J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Jul;27(7):803-810. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.7.803.
Impact of Lysophosphatidylcholine on the Plasminogen Activator System in Cultured Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bkyoon@skku.edu
- 2Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Sejong University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Functional Food Technology Research Group, Korea Food Research Institute, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2157928
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.7.803
Abstract
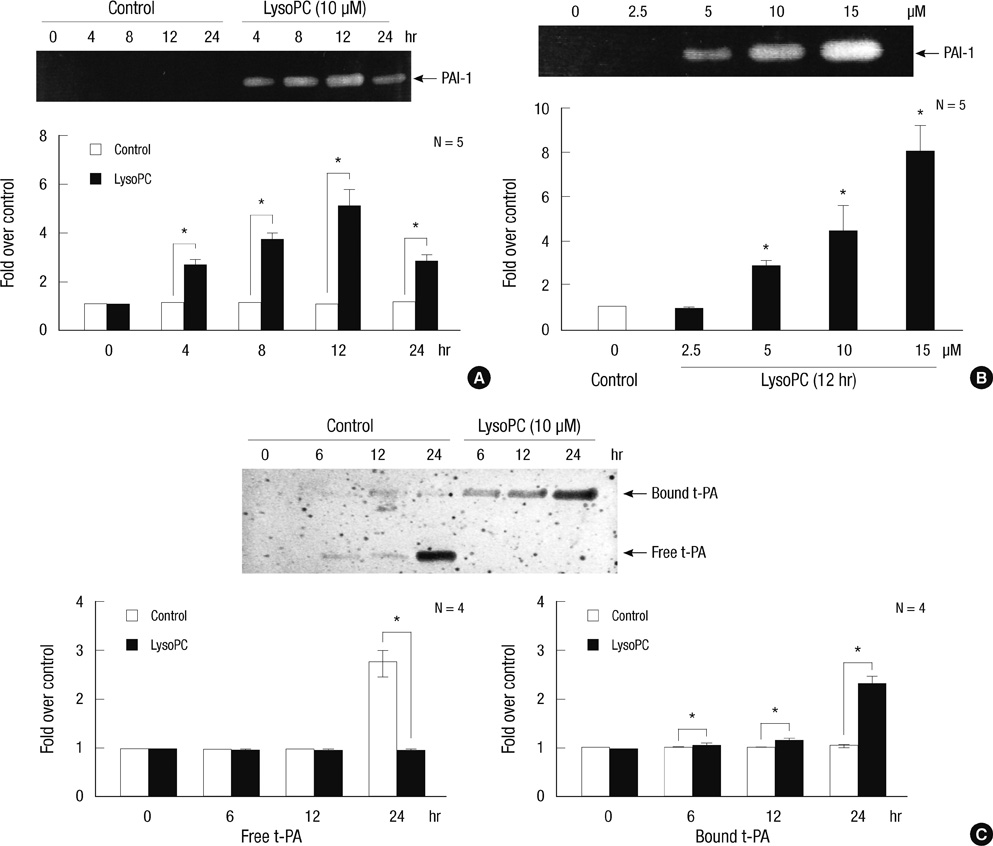
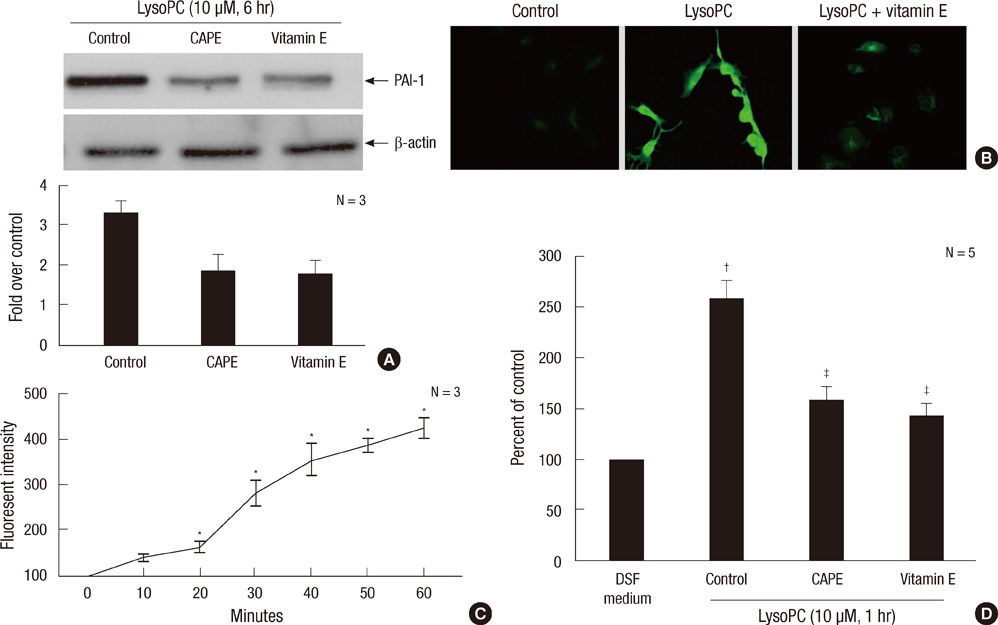
- The balance between tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) regulates fibrinolysis. PAI-1 expression increases in atherosclerotic arteries and vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) are one of major constituents of atheroma. We investigated the impact of lysophosphatidylcholine (lysoPC), an active component of oxidized low-density lipoprotein, on the plasminogen activator system of the rat VSMCs. The lysoPC stimulated the protein and gene expressions of PAI-1 but did not affect the protein expression of t-PA. Fibrin overlay zymography revealed that lysoPC increased the activity of PAI-1 in the conditioned media, while concurrently decreasing that of free t-PA. Vitamin E inhibited the lysoPC-induced PAI-1 expression. Further, lysoPC increased the intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester, an inhibitor of NF-kappaB, blocked this lysoPC effect. Indeed, lysoPC induced the NF-kappaB-mediated transcriptional activity as measured by luciferase reporter assay. In addition, genistein, an inhibitor of protein-tyrosine kinase (PTK), diminished the lysoPC effect, while 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene, a stimulator of PTK, stimulated PAI-1 production. In conclusion, lysoPC does not affect t-PA expression but induces PAI-1 expression in the VSMC by mediating NF-kappaB and the genistein-sensitive PTK signaling pathways via oxidative stress. Importantly, lysoPC stimulates the enzyme activity of PAI-1 and suppresses that of t-PA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Benz(a)Anthracenes/pharmacology
Caffeic Acids/pharmacology
Cells, Cultured
Genistein/pharmacology
Lipoproteins, LDL/metabolism
Lysophosphatidylcholines/*pharmacology
Muscle, Smooth, Vascular/cytology/*drug effects/metabolism
NF-kappa B/antagonists & inhibitors/metabolism
Oxidative Stress/drug effects
Phenylethyl Alcohol/analogs & derivatives/pharmacology
Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1/agonists/genetics/*metabolism
Protein Kinase Inhibitors/pharmacology
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases/antagonists & inhibitors/metabolism
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Reactive Oxygen Species/metabolism
Signal Transduction/drug effects
Tissue Plasminogen Activator/*metabolism
Transcription, Genetic/drug effects
Up-Regulation/drug effects
Vitamin E/pharmacology
Benz(a)Anthracenes
Caffeic Acids
Lipoproteins, LDL
Lysophosphatidylcholines
NF-kappa B
Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1
Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Reactive Oxygen Species
Vitamin E
Genistein
