Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2015 Sep;7(5):483-488. 10.4168/aair.2015.7.5.483.
Profiles of IgE Sensitization to Der f 1, Der f 2, Der f 6, Der f 8, Der f 10, and Der f 20 in Korean House Dust Mite Allergy Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Institute of Allergy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkjw@yuhs.ac
- 2Brain Korea 21 PLUS Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Environmental Medical Biology and Institute of Tropical Medicine, Arthropods of Medical Importance Resource Bank, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Dermatology, Institute of Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2147957
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.5.483
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Measurement of IgE specific to purified house dust mite (HDM) allergens may improve allergy diagnosis. This study aimed to investigate the sensitization profiles of Korean HDM allergic subjects suffering from respiratory allergy and atopic dermatitis (AD) to Der f 1, Der f 2, Der f 6, Der f 8, Der f 10, and Der f 20.
METHODS
Recombinant HDM allergens were produced in Pichia pastoris (Der f 1) or Escherichia coli (5 allergens). IgE reactivity to the individual recombinant allergens and total extract of mite was assessed by ELISA.
RESULTS
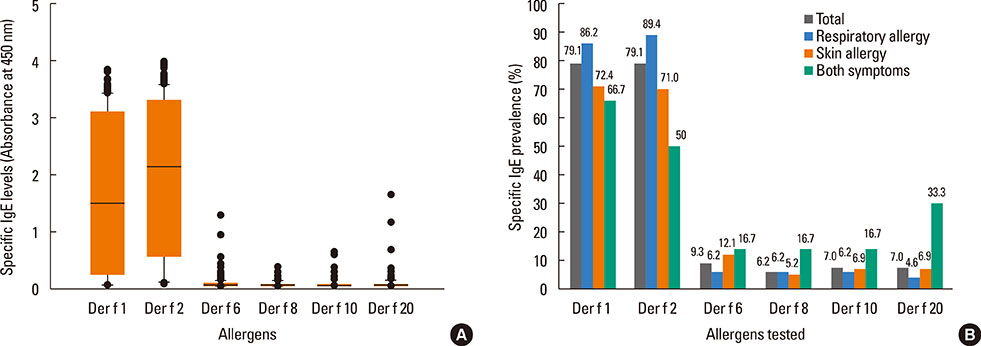
Der f 1 was recognized by 79.1%, Der f 2 by 79.1%, Der f 6 by 9.3%, Der f 8 by 6.2%, Der f 10 by 6.2%, and Der f 20 by 6.6% of the patients' sera tested, while the prevalence of IgE reactivity to total mite extract was 94.7%. Combination of Der f 1 and Der f 2 had a sensitivity of 87.6%. Specific IgE to Der f 2 alone was detected from 89.4% of HDM-sensitized respiratory allergy subjects and 92.3% to the combination of the 2 major allergens Der f 1 and Der f 2. However, sera from fewer patients with AD, namely 72.4% and 71.0%, recognized Der f 1 and Der f 2, respectively. The combination of 2 major allergens allowed diagnosis of 84.5% of the AD patients. No correlation between sensitization to specific allergens and HDM allergy entity was found.
CONCLUSIONS
Der f 2 was the most frequently sensitized allergen among the HDM-sensitized respiratory and AD patients in Korea, and the combination of the group 1 and 2 major allergens increased the diagnostic sensitivity. Minor allergens did not significantly improve diagnostic sensitivity. However, further studies are needed to analyze the relationship between sensitization to other HDM allergens and the disease entity of the HDM allergy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparison of IgE-binding components between 2 house dust mites in adult allergic patients
Hyun Jung Jin, Moon-Gyung Yoon, Young-Hee Nam, June Hong Ahn, Hae-Sim Park, Jin Hong Chung
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2016;4(3):199-204. doi: 10.4168/aard.2016.4.3.199.
