Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2010 Apr;2(2):134-140. 10.4168/aair.2010.2.2.134.
IL-13 Gene Polymorphisms are Associated With Rhinosinusitis and Eosinophilic Inflammation in Aspirin Intolerant Asthma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy and Rheumatology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hspark@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 2260600
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2010.2.2.134
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Aspirin-intolerant asthma (AIA) is characterized by moderate to severe asthma that is aggravated by aspirin or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Affected patients frequently have chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis due to persistent upper and lower airway inflammation with marked eosinophilia. IL-13 plays a crucial role in the development of allergic asthma by inducing airway eosinophilia and hyper-reactivity and it has been correlated with an increased eosinophil count.
METHODS
Two promoter polymorphisms of the IL-13 gene (-1510 A>C and -1055C>T) and one coding nonsynonymus Arg110Gln (110G>A) polymorphism were genotyped using primer extension methods in 162 patients with AIA, 301 patients with aspirin-tolerant asthma (ATA), and 430 normal healthy controls (NC).
RESULTS
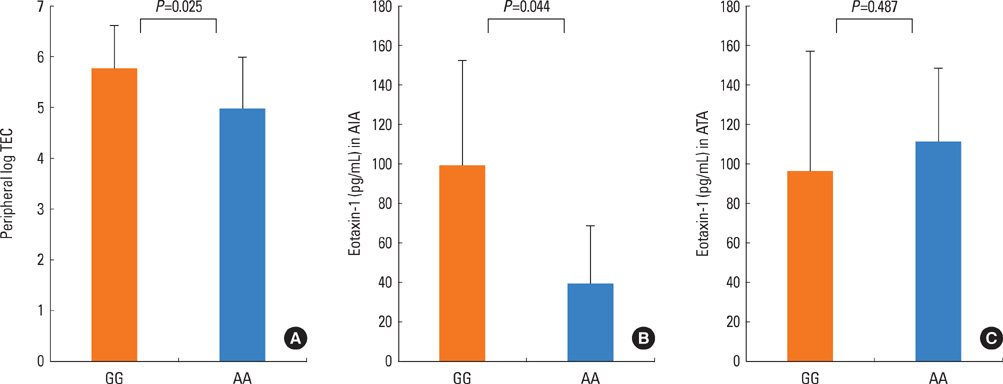
There was no significant difference in the genotype, allele, and haplotype frequencies of the three polymorphisms among the three groups. AIA patients with the AA genotype -1510A>C (P=0.012) and CC genotype -1055C>T (P<0.001) had a significantly higher frequency of rhinosinusitis, as compared to those with the minor alleles of these two single nucleotide polymorphisms. AIA patients with the GG genotype had a higher peripheral eosinophil count (P=0.025) and a higher serum eotaxin-1 level (P=0.044), as compared to patients with the AA genotype IL-13 Arg110Gln (110G>A).
CONCLUSIONS
These findings suggest that the IL-13 polymorphisms at -1510A>C and 1055C>T are associated with the development of rhinosinusitis in AIA patients. IL-13 Arg110Gln may be associated with an increased eosinophil count and eotaxin-1 level and could increase eosinophilic inflammation in the upper and lower airways of patients with AIA.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nasser SM, Pfister R, Christie PE, Sousa AR, Barker J, Schmitz-Schumann M, Lee TH. Inflammatory cell populations in bronchial biopsies from aspirin-sensitive asthmatic subjects. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996. 153:90–96.2. Sampson AP, Cowburn AS, Sladek K, Adamek L, Nizankowska E, Szczeklik A, Lam BK, Penrose JF, Austen KF, Holgate ST. Profound overexpression of leukotriene C4 synthase in bronchial biopsies from aspirin-intolerant asthmatic patients. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1997. 113:355–357.3. Wills-Karp M, Luyimbazi J, Xu X, Schofield B, Neben TY, Karp CL, Donaldson DD. Interleukin-13: central mediator of allergic asthma. Science. 1998. 282:2258–2261.4. van der Pouw Kraan TC, van Veen A, Boeije LC, van Tuyl SA, de Groot ER, Stapel SO, Bakker A, Verweij CL, Aarden LA, van der Zee JS. An IL-13 promoter polymorphism associated with increased risk of allergic asthma. Genes Immun. 1999. 1:61–65.5. Punnonen J, Aversa G, Cocks BG, McKenzie AN, Menon S, Zurawski G, de Waal Malefyt R, de Vries JE. Interleukin 13 induces interleukin 4-independent IgG4 and IgE synthesis and CD23 expression by human B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. 90:3730–3734.6. Truyen E, Coteur L, Dilissen E, Overbergh L, Dupont LJ, Ceuppens JL, Bullens DM. Evaluation of airway inflammation by quantitative Th1/Th2 cytokine mRNA measurement in sputum of asthma patients. Thorax. 2006. 