Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2015 Sep;7(5):497-506. 10.4168/aair.2015.7.5.497.
Enhanced Allergic Inflammation of Der p 2 Affected by Polymorphisms of MD-2 Promoter
- Affiliations
-
- 1Center for Translational Medicine, Department of Medical Research, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
- 2Department of BioIndustry Technology, Da Yeh University, Changhua, Taiwan.
- 3Department of Medical Technology, Jen Ten College of Medicine, Nursing and Management, Miaoli, Taiwan.
- 4Division of Allergy, Immunology & Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan. jawji@vghtc.gov.tw
- 5College of Life Sciences, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan.
- 6Institute of Clinical Medicine, National Yang Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan.
- KMID: 2147959
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.5.497
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Myeloid differentiation-2 (MD-2) has been associated with endotoxin and inflammatory disorders because it can recognize lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding and attenuate Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated signaling. However, its role in allergic inflammation has yet to be clarified. We examined whether single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in MD-2 promoter can affect MD-2 expression and aimed to clarify the relationship between Der p 2 allergy and SNPs of MD-2 promoter.
METHODS
The function of SNPs of MD-2 promoter and the effects of cytokines and immunoglobulin on the secretion and mRNA expression were investigated in 73 allergic subjects with different MD-2 gene promoter variants. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were cultured with or without LPS in the presence of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus group 2 allergen (Der p 2), followed by mRNA extraction and cytokine expression analysis. The culture supernatants were collected for cytokine measurement.
