagi K. Guinea pigs possess a highly mutated gene for L-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase, the key enzyme for L-ascorbic acid biosynthesis missing in this species. J Biol Chem. 1992; 267:21967–21972.14. Maeda N, Hagihara H, Nakata Y, Hiller S, Wilder J, Reddick R. Aortic wall damage in mice unable to synthesize ascorbic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000; 97:841–846.15. Bae S, Cho CH, Kim H, Kim Y, Kim HR, Hwang YI, Yoon JH, Kang JS, Lee WJ. In vivo consequence of vitamin C insufficiency in liver injury: vitamin C ameliorates T-cell-mediated acute liver injury in Gulo(-/-) mice. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013; 19:2040–2053.16. Kim H, Bae S, Yu Y, Kim Y, Kim HR, Hwang YI, Kang JS, Lee WJ. The analysis of vitamin C concentration in organs of gulo(-/-) mice upon vitamin C withdrawal. Immune Netw. 2012; 12:18–26.17. Alers JC, Krijtenburg PJ, Vissers KJ, van Dekken H. Effect of bone decalcification procedures on DNA in situ hybridization and comparative genomic hybridization: EDTA is highly preferable to a routinely used acid decalcifier. J Histochem Cytochem. 1999; 47:703–710.18. Sakamoto Y, Takano Y. Morphological influence of ascorbic acid deficiency on endochondral ossification in osteogenic disorder Shionogi rat. Anat Rec. 2002; 268:93–104.19. Hasegawa T, Li M, Hara K, Sasaki M, Tabata C, de Freitas PH, Hongo H, Suzuki R, Kobayashi M, Inoue K, Yamamoto T, Oohata N, Oda K, Akiyama Y, Amizuka N. Morphological assessment of bone mineralization in tibial metaphyses of ascorbic acid-deficient ODS rats. Biomed Res. 2011; 32:259–269.20. Tsuchiya H, Bates CJ. Ascorbic acid deficiency in guinea pigs: contrasting effects of tissue ascorbic acid depletion and of associated inanition on status indices related to collagen and vitamin D. Br J Nutr. 1994; 72:745–752.21. Mahmoodian F, Gosiewska A, Peterkofsky B. Regulation and properties of bone alkaline phosphatase during vitamin C deficiency in guinea pigs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1996; 336:86–96.22. Mohan S, Kapoor A, Singgih A, Zhang Z, Taylor T, Yu H, Chadwick RB, Chung YS, Donahue LR, Rosen C, Crawford GC, Wergedal J, Baylink DJ. Spontaneous fractures in the mouse mutant sfx are caused by deletion of the gulonolactone oxidase gene, causing vitamin C deficiency. J Bone Miner Res. 2005; 20:1597–1610.23. Kipp DE, McElvain M, Kimmel DB, Akhter MP, Robinson RG, Lukert BP. Scurvy results in decreased collagen synthesis and bone density in the guinea pig animal model. Bone. 1996; 18:281–288.24. Civitelli R, Armamento-Villareal R, Napoli N. Bone turnover markers: understanding their value in clinical trials and clinical practice. Osteoporos Int. 2009; 20:843–851.25. Kim DY. Biochemical markers of bone turnover. Korean J Nucl Med. 1999; 33:341–351.26. Green S, Anstiss CL, Fishman WH. Automated differential isoenzyme analysis. II. The fractionation of serum alkaline phosphatases into "liver", "intestinal" and "other" components. Enzymologia. 1971; 41:9–26.27. Wolf RL, Cauley JA, Pettinger M, Jackson R, Lacroix A, Leboff MS, Lewis CE, Nevitt MC, Simon JA, Stone KL, Wactawski-Wende J. Lack of a relation between vitamin and mineral antioxidants and bone mineral density: results from the Women's Health Initiative. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005; 82:581–588.28. Leveille SG, LaCroix AZ, Koepsell TD, Beresford SA, Van Belle G, Buchner DM. Dietary vitamin C and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women in Washington State, USA. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1997; 51:479–485.29. Tsunenari T, Fukase M, Fujita T. Bone histomorphometric analysis for the cause of osteopenia in vitamin C-deficient rat (ODS rat). Calcif Tissue Int. 1991; 48:18–27.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Ascorbic Acid on Keratinocyte and Epidermalization of Skin
- An Implant for Bone Formation using Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- The effect of preosteoblast graft on osseous regeneration of the cranial bone defect in mouse
- The Effect of Ascorbic acid on Endotoxin-induced Fibrosis
- An overview of the endocrine functions of osteocalcin