61:202–208.7. Park SW, Jangm HK, An MH, Min JW, Jang AS, Lee JH, Park CS. Interleukin-13 and interleukin-5 in induced sputum of eosinophilic bronchitis: comparison with asthma. Chest. 2005. 128:1921–1927.8. Rankin SM, Conroy DM, Williams TJ. Eotaxin and eosinophil recruitment: implications for human disease. Mol Med Today. 2000. 6:20–27.9. Marsh DG, Neely JD, Breazeale DR, Ghosh B, Freidhoff LR, Ehrlich-Kautzky E, Schou C, Krishnaswamy G, Beaty TH. Linkage analysis of IL4 and other chromosome 5q31.1 markers and total serum immunoglobulin E concentrations. Science. 1994. 264:1152–1156.10. Noguchi E, Shibasaki M, Arinami T, Takeda K, Maki T, Miyamoto T, Kawashima T, Kobayashi K, Hamaguchi H. Evidence for linkage between asthma/atopy in childhood and chromosome 5q31-q33 in a Japanese population. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997. 156:1390–1393.11. Palmer LJ, Daniels SE, Rye PJ, Gibson NA, Tay GK, Cookson WO, Goldblatt J, Burton PR, LeSöuef PN. Linkage of chromosome 5q and 11q gene markers to asthma-associated quantitative traits in Australian children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 158:1825–1830.12. Postma DS, Bleecker ER, Amelung PJ, Holroyd KJ, Xu J, Panhuysen CI, Meyers DA, Levitt RC. Genetic susceptibility to asthma--bronchial hyperresponsiveness coinherited with a major gene for atopy. N Engl J Med. 1995. 333:894–900.13. Graves PE, Kabesch M, Halonen M, Holberg CJ, Baldini M, Fritzsch C, Weiland SK, Erickson RP, von Mutius E, Martinez FD. A cluster of seven tightly linked polymorphisms in the IL-13 gene is associated with total serum IgE levels in three populations of white children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. 105:506–513.14. Heinzmann A, Mao XQ, Akaiwa M, Kreomer RT, Gao PS, Ohshima K, Umeshita R, Abe Y, Braun S, Yamashita T, Roberts MH, Sugimoto R, Arima K, Arinobu Y, Yu B, Kruse S, Enomoto T, Dake Y, Kawai M, Shimazu S, Sasaki S, Adra CN, Kitaichi M, Inoue H, Yamauchi K, Tomichi N, Kurimoto F, Hamasaki N, Hopkin JM, Izuhara K, Shirakawa T, Deichmann KA. Genetic variants of IL-13 signalling and human asthma and atopy. Hum Mol Genet. 2000. 9:549–559.15. Walter DM, McIntire JJ, Berry G, McKenzie AN, Donaldson DD, DeKruyff RH, Umetsu DT. Critical role for IL-13 in the development of allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity. J Immunol. 2001. 167:4668–4675.16. Park HS. Early and late onset asthmatic responses following lysineaspirin inhalation in aspirin-sensitive asthmatic patients. Clin Exp Allergy. 1995. 25:38–40.17. Kim SH, Bae JS, Holloway JW, Lee JT, Suh CH, Nahm DH, Park HS. A polymorphism of MS4A2 (-109T>C) encoding the beta-chain of the high-affinity immunoglobulin E receptor (FcepsilonR1beta) is associated with a susceptibility to aspirin-intolerant asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006. 36:877–883.18. Palikhe NS, Kim SH, Choi GS, Ye YM, Park HS. No evidence of association between interleukin-13 gene polymorphism in aspirin intolerant chronic urticaria. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2009. 1:36–40.19. Wynn TA. IL-13 effector functions. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003. 21:425–456.20. Hunninghake GM, Soto-Quirós ME, Avila L, Su J, Murphy A, Demeo DL, Ly NP, Liang C, Sylvia JS, Klanderman BJ, Lange C, Raby BA, Silverman EK, Celedón JC. Polymorphisms in IL13, total IgE, eosinophilia, and asthma exacerbations in childhood. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007. 120:84–90.21. Kim HB, Lee YC, Lee SY, Jung J, Jin HS, Kim JH, Kim BS, Kang MJ, Jang SO, Kim J, Kimm K, Shin ES, Lee SG, Hong SJ. Gene-gene interaction between IL-13 and IL-13R alpha 1 is associated with total IgE in Korean children with atopic asthma. J Hum Genet. 2006. 51:1055–1062.22. Vladich FD, Brazille SM, Stern D, Peck ML, Ghittoni R, Vercelli D. IL-13 R130Q, a common variant associated with allergy and asthma, enhances effector mechanisms essential for human allergic inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2005. 