RESULTS
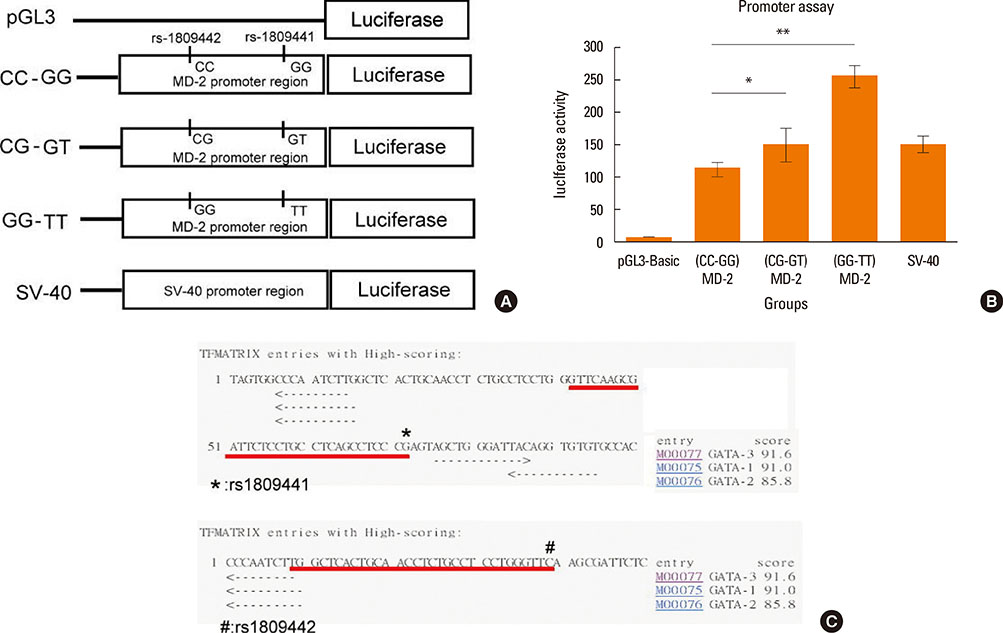
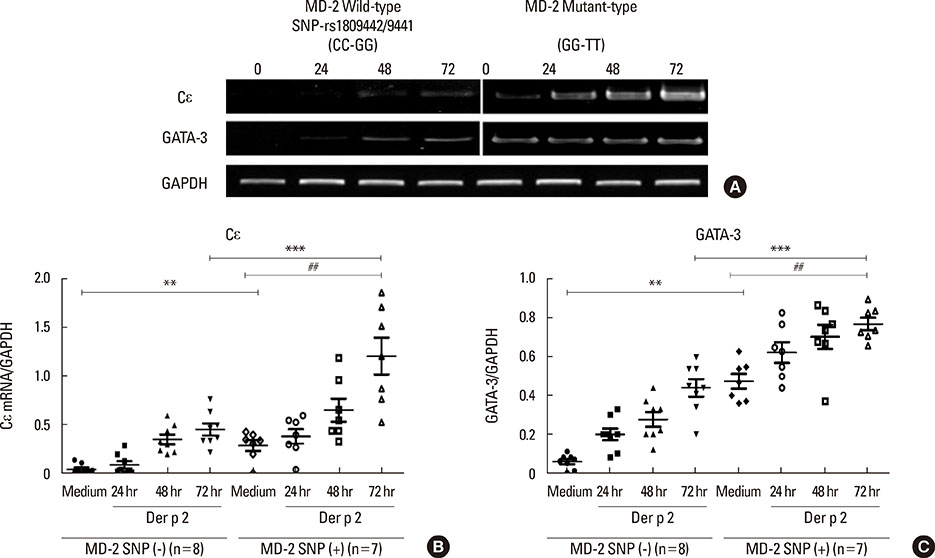
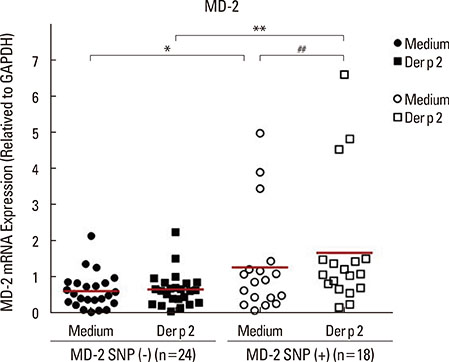
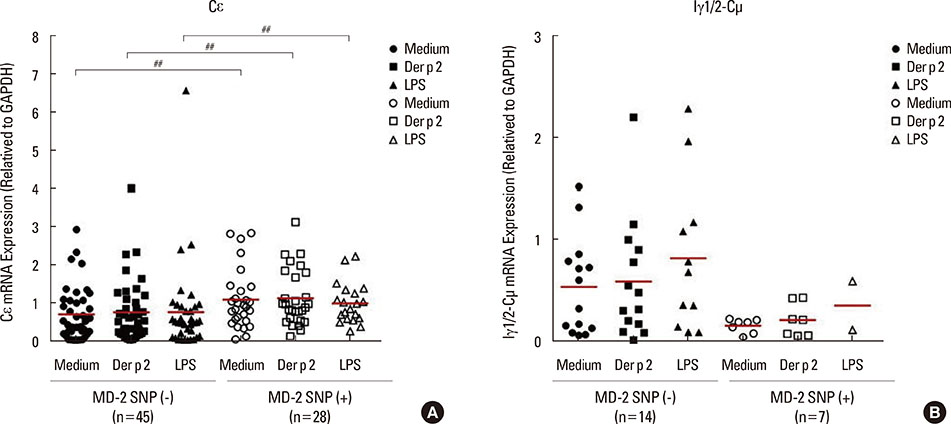
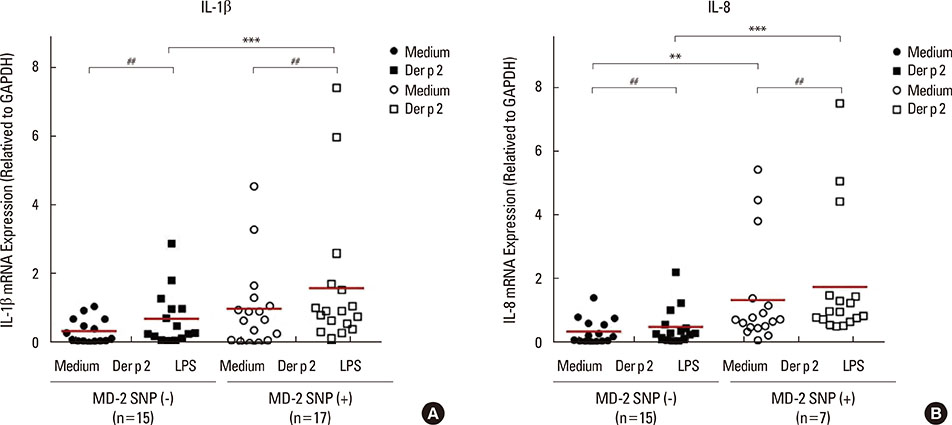
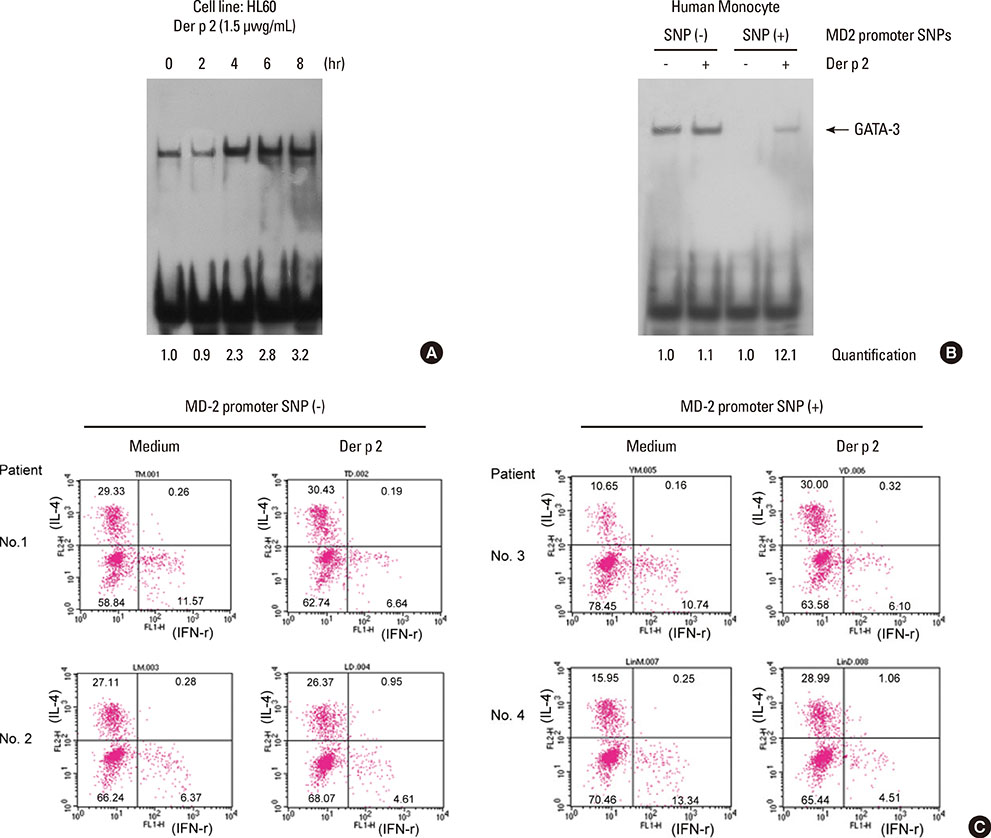
Patients with the MD-2 promoter SNPs (rs1809441/rs1809442) had increased mRNA expressions of MD-2, epsilon heavy chain of IgE (Cepsilon), and interleukin (IL)-8; however, only MD-2 and IL-8 were further up-regulated after Der p 2 stimulation. Patients with SNPs of MD-2 promoter tended to have high levels of IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha after Der p 2 and LPS stimulation. Increased secretions of IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 were found to be up-regulated by Der p 2 stimulation, and an increased secretion of IFN-gamma and decreased secretion of IL-4 were noted after LPS stimulation.
