J Rhinol.
2016 Nov;23(2):91-96. 10.18787/jr.2016.23.2.91.
Der p 1, Der p 2 and Der p 10 IgE Reactivities in Allergic Rhinitis Patients in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dongkim@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2361321
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2016.23.2.91
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
To evaluate IgE reactivity profiles to Der p 1, Der p 2, and Der p 10 in house dust mite (HDM) allergic rhinitis (AR) patients in Korea. Symptomatic and serologic changes after sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) were analyzed according to IgE profiles.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty AR patients diagnosed with an HDM allergy were tested for the presence of IgE antibodies against purified HDM allergen molecules (i.e., nDer p 1, rDer p 2, and rDer p 10) and native Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Dp) using ImmunoCAP 250®. Symptom scores and laboratory findings were analyzed after SLIT.
RESULTS
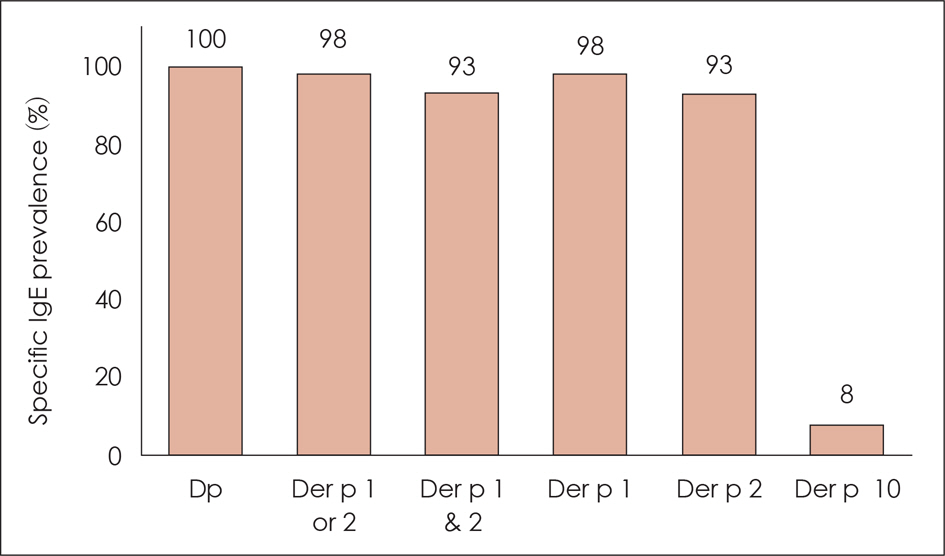
Prevalence rates of IgE for Dp, Der p 1, Der p 2, and Der p 10 were 100%, 98.3%, 93.3%, and 8.3%, respectively. After one year of immunotherapy with SLIToneâ—‹R (standardized to major allergens, but not Der p 10), symptom scores and laboratory findings improved in patients with and without Der p 10 IgE antibodies.
CONCLUSION
In Korean AR patients, specific IgE antibodies to Der p 1 or Der p 2 are present in most Dp-allergic patients, while reactivity to Der p 10 is very low. Allergic symptoms improved in patients with Der p 10 IgE antibodies after SLIT.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). Lee SI, Shin MH, Lee HB, Lee JS, Son BK, Koh YY, et al. Prevalences of symptoms of asthma and other allergic diseases in korean children: A nationwide questionnaire survey. J Korean Med Sci. 2001; 16:155–64.
Article2). Bang JH, Kim YJ, Shin HS, Lee BJ. Clinical analysis of allergic rhinitis in Seoul. J Rhinol. 1996; 3:130–4.3). Resch Y, Weghofer M, Seiberler S, Horak F, Scheiblhofer S, Lin-hart B, et al. Molecular characterization of Der p 10: A diagnostic marker for broad sensitization in house dust mite allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011; 41:1468–77.
Article4). Pittner G, Vrtala S, Thomas WR, Weghofer M, Kundi M, Horak F, et al. Component-resolved diagnosis of house-dust mite allergy with purified natural and recombinant mite allergens. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004; 34:597–603.
