J Korean Med Sci.
2015 Jan;30(1):54-59. 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.1.54.
Three-month Treatment Response and Exacerbation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, and Clinical Research Center for Chronic Obstructive Airway Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ymoh55@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 6Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea.
- 7Department of Internal Medicine and Environmental Health Center, Kangwon National University Hospital, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2155447
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.1.54
Abstract
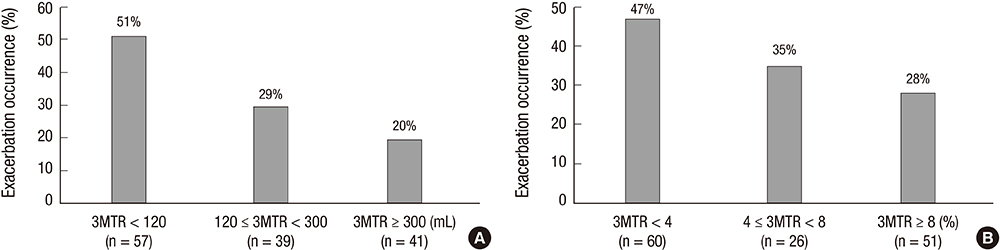
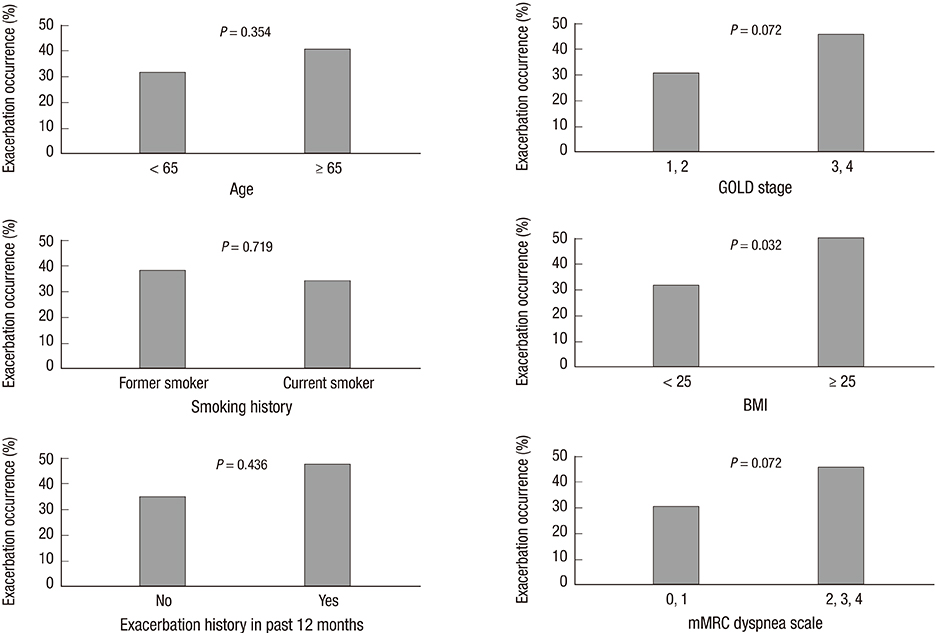
- The aim of this study was to investigate relationships between acute exacerbation and Forced Expiratory Volume 1 second (FEV1) improvement after treatment with combined long-acting beta-agonist (LABA) and inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). A total of 137 COPD patients were classified as responders or nonresponders according to FEV1 improvement after 3 months of LABA/ICS treatment in fourteen referral hospitals in Korea. Exacerbation occurrence in these two subgroups was compared over a period of 1 yr. Eighty of the 137 COPD patients (58.4%) were classified as responders and 57 (41.6%) as nonresponders. Acute exacerbations occurred in 25 patients (31.3%) in the responder group and in 26 patients (45.6%) in the nonresponder group (P=0.086). FEV1 improvement after LABA/ICS treatment was a significant prognostic factor for fewer acute exacerbations in a multivariate Cox proportional hazard model adjusted for age, sex, FEV1, smoking history, 6 min walk distance, body mass index, exacerbation history in the previous year, and dyspnea scale.Three-month treatment response to LABA/ICS might be a prognostic factor for the occurrence of acute exacerbation in COPD patients.
