Tuberc Respir Dis.
2016 Oct;79(4):307-311. 10.4046/trd.2016.79.4.307.
Pulmonary Strongyloidiasis Masquerading as Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pulmonary Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bhubaneswar, India. panigrahimanoj75@gmail.com
- 2Department of Microbiology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bhubaneswar, India.
- KMID: 2365324
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2016.79.4.307
Abstract
- Pulmonary strongyloidiasis is an uncommon presentation of Strongyloides infection, usually seen in immunocompromised hosts. The manifestations are similar to that of acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Therefore, the diagnosis of pulmonary strongyloidiasis could be challenging in a COPD patient, unless a high index of suspicion is maintained. Here, we present a case of Strongyloides hyperinfection in a COPD patient mimicking acute exacerbation, who was on chronic steroid therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
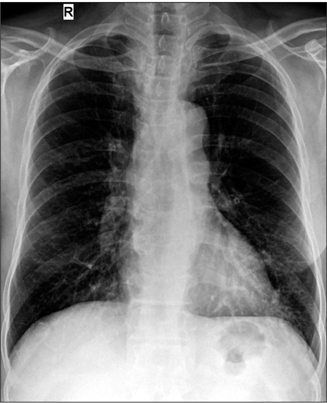
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Chronic Strongyloidiasis with Recurrent Hyperinfection
Kuenyoul Park, Min-Sun Kim, Jeonghyun Chang, Eo Jin Kim, Changhoon Yoo, Min Jae Kim, Heungsup Sung, Mi-Na Kim
Lab Med Online. 2019;9(3):171-176. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2019.9.3.171.
Reference
-
1. Sethi S, Murphy TF. Infection in the pathogenesis and course of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:2355–2365.2. Aaron SD. Management and prevention of exacerbations of COPD. BMJ. 2014; 349:g5237.3. Kassalik M, Monkemuller K. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome and disseminated disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2011; 7:766–768.4. Mejia R, Nutman TB. Screening, prevention, and treatment for hyperinfection syndrome and disseminated infections caused by Strongyloides stercoralis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2012; 25:458–463.5. Buonfrate D, Requena-Mendez A, Angheben A, Munoz J, Gobbi F, Van Den Ende J, et al. Severe strongyloidiasis: a systematic review of case reports. BMC Infect Dis. 2013; 13:78.6. Ghoshal U, Khanduja S, Chaudhury N, Gangwar D, Ghoshal UC. A series on intestinal strongyloidiasis in immunocompetent and immunocompromised hosts. Trop Gastroenterol. 2012; 33:135–139.7. Ortiz Romero Mdel M, Leon Martinez MD, Munoz Perez MAz, Altuna Cuesta A, Cano Sanchez A, Hernandez Martinez J. Strongyloides stercoralys as an unusual cause of COPD exacerbation. Arch Bronconeumol. 2008; 44:451–453.8. Liu HC, Hsu JY, Chang KM. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection presenting with symptoms mimicking acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Chin Med Assoc. 2009; 72:442–445.9. Vigg A, Mantri S, Reddy VA, Biyani V. Acute respiratory distress syndrome due to Strongyloides stercoralis in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2006; 48:67–69.10. Feely NM, Waghorn DJ, Dexter T, Gallen I, Chiodini P. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection: difficulties in diagnosis and treatment. Anaesthesia. 2010; 65:298–301.11. Woodring JH, Halfhill H 2nd, Berger R, Reed JC, Moser N. Clinical and imaging features of pulmonary strongyloidiasis. South Med J. 1996; 89:10–19.12. Choi KS, Whang YN, Kim YJ, Yang YM, Yoon K, Kim JK, et al. A case of hyperinfection syndrome with Strongyloides stercoralis. Korean J Parasitol. 1985; 23:236–240.13. Lee SK, Shin BM, Khang SK, Chai JY, Kook J, Hong ST, et al. Nine cases of strongyloidiasis in Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 1994; 32:49–52.14. Hong SJ, Han JH. A case of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Korean J Parasitol. 1999; 37:117–120.15. Kim YK, Kim H, Park YC, Lee MH, Chung ES, Lee SJ, et al. A case of hyperinfection with Strongyloides stercoralis in an immunosuppressed patient. Korean J Intern Med. 1989; 4:165–170.16. Kim J, Joo HS, Ko HM, Na MS, Hwang SH, Im JC. A case of fatal hyperinfective strongyloidiasis with discovery of autoinfective filariform larvae in sputum. Korean J Parasitol. 2005; 43:51–55.17. Kim YJ, Ahn MJ, Park KC, Lee HY, Kim KH, Byeon KM, et al. Pulmonary strongyloidiasis with alveolar hemorrhage in a patient receiving chemotherapy. Korean J Med. 2009; 76:502–505.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Study of Clarithromycin for the Treatment of Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Respiratory Review of 2014
- Treatment of Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- The Relationship between Airway Inflammation and Exacerbation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Desaturaton due to Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in the Patient Who Underwent the Cephalic Vein Bypass Surgery under Epidural Anesthesia