CONCLUSIONS
The high levels of proinflammatory cytokines secreted by Der p 2 were predetermined by MD-2 promoter SNPs (rs1809441/rs1809442). Through cytokine secretion by Der p 2 and LPS, these SNPs may serve as an indicator of the pathological phenotype of Der p 2-induced allergic inflammation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Cytokines
Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus
Humans
Hypersensitivity
Immunoglobulin E
Immunoglobulins
Inflammation*
Interleukin-10
Interleukin-4
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Interleukins
Phenotype
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide
RNA, Messenger
Toll-Like Receptor 4
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Cytokines
Immunoglobulin E
Immunoglobulins
Interleukin-10
Interleukin-4
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Interleukins
RNA, Messenger
Toll-Like Receptor 4
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tovey ER, Chapman MD, Platts-Mills TA. Mite faeces are a major source of house dust allergens. Nature. 1981; 289:592–593.2. Boulet LP, Turcotte H, Laprise C, Lavertu C, Bédard PM, Lavoie A, et al. Comparative degree and type of sensitization to common indoor and outdoor allergens in subjects with allergic rhinitis and/or asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 1997; 27:52–59.3. Thomas WR, Smith WA, Hales BJ, Mills KL, O'Brien RM. Characterization and immunobiology of house dust mite allergens. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002; 129:1–18.4. Tsai JJ, Shen HD, Chua KY. Purification of group 2 Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus allergen and prevalence of its specific IgE in asthmatics. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2000; 121:205–210.5. Shin JW, Sue JH, Song TW, Kim KW, Kim ES, Sohn MH, et al. Atopy and house dust mite sensitization as risk factors for asthma in children. Yonsei Med J. 2005; 46:629–634.6. Park SH, Kim ND, Jung JK, Lee CK, Han SB, Kim Y. Myeloid differentiation 2 as a therapeutic target of inflammatory disorders. Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 133:291–298.7. Ohto U, Fukase K, Miyake K, Satow Y. Crystal structures of human MD-2 and its complex with antiendotoxic lipid IVa. Science. 2007; 316:1632–1634.8. Trompette A, Divanovic S, Visintin A, Blanchard C, Hegde RS, Madan R, et al. Allergenicity resulting from functional mimicry of a Toll-like receptor complex protein. Nature. 2009; 457:585–588.9. Vasl J, Prohinar P, Gioannini TL, Weiss JP, Jerala R. Functional activity of MD-2 polymorphic variant is significantly different in soluble and TLR4-bound forms: decreased endotoxin binding by G56R MD-2 and its rescue by TLR4 ectodomain. J Immunol. 2008; 180:6107–6115.10. Tsai JJ, Liu SH, Yin SC, Yang CN, Hsu HS, Chen WB, et al. Mite allergen Der-p2 triggers human B lymphocyte activation and Toll-like receptor-4 induction. PLoS ONE. 2011; 6:e23249.11. Hasegawa M, Nishiyama C, Nishiyama M, Akizawa Y, Mitsuishi K, Ito T, et al. A novel -66T/C polymorphism in Fc epsilon RI alpha-chain promoter affecting the transcription activity: possible relationship to allergic diseases. J Immunol. 2003; 171:1927–1933.12. Liao EC, Chang CY, Wu CC, Wang GJ, Tsai JJ. Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the MD-2 gene promoter region with Der p 2 allergy. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015; 7:249–255.13. Gu W, Shan YA, Zhou J, Jiang DP, Zhang L, Du DY, et al. Functional significance of gene polymorphisms in the promoter of myeloid differentiation-2. Ann Surg. 2007; 246:151–158.14. Bousquet J, Van Cauwenberge P, Khaltaev N. Aria Workshop Group. World Health Organization. Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:S147–S334.15. Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 2008; 63:Suppl 86. 8–160.16. Noguchi T, Matsuda H, Akiyama Y. PDB-REPRDB: a database of representative protein chains from the Protein Data Bank (PDB). Nucleic Acids Res. 2001; 29:219–220.17. Mendy A, Gasana J, Vieira ER, Forno E, Patel J, Kadam P, et al. Endotoxin exposure and childhood wheeze and asthma: a meta-analysis of observational studies. J Asthma. 2011; 48:685–693.18. Chiou YL, Lin CY. Der p2 activates airway smooth muscle cells in a TLR2/MyD88-dependent manner to induce an inflammatory response. J Cell Physiol. 2009; 220(2):311–318.19. Osterlund C, Grönlund H, Polovic N, Sundström S, Gafvelin G, Bucht A. The non-proteolytic house dust mite allergen Der p 2 induce NF-κB and MAPK dependent activation of bronchial epithelial cells. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009; 39:1199–1208.20. Zhu J, Yamane H, Cote-Sierra J, Guo L, Paul WE. GATA-3 promotes Th2 responses through three different mechanisms: induction of Th2 cytokine production, selective growth of Th2 cells and inhibition of Th1 cell-specific factors. Cell Res. 2006; 16:3–10.21. Paul WE, Zhu J. How are T(H)2-type immune responses initiated and amplified? Nat Rev Immunol. 2010; 10:225–235.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Association of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the MD-2 Gene Promoter Region With Der p 2 Allergy
- Der p 1, Der p 2 and Der p 10 IgE Reactivities in Allergic Rhinitis Patients in Korea
- Immunoglobulin E to allergen components of house dust mite in Korean children with allergic disease
- Strain-Specific Differences in House Dust Mite (Dermatophagoides farinae)-Induced Mouse Models of Allergic Rhinitis
- IL-13 Gene Polymorphisms are Associated With Rhinosinusitis and Eosinophilic Inflammation in Aspirin Intolerant Asthma