Article5). Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2) LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 2008; 63:8–160.6). Des Roches A, Paradis L, Menardo JL, Bouges S, Daures JP, Bousquet J. Immunotherapy with a standardized Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus extract. VI. Specific immunotherapy prevents the onset of new sensitizations in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 99:450–3.7). Pajno GB, Barberio G, De Luca F, Morabito L, Parmiani S. Prevention of new sensitizations in asthmatic children monosensitized to house dust mite by specific immunotherapy. A six-year follow-up study. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001; 31:1392–7.
Article8). Meyer CH, Bond JF, Chen MS, Kasaian MT. Comparison of the levels of the major allergens Der p I and Der p II in standardized extracts of the house dust mite, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. Clin Exp Allergy. 1994; 24:1041–8.9). Becker S, Groger M, Canis M, Pfrogner E, Kramer MF. Tropomyo-sin sensitization in house dust mite allergic patients. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; 269:1291–6.
Article10). Yadzir ZHM, Misnan R, Abdullah N, Bakhtiar F, Leecyous B, Murad S. Component-Resolved Diagnosis (CRD): Is It Worth It? Frequency and Differentiation in Rhinitis Patients with Mite Reactivity. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014; 13:240–6.11). Becker S, Kramer MF, Havel M, Welz C, Markmann S, Groger M. IgE reactivity profiles among house dust mite allergic patients in Bavaria. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013; 270:3177–82.
Article12). Weghofer M, Thomas WR, Kronqvist M, Mari A, Purohit A, Pauli G, et al. Variability of IgE reactivity profiles among European mite allergic patients. Eur J Clin Invest. 2008; 38:959–65.
Article13). Thomas WR, Smith W. Towards defining the full spectrum of important house dust mite allergens. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999; 29:1583–7.
Article14). Rossi RE, Monasterolo G, Monasterolo S. Measurement of IgE antibodies against purified grass-pollen allergens (Phl p 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 11, and 12) in sera of patients allergic to grass pollen. Allergy. 2001; 56:1180–5.
Article15). Bronnert M, Mancini J, Birnbaum J, Agabriel C, Liabeuf V, Porri F, et al. Component-resolved diagnosis with commercially available D. pteronyssinus Der p 1, Der p 2 and Der p 10: relevant markers for house dust mite allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012; 42:1406–15.16). Kidon MI, Chin CW, Kang LW, Ching OT, Seng TY, Ning WK, et al. Mite component-specific IgE repertoire and phenotypes of allergic disease in childhood: The tropical perspective. Pediatr Allergy and Immunol. 2011; 22:202–10.
Article17). Sanza ML, Bla´zquezb AB, Garciac BE. Microarray of allergenic component-based diagnosis in food allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 11:204–9.18). Sampson HA. Food allergy-accurately identifying clinical reactivity. Allergy. 2005; 60:19–24.19). Szefler SJ, Wenzel S, Brown R, Erzurum SC, Fahy JV, Hamilton RG, et al. Asthma outcomes: Biomarkers. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129:S9–23.
Article20). Cain TW, Ford J, Dolen WK. A-low level method for measurement of specific immunoglobulin E antibody in serum. Allergy Clin Immunol Int-J World Allergy Org. 2006; 18:230–3.21). Brunetto B, Tinghino R, Braschi MC, Antonicelli L, Pini C, Iacovac-ci P. Characterization and comparison of commercially available mite extracts for in vivo diagnosis. Allergy. 2010; 65:184–90.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunoglobulin E to allergen components of house dust mite in Korean children with allergic disease
- Inhibition of Allergic Response by CpG Motif Immunostimulatory Oligodeoxynucleotide in a Murine Model of Allergic Rhinitis
- Measurement of IgE and IgG subclass antibodies to whole body antigen and two major allergens (Der fI & Der fII) of Dermatophagoides farinae in normal subjects and asthmatics
- Profiles of IgE Sensitization to Der f 1, Der f 2, Der f 6, Der f 8, Der f 10, and Der f 20 in Korean House Dust Mite Allergy Patients
- Effect of Amino Acid Polymorphisms of House Dust Mite Der p 2 Variants on Allergic Sensitization