Reference
-
1. Valenta R, Lidholm J, Niederberger V, Hayek B, Kraft D, Grönlund H. The recombinant allergen-based concept of component-resolved diagnostics and immunotherapy (CRD and CRIT). Clin Exp Allergy. 1999; 29:896–904.2. Treudler R, Simon JC. Overview of component resolved diagnostics. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013; 13:110–117.3. Taketomi EA, Silva DA, Sopelete MC, Gervásio AM, Alves R, Sung SJ. Differential IgE reactivity to Der p 1 and Der p 2 allergens of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus in mite-sensitized patients. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2006; 16:104–109.4. Weghofer M, Thomas WR, Kronqvist M, Mari A, Purohit A, Pauli G, et al. Variability of IgE reactivity profiles among European mite allergic patients. Eur J Clin Invest. 2008; 38:959–965.5. Hales BJ, Laing IA, Pearce LJ, Hazell LA, Mills KL, Chua KY, et al. Distinctive immunoglobulin E anti-house dust allergen-binding specificities in a tropical Australian Aboriginal community. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007; 37:1357–1363.6. Pittner G, Vrtala S, Thomas WR, Weghofer M, Kundi M, Horak F, et al. Component-resolved diagnosis of house-dust mite allergy with purified natural and recombinant mite allergens. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004; 34:597–603.7. Resch Y, Weghofer M, Seiberler S, Horak F, Scheiblhofer S, Linhart B, et al. Molecular characterization of Der p 10: a diagnostic marker for broad sensitization in house dust mite allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011; 41:1468–1477.8. Mohamad Yadzir ZH, Misnan R, Abdullah N, Bakhtiar F, Leecyous B, Murad S. Component-resolved diagnosis (CRD): Is it worth it? Frequency and differentiation in rhinitis patients with mite reactivity. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014; 13:240–246.9. Kidon MI, Chiang WC, Liew WK, Ong TC, Tiong YS, Wong KN, et al. Mite component-specific IgE repertoire and phenotypes of allergic disease in childhood: the tropical perspective. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2011; 22:202–210.10. Jeong KY, Choi SY, Lee JH, Lee IY, Yong TS, Lee JS, et al. Standardization of house dust mite extracts in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:346–350.11. Jeong KY, Lee JH, Kim EJ, Lee JS, Cho SH, Hong SJ, et al. Current status of standardization of inhalant allergen extracts in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:196–200.12. Yasuhara T, Takai T, Yuuki T, Okudaira H, Okumura Y. Biologically active recombinant forms of a major house dust mite group 1 allergen Der f 1 with full activities of both cysteine protease and IgE binding. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001; 31:116–124.13. Jeong KY, Lee IY, Yong TS, Lee JH, Kim EJ, Lee JS, et al. Sequence polymorphisms of Der f 1, Der p 1, Der f 2 and Der p 2 from Korean house dust mite isolates. Exp Appl Acarol. 2012; 58:35–42.14. Jeong KY, Lee H, Lee JS, Lee J, Lee IY, Ree HI, et al. Molecular cloning and the allergenic characterization of tropomyosin from Tyrophagus putrescentiae. Protein Pept Lett. 2007; 14:431–436.15. Jeong KY, Park JW, Hong CS. House dust mite allergy in Korea: the most important inhalant allergen in current and future. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:313–325.16. Park JW, Nahm DH, Hong CS. Determination of specific IgE to two major allergens (Der f I and Der f II) of house dust mite (D. farinae) in Korean adult respiratory allergy patients. Allergy. 1993; 13:476–486.17. Jeong KY, Hong CS, Yong TS. Allergenic tropomyosins and their cross-reactivities. Protein Pept Lett. 2006; 13:835–845.18. Arruda LK, Santos AB. Immunologic responses to common antigens in helminthic infections and allergic disease. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 5:399–402.19. Santos AB, Rocha GM, Oliver C, Ferriani VP, Lima RC, Palma MS, et al. Cross-reactive IgE antibody responses to tropomyosins from Ascaris lumbricoides and cockroach. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:1040–1046.e1.20. Binder M, Mahler V, Hayek B, Sperr WR, Schöller M, Prozell S, et al. Molecular and immunological characterization of arginine kinase from the Indianmeal moth, Plodia interpunctella, a novel cross-reactive invertebrate pan-allergen. J Immunol. 2001; 167:5470–5477.21. Santiago HC, LeeVan E, Bennuru S, Ribeiro-Gomes F, Mueller E, Wilson M, et al. Molecular mimicry between cockroach and helminth glutathione S-transferases promotes cross-reactivity and cross-sensitization. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 130:248–256.e9.22. Acevedo N, Mohr J, Zakzuk J, Samonig M, Briza P, Erler A, et al. Proteomic and immunochemical characterization of glutathione transferase as a new allergen of the nematode Ascaris lumbricoides. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e78353.23. Thomas WR, Heinrich TK, Smith WA, Hales BJ. Pyroglyphid house dust mite allergens. Protein Pept Lett. 2007; 14:943–953.24. Weghofer M, Grote M, Resch Y, Casset A, Kneidinger M, Kopec J, et al. Identification of Der p 23, a peritrophin-like protein, as a new major Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus allergen associated with the peritrophic matrix of mite fecal pellets. J Immunol. 2013; 190:3059–3067.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Der p 1, Der p 2 and Der p 10 IgE Reactivities in Allergic Rhinitis Patients in Korea
- Determination of specific IgE to two major allergens(Der fI and Der fII) of house dust mite(D.farinae) in Korean adult respiratory allergy patients
- Immunoglobulin E to allergen components of house dust mite in Korean children with allergic disease
- Concentrations of Dust Mite in The Dust of Childhood Bedclothing, Cloth Wrappers, and Sewing Dolls
- Correlation between House Dust Mite Allergen Concentrations in Scalp Dander and Clinical Severity of Atopic Dermatitis in Children