MeSH Terms
-
Adrenal Cortex Hormones/*therapeutic use
Adrenergic beta-2 Receptor Agonists/*therapeutic use
Bronchodilator Agents/*therapeutic use
Budesonide/therapeutic use
Drug Therapy, Combination
Female
Fluticasone/therapeutic use
Forced Expiratory Volume/drug effects/*physiology
Formoterol Fumarate/therapeutic use
Humans
Male
Pulmonary Disease, Chronic Obstructive/*drug therapy/physiopathology
Recurrence
Republic of Korea
Salmeterol Xinafoate/therapeutic use
Smoking
Spirometry
Treatment Outcome
Adrenal Cortex Hormones
Adrenergic beta-2 Receptor Agonists
Bronchodilator Agents
Budesonide
Fluticasone
Formoterol Fumarate
Salmeterol Xinafoate
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee JH, Lee YK, Kim EK, Kim TH, Huh JW, Kim WJ, Lee JH, Lee SM, Lee S, Lim SY, et al. Responses to inhaled long-acting beta-agonist and corticosteroid according to COPD subtype. Respir Med. 2010; 104:542–549.2. Donohue JF, Jones PW. Changing patterns in long-acting bronchodilator trials in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2011; 6:35–45.3. Miles MC, Donohue JF, Ohar JA. Optimum bronchodilator combinations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: what is the current evidence? Drugs. 2012; 72:301–308.4. Lee JS, Huh JW, Chae EJ, Seo JB, Ra SW, Lee JH, Kim EK, Lee YK, Kim TH, Kim WJ, et al. Different therapeutic responses in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease subgroups. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2011; 15:1104–1110.5. Alvarez-Gutiérrez FJ, Miravitlles M, Calle M, Gobartt E, López F, Martin A. Grupo de Estudio EIME. Impact of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease on activities of daily living: results of the EIME multicenter study. Arch Bronconeumol. 2007; 43:64–72.6. Mannino DM, Davis KJ. Lung function decline and outcomes in an elderly population. Thorax. 2006; 61:472–477.7. Niewoehner DE, Lokhnygina Y, Rice K, Kuschner WG, Sharafkhaneh A, Sarosi GA, Krumpe P, Pieper K, Kesten S. Risk indexes for exacerbations and hospitalizations due to COPD. Chest. 2007; 131:20–28.8. Niewoehner DE, Collins D, Erbland ML. Relation of FEV(1) to clinical outcomes during exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 161:1201–1205.9. Donaldson GC, Seemungal TA, Bhowmik A, Wedzicha JA. Relationship between exacerbation frequency and lung function decline in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 2002; 57:847–852.10. Jones PW, Donohue JF, Nedelman J, Pascoe S, Pinault G, Lassen C. Correlating changes in lung function with patient outcomes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a pooled analysis. Respir Res. 2011; 12:161.11. Westwood M, Bourbeau J, Jones PW, Cerulli A, Capkun-Niggli G, Worthy G. Relationship between FEV1 change and patient-reported outcomes in randomised trials of inhaled bronchodilators for stable COPD: a systematic review. Respir Res. 2011; 12:40.12. Albert P, Agusti A, Edwards L, Tal-Singer R, Yates J, Bakke P, Celli BR, Coxson HO, Crim C, Lomas DA, et al. Bronchodilator responsiveness as a phenotypic characteristic of established chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 2012; 67:701–708.13. Hanania NA, Celli BR, Donohue JF, Martin UJ. Bronchodilator reversibility in COPD. Chest. 2011; 140:1055–1063.14. Kim WJ, Oh YM, Sung J, Kim TH, Huh JW, Jung H, Lee JH, Kim EK, Lee JH, Lee SM, et al. Lung function response to 12-week treatment with combined inhalation of long-acting beta2 agonist and glucocorticoid according to ADRB2 polymorphism in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lung. 2008; 186:381–386.15. Lee YK, Oh YM, Lee JH, Kim EK, Lee JH, Kim N, Seo JB, Lee SD. KOLD Study Group. Quantitative assessment of emphysema, air trapping, and airway thickening on computed tomography. Lung. 2008; 186:157–165.16. Choi JK, Paek D, Lee JO. Normal predictive values of spirometry in Korean population. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2005; 58:230–242.17. Cazzola M, MacNee W, Martinez FJ, Rabe KF, Franciosi LG, Barnes PJ, Brusasco V, Burge PS, Calverley PM, Celli BR, et al. American Thoracic Society. European Respiratory Society Task Force on outcomes of COPD. Outcomes for COPD pharmacological trials: from lung function to biomarkers. Eur Respir J. 2008; 31:416–469.18. Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, Crapo R, Enright P, van der Grinten CP, Gustafsson P, et al. ATS/ERS Task Force. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J. 2005; 26:319–338.19. Park J, Choi I, Park K. Normal predicted standards of single breath carbon monoxide diffusing capacity of lung in healthy nonsmoking adults. Korean J Intern Med. 1985; 28:176–183.20. Vestbo J, Hurd SS, Agusti AG, Jones PW, Vogelmeier C, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ, Nishimura M, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013; 187:347–365.21. Wedzicha JA, Donaldson GC. Exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Care. 2003; 48:1204–1213. discussion 13-5.22. Kitaguchi Y, Fujimoto K, Kubo K, Honda T. Characteristics of COPD phenotypes classified according to the findings of HRCT. Respir Med. 2006; 100:1742–1752.23. Celli BR, Cote CG, Marin JM, Casanova C, Montes de Oca M, Mendez RA, Pinto Plata V, Cabral HJ. The body-mass index, airflow obstruction, dyspnea, and exercise capacity index in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:1005–1012.24. Kessler R, Faller M, Fourgaut G, Mennecier B, Weitzenblum E. Predictive factors of hospitalization for acute exacerbation in a series of 64 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999; 159:158–164.25. Hurst JR, Vestbo J, Anzueto A, Locantore N, Mullerova H, Tal-Singer R, Miller B, Lomas DA, Agusti A, Macnee W, et al. Evaluation of COPD Longitudinally to Identify Predictive Surrogate Endpoints (ECLIPSE) Investigators. Susceptibility to exacerbation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:1128–1138.26. Soler-Cataluña JJ, Cosío B, Izquierdo JL, López-Campos JL, Marín JM, Agüero R, Baloira A, Carrizo S, Esteban C, Galdiz JB, et al. Consensus document on the overlap phenotype COPD-asthma in COPD. Arch Bronconeumol. 2012; 48:331–337.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Study of Clarithromycin for the Treatment of Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- The Relationship between Airway Inflammation and Exacerbation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Respiratory Review of 2014
- Pulmonary Strongyloidiasis Masquerading as Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Bacterial etiology of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in hospitalized patients