Phenylethyl Alcohol
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Tissue Plasminogen Activator
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ilić M, Majkić-Singh N, Lalić K. Plasminogen activator inhibitor in patients with acute myocardial infarction and re-infarction in syndrome X. Clin Lab. 2002. 48:125–128.2. Schneiderman J, Sawdey MS, Keeton MR, Bordin GM, Bernstein EF, Dilley RB, Loskutoff DJ. Increased type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in atherosclerotic human arteries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992. 89:6998–7002.3. Schäfer K, Muller K, Hecke A, Mounier E, Goebel J, Loskutoff DJ, Konstantinides S. Enhanced thrombosis in atherosclerosis-prone mice is associated with increased arterial expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003. 23:2097–2103.4. Cherubini A, Vigna GB, Zuliani G, Ruggiero C, Senin U, Fellin R. Role of antioxidants in atherosclerosis: epidemiological and clinical update. Curr Pharm Des. 2005. 11:2017–2032.5. Rong JX, Berman JW, Taubman MB, Fisher EA. Lysophosphatidylcholine stimulates monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene expression in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002. 22:1617–1623.6. Sakai M, Miyazaki A, Hakamata H, Sasaki T, Yui S, Yamazaki M, Shichiri M, Horiuchi S. Lysophosphatidylcholine plays an essential role in the mitogenic effect of oxidized low density lipoprotein on murine macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1994. 269:31430–31435.7. Zou Y, Kim CH, Chung JH, Kim JY, Chung SW, Kim MK, Im DS, Lee J, Yu BP, Chung HY. Upregulation of endothelial adhesion molecules by lysophosphatidylcholine. Involvement of G protein-coupled receptor GPR4. FEBS J. 2007. 274:2573–2584.8. Kugiyama K, Sakamoto T, Misumi I, Sugiyama S, Ohgushi M, Ogawa H, Horiguchi M, Yasue H. Transferable lipids in oxidized low-density lipoprotein stimulate plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and inhibit tissue-type plasminogen activator release from endothelial cells. Circ Res. 1993. 73:335–343.9. Chai YC, Binion DG, Macklis R, Chisolm GM 3rd. Smooth muscle cell proliferation induced by oxidized LDL-borne lysophosphatidylcholine. Evidence for FGF-2 release from cells not extracellular matrix. Vascul Pharmacol. 2002. 38:229–237.10. Kim SH, Kim IW, Lee HY, Chae IH, Kim MA, Kim HS, Kim CH, Sohn DW, Oh BH, Lee MM, et al. The effect of naringin on the lysophosphatidylcholine-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Korean Circ J. 2002. 32:61–70.11. Lupu F, Bergonzelli GE, Heim DA, Cousin E, Genton CY, Bachmann F, Kruithof EK. Localization and production of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in human healthy and atherosclerotic arteries. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993. 13:1090–1100.12. Owens GK, Loeb A, Gordon D, Thompsin MM. Expression of smooth muscle-specific alpha-isoactin in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1986. 102:343–352.13. Yoon BK, Oh WJ, Kessel B, Roh CR, Choi DS, Lee JH, Kim DK. 17β-estradiol inhibits proliferation of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells induced by lysophosphatidylcholine via a nongenomic antioxidant mechanism. Menopause. 2001. 