115:747–754.23. Arima K, Umeshita-Suyama R, Sakata Y, Akaiwa M, Mao XQ, Enomoto T, Dake Y, Shimazu S, Yamashita T, Sugawara N, Brodeur S, Geha R, Puri RK, Sayegh MH, Adra CN, Hamasaki N, Hopkin JM, Shirakawa T, Izuhara K. Upregulation of IL13 concentration in vivo by the IL-13 variant associated with bronchial asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002. 109:980–987.24. Chen W, Ericksen MB, Levin LS, Khurana Hershey GK. Functional effect of the R110Q IL13 genetic variant alone and in combination with IL4RA genetic variants. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 114:553–560.25. Kim SH, Park HS, Holloway JW, Shin HD, Park CS. Association between a TGFbeta1 promoter polymorphism and rhinosinusitis in aspirin-intolerant asthmatic patients. Respir Med. 2007. 101:490–495.26. Kim SH, Yang EM, Lee HN, Cho BY, Ye YM, Park HS. Combined effect of IL-10 and TGF-beta1 promoter polymorphisms as a risk factor for aspirin-intolerant asthma and rhinosinusitis. Allergy. 2009. 64:1221–1225.27. Sauter A, Stern-Straeter J, Chang RC, Hörmann K, Naim R. Influence of interleukin-13 on beta-catenin levels in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis cell culture. Int J Mol Med. 2008. 21:447–452.28. Cameron L, Webster RB, Strempel JM, Kiesler P, Kabesch M, Ramachandran H, Yu L, Stern DA, Graves PE, Lohman IC, Wright AL, Halonen M, Klimecki WT, Vercelli D. Th2 cell-selective enhancement of human IL13 transcription by IL13-1112C>T, a polymorphism associated with allergic inflammation. J Immunol. 2006. 177:8633–8642.29. Ober C, Hoffjan S. Asthma genetics 2006: the long and winding road to gene discovery. Genes Immun. 2006. 7:95–100.30. Li L, Xia Y, Nguyen A, Lai YH, Feng L, Mosmann TR, Lo D. Effects of Th2 cytokines on chemokine expression in the lung: IL-13 potently induces eotaxin expression by airway epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1999. 162:2477–2487.31. Hirst SJ, Hallsworth MP, Peng Q, Lee TH. Selective induction of eotaxin release by interleukin-13 or interleukin-4 in human airway smooth muscle cells is synergistic with interleukin-1beta and is mediated by the interleukin-4 receptor alpha-chain. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002. 165:1161–1171.32. Moore PE, Church TL, Chism DD, Panettieri RA Jr, Shore SA. IL-13 and IL-4 cause eotaxin release in human airway smooth muscle cells: a role for ERK. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002. 282:L847–L853.33. Zhu Z, Homer RJ, Wang Z, Chen Q, Geba GP, Wang J, Zhang Y, Elias JA. Pulmonary expression of interleukin-13 causes inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, subepithelial fibrosis, physiologic abnormalities, and eotaxin production. J Clin Invest. 1999. 103:779–788.34. Nakamura H, Weiss ST, Israel E, Luster AD, Drazen JM, Lilly CM. Eotaxin and impaired lung function in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999. 160:1952–1956.35. Lamkhioued B, Renzi PM, Abi-Younes S, Garcia-Zepada EA, Allakhverdi Z, Ghaffar O, Rothenberg MD, Luster AD, Hamid Q. Increased expression of eotaxin in bronchoalveolar lavage and airways of asthmatics contributes to the chemotaxis of eosinophils to the site of inflammation. J Immunol. 1997. 159:4593–4601.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- No evidence of association between interleukin-13 gene polymorphism in aspirin intolerant chronic urticaria
- Prevalence of Subclinical Aspirin-Intolerant Asthma in Patients with Nasal Polyposis and Chronic Rhinosinusitis
- Interleukin (IL)-13 Gene Polymorphism in Patients with Bronchial Asthma
- Association of IL-1 gene polymorphisms with chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyp
- IL-13 And IL-5 in Induced Sputum in Patients with Eosinophilic Bronchitis and Asthma: an Association with Airway Hyperresponsiveness