8:58–64.14. Schmidt C, Peng B, Li Z, Sclabas GM, Fujioka S, Niu J, Schmidt-Supprian M, Evans DB, Abbruzzese JL, Chiao PJ. Mechanisms of proinflammatory cytokine-induced biphasic NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell. 2003. 12:1287–1300.15. Grilli M, Chiu JJ, Lenardo MJ. NF-kB and Rel: Participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993. 143:1–62.16. Collen D, Juhan-Vague I. Fibrinolysis and atherosclerosis. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1988. 14:180–183.17. Nassar T, Akkawi S, Shina A, Haj-Yehia A, Bdeir K, Tarshis M, Heyman SN, Higazi AA. In vitro and in vivo effects of tPA and PAI-1 on blood vessel tone. Blood. 2004. 103:897–902.18. Kruithof EK, Tran-Thang C, Bachmann F. The fast-acting inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator in plasma is also the primary plasma inhibitor of urokinase. Thromb Haemost. 1986. 55:65–69.19. Dichtl W, Stiko A, Eriksson P, Goncalves I, Calara F, Banfi C, Ares MP, Hamsten A, Nilsson J. Oxidized LDL and lysophosphatidylcholine stimulate plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1999. 19:3025–3032.20. Cockell KA, Ren S, Sun J, Angel A, Shen GX. Effect of thrombin on release of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 from cultured primate arterial smooth muscle cells. Thromb Res. 1995. 77:119–131.21. Wojta J, Gallicchio M, Zoellner H, Hufnagl P, Last K, Filonzi EL, Binder BR, Hamilton JA, McGrath K. Thrombin stimulates expression of tissue-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in cultured human vascular smooth muscle cells. Thromb Haemost. 1993. 70:469–474.22. van Leeuwen RT, Kol A, Andreotti F, Kluft C, Maseri A, Sperti G. Angiotensin II increases plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 and tissue-type plasminogen activator messenger RNA in cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Circulation. 1994. 90:362–368.23. Madamanchi NR, Vendrov A, Runge MS. Oxidative stress and vascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005. 25:29–38.24. Griendling KK, FitzGerald GA. Oxidative stress and cardiovascular injury: Part I: basic mechanisms and in vivo monitoring of ROS. Circulation. 2003. 108:1912–1916.25. Kondo T, Hirose M, Kageyama K. Roles of oxidative stress and redox regulation in atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2009. 16:532–538.26. Kabe Y, Ando K, Hirao S, Yoshida M, Handa H. Redox regulation of NF-kappaB activation: distinct redox regulation between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005. 7:395–403.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of immune-mediated vascular injury on the coagulation- regulatory mechanism of the human endothelial cells; changes of tissue-type plasminogen activator, plasminogen activator inhibitor- 1 and von Willebrand factor
- Effects of 17β-Estradiol on the Plasminogen Activator System in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Treated with Lysophophatidylcholine
- The Effects of Glucose , Insulin and Angiotensin II on Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Expression and Growth of Aortic Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell in Rats
- Lysophosphatidylcholine Increases Ca2+ Current via Activation of Protein Kinase C in Rabbit Portal Vein Smooth Muscle Cells
- Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor in IgA nephropathy